Biology:Bacillus odysseyi
| Bacillus odysseyi | |
|---|---|
| |
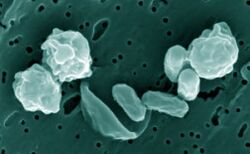
| Colored micrograph of Bacillus odysseyi spores taken by a field-emission environmental SEM and magnified by 107. Spherical figures (about 2 µm diameter) are intact spores with exosporia. In center of image, spores (rod-shaped) were exposed to 0.5 mrad gamma radiation for 60 min, thus the exosporium (ribbon-shaped) separated.[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | B. odysseyi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bacillus odysseyi | |
Bacillus odysseyi is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, round-spore- and endospore-forming eubacterium of the genus Bacillus.[1] This novel species was discovered by scientist Myron T. La Duc of NASA’s Biotechnology and Planetary Protection Group, a unit whose purpose is to clean and sterilize spacecraft so as not to have microorganisms contaminate other celestial bodies or foreign microorganisms contaminate Earth, on the surface of the Mars Odyssey in a clean room at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge before the spacecraft was launched to space. La Duc named the bacterium Bacillus odysseyi sp. nov. after the Odyssey mission. It had apparently evolved to live in the sparse environment of a clean room, and its secondary spore coat makes it especially resistant to radiation.[2]
B. odysseyi consists of an exosporium, spore coat, cortex, and core. In a test performed by the Planetary Protection unit, its spores were the most consistently resistant, and it survived exposure to all of the challenges posed against it: desiccation (100% survival), Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 26% survival), ultraviolet radiation (10% survival at 660 J ∙ m−2), and gamma radiation (0.4% survival). B. odysseyi shares many DNA similarities with Bacillus fusiformis and Solibacillus silvestris. The type strain for B. odysseyi is 34hs-1T (=ATCC PTA-4993T=NRRL B-30641T=NBRC 100172T).[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 La Duc, Myron T.; Satomi, Masataka; Venkateswaran, Kasthuri (2004). "Bacillus odysseyi sp. nov., a round-spore-forming bacillus isolated from the Mars Odyssey spacecraft". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 54 (1): 195–201. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02747-0. PMID 14742480. http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/cgi/content/full/54/1/195.
- ↑ Dance, Amber. “Specialized Unit Helps NASA Keep Its Dirty Little Secrets on Earth.” Los Angeles Times 6 Aug. 2007: B1, B8.
Further reading
- Jung, Min Young; Kim, Joong-Su; Paek, Woon Kee (October 2012). "Description of Lysinibacillus sinduriensis sp. nov., and transfer of Bacillus massiliensis and Bacillus odysseyi to the genus Lysinibacillus as Lysinibacillus massiliensis comb. nov. and Lysinibacillus odysseyi comb. nov. with emended description of the genus Lysinibacillus". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 62 (Part 10): 2347–2355. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.033837-0. PMID 22140163.
External links
- U.S. patent 7,189,556 of a “biologically pure culture of a Bacillus odysseyi isolate with high adherence and sterilization-resistant properties”
- U.S. patent 20,040,158,042 of a “biologically pure culture of a Bacillus odysseyi isolate with high adherence and sterilization-resistant properties”
Wikidata ☰ Q4838973 entry
 |

