Medicine:Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome
| Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Progressive pancytopenia-immunodeficiency-cerebellar hypoplasia syndrome[1] |
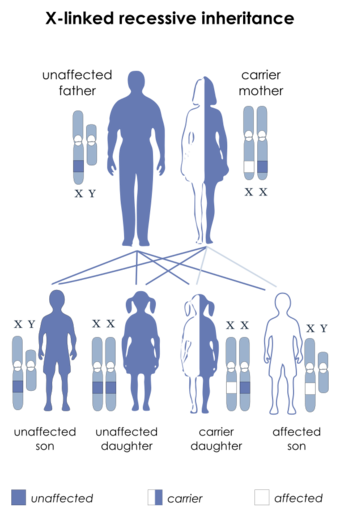 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. | |
| Causes | Mutation in genes related to telomere maintenance |
Hoyeraal–Hreidasson syndrome[2] is a very rare multisystem X-linked recessive disorder characterized by excessively short telomeres and is considered a severe form of dyskeratosis congenita.[2][3] Being an X-linked disorder, Hoyeraal–Hreidasson syndrome primarily affects males. Patients typically present in early childhood with cerebellar hypoplasia, immunodeficiency, progressive bone marrow failure, and intrauterine growth restriction.[2] The primary cause of death in Hoyeraal–Hreidasson syndrome is bone marrow failure, but mortality from cancer and pulmonary fibrosis is also significant.[4][5][6]
Presentation
The currently recognized features are cerebellar hypoplasia, immunodeficiency, progressive bone marrow failure, and intrauterine growth restriction. Patients also commonly exhibit symptoms such as microcephaly, aplastic anemia, and intellectual disability.[3]
Overlap with dyskeratosis congenita
Patients with Hoyeraal–Hreidasson syndrome frequently present with the mucocutaneous triad of nail dysplasia, lacy skin pigmentation, and oral leukoplakia.[citation needed]
Pathogenesis
Although the pathogenesis remains unknown, it is strongly suspected that the clinical sequelae of Hoyeraal–Hreidasson syndrome arise from the accelerated telomere shortening.[2] It has been associated with mutations in DKC1, TERT, RTEL1, TINF2, ACD, and PARN.[7][8]
Diagnosis
- Neuroimaging – cerebellar hypoplasia/atrophy, small brainstem, thin corpus callosum and cerebral calcifications
- Molecular genetic testing – for confirmation
Treatment
Current treatment is supportive:[citation needed]
- The aplastic anemia and immunodeficiency can be treated by bone marrow transplantation.
- Supportive treatment for gastrointestinal complications and infections.
- Genetic counselling.
See also
References
- ↑ "Orphanet: Hoyeraal Hreidarsson syndrome" (in en). https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=EN&Expert=3322.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Unraveling the pathogenesis of Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome, a complex telomere biology disorder". British Journal of Haematology 170 (4): 457–71. August 2015. doi:10.1111/bjh.13442. PMID 25940403.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Unexplained aplastic anaemia, immunodeficiency, and cerebellar hypoplasia (Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome) due to mutations in the dyskeratosis congenita gene, DKC1". British Journal of Haematology 107 (2): 335–9. November 1999. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01690.x. PMID 10583221.
- ↑ "Inherited mutations in the helicase RTEL1 cause telomere dysfunction and Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110 (36): E3408-16. September 2013. doi:10.1073/pnas.1300600110. PMID 23959892. Bibcode: 2013PNAS..110E3408D.
- ↑ "Human RTEL1 deficiency causes Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome with short telomeres and genome instability". Human Molecular Genetics 22 (16): 3239–49. August 2013. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt178. PMID 23591994.
- ↑ "Mutations of the RTEL1 Helicase in a Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson Syndrome Patient Highlight the Importance of the ARCH Domain". Human Mutation 37 (5): 469–72. May 2016. doi:10.1002/humu.22966. PMID 26847928.
- ↑ "Impaired telomere integrity and rRNA biogenesis in PARN-deficient patients and knock-out models". EMBO Molecular Medicine 11 (7): e10201. July 2019. doi:10.15252/emmm.201810201. PMID 31273937.
- ↑ "Hoyeraal Hreidarsson syndrome". National Institutes of Health. 1 August 2019. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/346/hoyeraal-hreidarsson-syndrome.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
 |

