Medicine:Carotid triangle
| Carotid triangle | |
|---|---|
 Carotid triangle | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum caroticum |
| Anatomical terminology | |
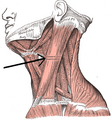
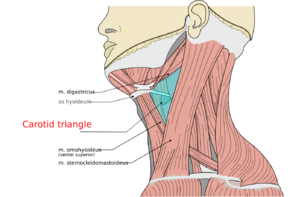
The carotid triangle (or superior carotid triangle) is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.
Anatomy
Boundaries
It is bounded:
- Posteriorly by (the anterior border of) the sternocleidomastoid muscle,
- Anteroinferiorly by (the superior belly of) the omohyoid muscle.
- Superiorly by (the posterior belly of) the digastric muscle.
Roof
The roof is formed by:
- Integument,
- Superficial fascia,
- Platysma,
- Deep fascia.
Floor
The floor is formed by (parts of) the:
- Hyoglossus,
- Constrictor pharyngis medius and constrictor pharyngis inferior muscles.
Contents
Arteries
- Internal carotid artery
- External carotid artery and some of its branches:
- Superior thyroid artery,
- Ascending pharyngeal artery,
- Lingual artery,
- Facial artery,
- Occipital artery.
Veins
- internal jugular vein and its tributaries (correspondng to the branches of the corresponding artery):
- Superior thyroid vein,
- Lingual veins,
- Common facial vein (draining into the internal jugular vein)
- Ascending pharyngeal vein,
- Occipital vein (sometimes).
Nerves
Superficial to the carotid sheath lies the hypoglossal nerve, and ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus.
The hypoglossal nerve crosses both the internal and external carotids, curving around the origin of the occipital artery.
Within the sheath, between the artery and vein, and behind both, is the vagus nerve; behind the sheath, the sympathetic trunk.
On the lateral side of the vessels, the accessory nerve runs for a short distance before it pierces the Sternocleidomastoideus; and on the medial side of the external carotid, just below the hyoid bone, the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve may be seen; and, still more inferiorly, the external branch of the same nerve.
Other
The superior portion of the larynx and inferior portion of the pharynx are also found in the anterior portion part of this space.
See also
Additional images
References
External links
- lesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (necktriangle)
- lesson6 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Anatomy figure: 25:01-05 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
 |