Engineering:Motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, MB, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, mobo; or in Apple computers logic board) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.
Motherboard means specifically a PCB with expansion capabilities. As the name suggests, this board is often referred to as the "mother" of all components attached to it, which often include peripherals, interface cards, and daughterboards: sound cards, video cards, network cards, host bus adapters, TV tuner cards, IEEE 1394 cards, and a variety of other custom components.
Similarly, the term mainboard describes a device with a single board and no additional expansions or capability, such as controlling boards in laser printers, television sets, washing machines, mobile phones, and other embedded systems with limited expansion abilities.
History
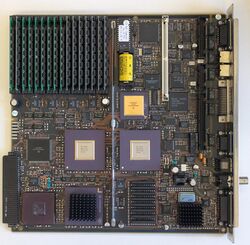
Prior to the invention of the microprocessor, the CPU of a digital computer consisted of multiple circuit boards in a card-cage case with components connected by a backplane containing a set of interconnected sockets into which the circuit boards are plugged. In very old designs, copper wires were the discrete connections between card connector pins, but printed circuit boards soon became the standard practice. The central processing unit (CPU), memory, and peripherals were housed on individually printed circuit boards, which were plugged into the backplane.
In older microprocessor-based systems, the CPU and some support circuitry would fit on a single CPU board, with memory and peripherals on additional boards, all plugged into the backplane. The ubiquitous S-100 bus of the 1970s is an example of this type of backplane system.
The most popular computers of the 1980s such as the Apple II and IBM PC had published schematic diagrams and other documentation which permitted rapid reverse engineering and third-party replacement motherboards. Usually intended for building new computers compatible with the exemplars, many motherboards offered additional performance or other features and were used to upgrade the manufacturer's original equipment.
During the late 1980s and early 1990s, it became economical to move an increasing number of peripheral functions onto the motherboard. In the late 1980s, personal computer motherboards began to include single ICs (also called Super I/O chips) capable of supporting a set of low-speed peripherals: PS/2 keyboard and mouse, floppy disk drive, serial ports, and parallel ports. By the late 1990s, many personal computer motherboards included consumer-grade embedded audio, video, storage, and networking functions without the need for any expansion cards at all; higher-end systems for 3D gaming and computer graphics typically retained only the graphics card as a separate component. Business PCs, workstations, and servers were more likely to need expansion cards, either for more robust functions, or for higher speeds; those systems often had fewer embedded components.
Laptop and notebook computers that were developed in the 1990s integrated the most common peripherals. This even included motherboards with no upgradeable components, a trend that would continue as smaller systems were introduced after the turn of the century (like the tablet computer and the netbook). Memory, processors, network controllers, power source, and storage would be integrated into some systems.
Design

A motherboard provides the electrical connections by which the other components of the system communicate. Unlike a backplane, it also contains the central processing unit and hosts other subsystems and devices.
A typical desktop computer has its microprocessor, main memory, and other essential components connected to the motherboard. Other components such as external storage, controllers for video display and sound, and peripheral devices may be attached to the motherboard as plug-in cards or via cables; in modern microcomputers, it is increasingly common to integrate some of these peripherals into the motherboard itself.
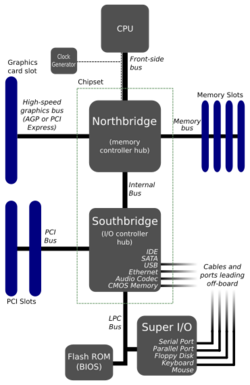
An important component of a motherboard is the microprocessor's supporting chipset, which provides the supporting interfaces between the CPU and the various buses and external components. This chipset determines, to an extent, the features and capabilities of the motherboard.
Modern motherboards include:
- CPU sockets (or CPU slots) in which one or more microprocessors may be installed. In the case of CPUs in ball grid array packages, such as the VIA Nano and the Goldmont Plus, the CPU is directly soldered to the motherboard.[2]
- Memory slots into which the system's main memory is to be installed, typically in the form of DIMM modules containing DRAM chips. Can be DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, or onboard LPDDRx.
- The chipset which forms an interface between the CPU, main memory, and peripheral buses
- Non-volatile memory chips (usually flash memory in modern motherboards) containing the system's firmware or BIOS
- The clock generator which produces the system clock signal to synchronize the various components
- Slots for expansion cards (the interface to the system via the buses supported by the chipset)
- Power connectors, which receive electrical power from the computer power supply and distribute it to the CPU, chipset, main memory, and expansion cards. (As of 2007), some graphics cards (e.g. GeForce 8 and Radeon R600) require more power than the motherboard can provide, and thus dedicated connectors have been introduced to attach them directly to the power supply.[3]
- Connectors for hard disk drives, optical disc drives, or solid-state drives, typically SATA and NVMe now[when?]
Additionally, nearly all motherboards include logic and connectors to support commonly used input devices, such as USB for mouse devices and keyboards. Early personal computers such as the Apple II or IBM PC included only this minimal peripheral support on the motherboard. Occasionally video interface hardware was also integrated into the motherboard; for example, on the Apple II and rarely on IBM-compatible computers such as the IBM PCjr. Additional peripherals such as disk controllers and serial ports were provided as expansion cards.
