Chemistry:Dichlofenthion
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
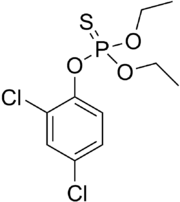
| Preferred IUPAC name
O-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl) O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate | |
| Other names
Dichlofenthion, Dichlofention, Dichlorfenthion, Dichlorofenthion, Diclophenthion, Diclofenthion, Hexanema, Mobilawn, Nemacide, Phosphorothioic acid, ECP, VC-13
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13Cl2O3PS | |
| Molar mass | 315.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | liquid |
| Boiling point | 123 °C (253 °F; 396 K) |
| 0.245 mg/L | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dichlofenthion (IUPAC name: O-(2,4-dichlorophenyl) O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate) is a phosphorothioate which is primarily used as a pesticide and nematicide.
Environmental fate
Dichlofenthion has a relatively short half-life of only a few minutes in both water and soils. While little research has been conducted over the environmental fate this compound, much is known about the compound class in which it resides.
Dichlofenthion is generally considered to be an organophosphate pesticide, although in a strict chemical sense, it is a phosphorothioate. Because most organophosphate pesticides biodegrade relatively quickly, they are generally regarded as safe for use. While this may be true for most compounds, bacteria still require time to adapt to break down new compounds introduced to the soil.[1] It has been shown that degradation rates increase as the same compounds are introduced repeatedly into the soil.
Because the sorption to soil and sediment is considered high, dichlofenthion is not a highly mobile compound. The estimated half-life of dichlofenthion in water, soil, and sediment is less than a few minutes. The estimated half-life in the air is 2.78 hours, much higher than that in water, soil, and sediment. The estimated wastewater treatment removal efficiency is 84 percent with approximately 5% to air.
References
- ↑ Ragnarsdottir, K (2007). "Environmental Fate and Toxicology of Organophosphate Pesticides". Journal of the Geological Society 157. doi:10.1144/jgs.157.4.859.
 |

