Medicine:Orbital apex syndrome
| Orbital apex syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Jacod syndrome |
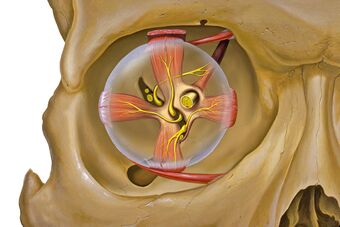 | |
| Eye orbit anterior | |
| Specialty | Neurology/ophthalmology |
Orbital apex syndrome, is a collection of cranial nerve deficits associated with a mass lesion near the apex of the orbit of the eye. This syndrome is a separate entity from Rochon–Duvigneaud syndrome, which occurs due to a lesion immediately anterior to the orbital apex. Most commonly optic nerve is involved.
Presentation
The most common finding is oculomotor nerve dysfunction leading to ophthalmoplegia. This is often accompanied by ophthalmic nerve dysfunction, leading to hypoesthesia of the upper face. The optic nerve may eventually be involved, with resulting visual loss.[citation needed]
Causes
Jacod Syndrome is commonly associated with a tumor of the middle cranial fossa (near the apex of the orbit); but it can have several other causes.[citation needed]
Neoplastic causes
- Head and neck cancer
- Neural tumors
- Hematological cancer
Inflammatory causes
- Sarcoidosis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Giant cell arteritis
- Thyroid disease
Traumatic causes
- Iatrogenic (following surgery)
- Orbital apex fracture
- Penetrating injury
Vascular causes
- Carotid aneurysm
Diagnosis
Diagnostic methods vary, and are based on specific possible etiologies; however, an X-ray computed tomography scan of the face (or magnetic resonance imaging, or both) may be helpful.[citation needed]
Treatment
References
- Bailey, Byron J., and Jonas T. Johnson. Head and neck surgery – Otolaryngology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Wilkins and Williams, 2006, p. 2792.
- Yeh, S.; Foroozan, R. (2004). "Orbital apex syndrome". Current Opinion in Ophthalmology 15 (6): 490–498. doi:10.1097/01.icu.0000144387.12739.9c. PMID 15523194..
 |