Given the high thermal design power of high-speed computer CPUs and components, modern motherboards nearly always include heat sinks and mounting points for fans to dissipate excess heat.
Form factor
Motherboards are produced in a variety of sizes and shapes called form factors, some of which are specific to individual computer manufacturers. However, the motherboards used in IBM-compatible systems are designed to fit various case sizes. (As of 2005), most desktop computer motherboards use the ATX standard form factor — even those found in Macintosh and Sun computers, which have not been built from commodity components. A case's motherboard and power supply unit (PSU) form factor must all match, though some smaller form factor motherboards of the same family will fit larger cases. For example, an ATX case will usually accommodate a microATX motherboard. Laptop computers generally use highly integrated, miniaturized, and customized motherboards. This is one of the reasons that laptop computers are difficult to upgrade and expensive to repair. Often the failure of one laptop component requires the replacement of the entire motherboard, which is usually more expensive than a desktop motherboard.
CPU sockets
A CPU socket (central processing unit) or slot is an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a CPU (also called a microprocessor). It is a special type of integrated circuit socket designed for very high pin counts. A CPU socket provides many functions, including a physical structure to support the CPU, support for a heat sink, facilitating replacement (as well as reducing cost), and most importantly, forming an electrical interface both with the CPU and the PCB. CPU sockets on the motherboard can most often be found in most desktop and server computers (laptops typically use surface mount CPUs), particularly those based on the Intel x86 architecture. A CPU socket type and motherboard chipset must support the CPU series and speed.
Integrated peripherals
With the steadily declining costs and size of integrated circuits, it is now possible to include support for many peripherals on the motherboard. By combining many functions on one PCB, the physical size and total cost of the system may be reduced; highly integrated motherboards are thus especially popular in small form factor and budget computers.
- Disk controllers for SATA drives, and historical PATA drives
- Historical floppy-disk controller
- Integrated graphics controller supporting 2D and 3D graphics, with VGA, DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort, and TV output
- integrated sound card supporting 8-channel (7.1) audio and S/PDIF output
- Ethernet network controller for connection to a LAN and to receive Internet
- USB controller
- Wireless network interface controller
- Bluetooth controller
- Temperature, voltage, and fan-speed sensors that allow software to monitor the health of computer components.
Peripheral card slots
A typical motherboard will have a different number of connections depending on its standard and form factor.
A standard, modern ATX motherboard will typically have two or three PCI-Express x16 connection for a graphics card, one or two legacy PCI slots for various expansion cards, and one or two PCI-E x1 (which has superseded PCI). A standard EATX motherboard will have two to four PCI-E x16 connection for graphics cards, and a varying number of PCI and PCI-E x1 slots. It can sometimes also have a PCI-E x4 slot (will vary between brands and models).
Some motherboards have two or more PCI-E x16 slots, to allow more than 2 monitors without special hardware, or use a special graphics technology called SLI (for Nvidia) and Crossfire (for AMD). These allow 2 to 4 graphics cards to be linked together, to allow better performance in intensive graphical computing tasks, such as gaming, video editing, etc.
In newer motherboards, the M.2 slots are for SSD and/or wireless network interface controller.
Temperature and reliability
Motherboards are generally air cooled with heat sinks often mounted on larger chips in modern motherboards.[4] Insufficient or improper cooling can cause damage to the internal components of the computer, or cause it to crash. Passive cooling, or a single fan mounted on the power supply, was sufficient for many desktop computer CPU's until the late 1990s; since then, most have required CPU fans mounted on heat sinks, due to rising clock speeds and power consumption. Most motherboards have connectors for additional computer fans and integrated temperature sensors to detect motherboard and CPU temperatures and controllable fan connectors which the BIOS or operating system can use to regulate fan speed.[5] Alternatively computers can use a water cooling system instead of many fans.
Some small form factor computers and home theater PCs designed for quiet and energy-efficient operation boast fan-less designs. This typically requires the use of a low-power CPU, as well as a careful layout of the motherboard and other components to allow for heat sink placement.
A 2003 study found that some spurious computer crashes and general reliability issues, ranging from screen image distortions to I/O read/write errors, can be attributed not to software or peripheral hardware but to aging capacitors on PC motherboards.[6] Ultimately this was shown to be the result of a faulty electrolyte formulation,[7] an issue termed capacitor plague.
Modern motherboards use electrolytic capacitors to filter the DC power distributed around the board. These capacitors age at a temperature-dependent rate, as their water based electrolytes slowly evaporate. This can lead to loss of capacitance and subsequent motherboard malfunctions due to voltage instabilities. While most capacitors are rated for 2000 hours of operation at 105 °C (221 °F),[8] their expected design life roughly doubles for every 10 °C (18 °F) below this. At 65 °C (149 °F) a lifetime of 3 to 4 years can be expected. However, many manufacturers deliver substandard capacitors,[9] which significantly reduce life expectancy. Inadequate case cooling and elevated temperatures around the CPU socket exacerbate this problem. With top blowers, the motherboard components can be kept under 95 °C (203 °F), effectively doubling the motherboard lifetime.
Mid-range and high-end motherboards, on the other hand, use solid capacitors exclusively. For every 10 °C less, their average lifespan is multiplied approximately by three, resulting in a 6-times higher lifetime expectancy at 65 °C (149 °F).[10] These capacitors may be rated for 5000, 10000 or 12000 hours of operation at 105 °C (221 °F), extending the projected lifetime in comparison with standard solid capacitors.
In desktop PCs and notebook computers, the motherboard cooling and monitoring solutions are usually based on a super I/O chip or an embedded controller.
Bootstrapping
Motherboards contain a ROM (and later EPROM, EEPROM, NOR flash) that stores to initialize hardware devices and boot an operating system from a peripheral device.
Microcomputers such as the Apple II and IBM PC used ROM chips mounted in sockets on the motherboard. At power-up, the central processor unit would load its program counter with the address of the Boot ROM and start executing instructions from the Boot ROM. These instructions initialized and tested the system hardware, displayed system information on the screen, performed RAM checks, and then attempts to boot an operating system from a peripheral device. If no peripheral device containing an operating system was available, then the computer would perform tasks from other ROM stores or display an error message, depending on the model and design of the computer. For example, both the Apple II and the original IBM PC had Cassette BASIC (ROM BASIC) and would start that if no operating system could be loaded from the floppy disk or hard disk.
The boot firmware in modern IBM PC compatible motherboard designs contains either a BIOS, as did the boot ROM on the original IBM PC, or UEFI. UEFI is a successor to BIOS that became popular after Microsoft began requiring it for a system to be certified to run Windows 8.[11][12]
When the computer is powered on, the boot firmware tests and configures memory, circuitry, and peripherals. This Power-On Self Test (POST) may include testing some of the following things:
- Video card
- Expansion cards inserted into slots, such as conventional PCI and PCI Express
- Historical floppy drive
- Temperatures, voltages, and fan speeds for hardware monitoring
- CMOS memory used to store BIOS configuration
- Keyboard and mouse
- Sound card
- Network adapter
- Optical drives: CD-ROM or DVD-ROM
- Hard disk drive and solid-state drive
- Security devices, such as a fingerprint reader
- USB devices, such as a USB mass storage device
See also
- Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)
- Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
- Chip creep
- CMOS battery
- Computer case screws
- Expansion card
- List of computer hardware manufacturers
- M.2
- Overclocking
- Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
- PCI-X
- PCI Express (PCIe)
- Single-board computer
- Switched-mode power supply
- Symmetric multiprocessing
- System on a chip
- U.2
- UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
References
- ↑ "Golden Oldies: 1993 mainboards". http://redhill.net.au/b/b-93.html.
- ↑ "CPU Socket Types Explained: From Socket 5 To BGA [MakeUseOf Explains"]. 2013-01-25. http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/cpu-socket-types-explained-from-socket-5-to-bga-makeuseof-explains/.
- ↑ W1zzard (2005-04-06). "Pinout of the PCI-Express Power Connector". techPowerUp. http://www.techpowerup.com/articles/overclocking/psu/116.
- ↑ Karbo, Michael. "The CPU and the motherboard". Karbos Guide. http://www.karbosguide.com/books/pcarchitecture/chapter26.htm.
- ↑ "Temperatures". https://sites.google.com/site/visualbios/advanced/cooling/temperatures.
- ↑ c't Magazine, vol. 21, pp. 216-221. 2003.
- ↑ Chiu, Yu-Tzu; Moore, Samuel K. (2003-01-31). "Faults & Failures: Leaking Capacitors Muck up Motherboards". IEEE Spectrum. http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/WEBONLY/resource/feb03/ncap.html.
- ↑ "Capacitor lifetime formula". Low-esr.com. http://www.low-esr.com/endurance.asp.
- ↑ Carey Holzman The healthy PC: preventive care and home remedies for your computer McGraw-Hill Professional, 2003 ISBN:0-07-222923-3 page 174
- ↑ "-- GIGABYTE, --Geeks Column of the Week - All Solid Capacitor". http://www.gigabyte.com/webpage/8/article_02_all_solid.htm.
- ↑ "Windows Hardware Certification Requirements for Client and Server Systems". Microsoft. January 2013. http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/hardware/jj128256.aspx. "System.Fundamentals.Firmware.CS.UEFISecureBoot.ConnectedStandby ... Platforms shall be UEFI Class Three (see UEFI Industry Group, Evaluating UEFI using Commercially Available Platforms and Solutions, version 0.3, for a definition) with no Compatibility Support Module installed or installable. BIOS emulation and legacy PC/AT boot must be disabled."
- ↑ "Microsoft: All You Need to Know About Windows 8 on ARM". PC Magazine. https://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2400059,00.asp.
External links
- The Making of a Motherboard: ECS Factory Tour
- The Making of a Motherboard: Gigabyte Factory Tour
- Front Panel I/O Connectivity Design Guide - v1.3 (pdf file)
 |