Social:Chʼortiʼ language
| Chʼortiʼ | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador |
| Region | Copán |
| Ethnicity | Chʼortiʼ |
Native speakers | (30,000 cited 2000)[1] |
Mayan
| |
Early form | Classic Maya
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | caa |
| Glottolog | chor1273[2] |
The Chʼortiʼ language (sometimes also Chorti) is a Mayan language, spoken by the indigenous Maya people who are also known as the Chʼortiʼ or Chʼortiʼ Maya. Chʼortiʼ is a direct descendant of the Classic Maya language in which many of the pre-Columbian inscriptions using the Maya script were written.[3] Chʼortiʼ is the modern version of the ancient Mayan language Chʼolan (which was actively used and most popular between the years of A.D 250 and 850).[3]
Relationship to other Mayan languages
Chʼortiʼ can be called a living "Rosetta Stone" of Mayan languages. The Chʼortiʼ language is an important factor to comprehend the contents of Maya glyphic writings, some of which are not yet fully understood. Over several years, many linguists and anthropologists expected to realize the Chʼortiʼ culture and language by studying its words and expressions.[4] Chʼortiʼ is spoken mainly in and around Jocotán and Camotán, Chiquimula department, Guatemala, as well as adjacent areas of parts of western Honduras near the Copán Ruins.[5] Because the Classic Mayan language was ancestral to the modern Chʼorti, Chʼorti can be used to decipher the ancient language.[3] Researchers realized that the ancient language was based more on phonetics than previously thought.[3]
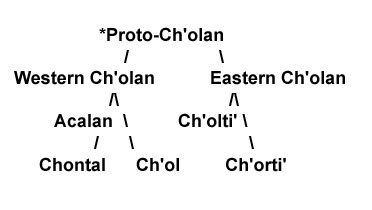
The name Chʼortiʼ (with unglottalized <ch>) means 'language of the corn farmers', which references to the traditional agricultural activity of the Chʼortiʼ families. Chʼortiʼ is one of the three modern descendants of Chʼolan language which is a sub-group of Mayan languages. Other two modern descendants are Chontal and Chʼol.[6] These three descendants are still spoken by people. Chʼortiʼ language and Chʼolti language are two sub-branches belong to the Eastern Chʼolan. And Chʼolti language is already extinct today.
There are some debates among the scholars how the Chʼolan language should be classified. John Robertson considered the direct ancestor of colonial Chʼoltiʼ is the language of the Mayan script (also known as Mayan Glyphs). The language of the Mayan Glyphs is realized as 'Classic Chʼoltiʼan' by John Robertson, David Stuart, and Stephen Houston. And then the language of the Mayan script in turn becomes the ancestor of Chʼortiʼ. The relationship shows as the chart below.[5]
Language Endangerment
The Chʼortiʼ people are descendants of the people who lived in and around Copán, one of the cultural capitals of the ancient Maya area. This covers parts of modern-day Honduras and Guatemala. Chʼorti is considered an endangered language as well as an endangered culture.
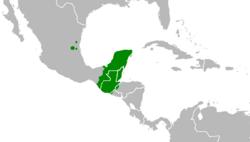
Geographic location of Chʼortiʼ speakers
This region is the only region in the world that Chʼorti speakers can be found. Although the area is completely shaded in, the majority of speakers reside in Guatemala, while the rest are sparsely distributed throughout the rest of the area.[7]
Honduras
The government of Honduras has been trying to promote a uniform national language of Spanish, and therefore discourages the use and teaching of native languages such as Chʼorti. The Chʼortiʼ people in Honduras face homogenization and have to assimilate to their surroundings. The government has been clashing with the Chʼorti people over land disputes from the 1800s, which puts the people (and thus the language) at risk. In 1997, 2 prominent Chʼorti leaders were assassinated. This assassination is just one example of many cases where Chʼorti advocates have been harmed or killed. Every one of these killings reduces the number of Chʼorti speakers. As of right now, there are only 10 remaining native speakers in Honduras.[8]
Guatemala
The government of Guatemala has been more supportive of Chʼorti speakers and has promoted programs that encourage the learning and teaching of Chʼorti. The Chʼorti's in Guatemala wear traditional clothing, unlike their counterparts in Honduras, who wear modern-day clothing.[8] Currently there are about 55,250 Chʼorti speakers in Guatemala. Even though Guatemala has established Spanish as its official language, it supports the teaching of these native languages.
Ethnonyms: Cholotí, Chorté, Chortí
The majority of Chʼortiʼ live in the Chiquimula Department of Guatemala, approximately 52,000. The remaining 4,000 live in Copán, Honduras. The Kʼicheʼ Maya however, dominated the Chʼortiʼ dating back to the early fifteenth century. Warfare as well as disease devastated much of the Chʼortiʼ during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Much of their land was lost to the Guatemalan government in the nineteenth century as well. More recently, 25 percent of the Guatemalan Chʼortiʼ went to the United States during the 1980s to escape political persecution.[9]
Phonology and orthography
The Chʼortiʼ have their own standard way of writing their language. However, inaccurate ways to represent phonemes led to some variation among recent publications.[10][11]
Consonants
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m ⟨m⟩ | n ⟨n⟩ | ||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p ⟨p⟩ | t ⟨t⟩ | k ⟨k⟩ | ʔ ⟨ʼ⟩ | |
| ejective | tʼ ⟨tʼ⟩ | kʼ ⟨kʼ⟩ | ||||
| voiced | (b ⟨b⟩) | (d ⟨d⟩) | (ɡ ⟨g⟩) | |||
| implosive | ɓ ⟨bʼ⟩ | |||||
| Affricate | voiceless | ts ⟨tz⟩ | tʃ ⟨ch⟩ | |||
| glottalic | tsʼ ⟨tzʼ⟩ | tʃʼ ⟨chʼ⟩ | ||||
| Fricative | s ⟨s⟩ | ʃ ⟨x⟩ | x ⟨j⟩ | |||
| Trill | r ⟨r⟩ | |||||
| Approximant | l ⟨l⟩ | j ⟨y⟩ | w ⟨w⟩ | |||
The consonants of Chʼortiʼ include glottal stop [ʼ], b, bʼ, ch, chʼ, d, g, j, k, kʼ, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, tʼ, tz, tzʼ, w, x, y.
Instances of both /b/, /d/ and /ɡ/ usually only appear in Spanish loan words. The j has two pronunciations, as either a voiceless velar fricative [x] or a voiceless glottal fricative [h]. Classic Mayan differentiated between the [x] and the [h]. This differentiation can be seen in some Chʼortiʼ literature, such as with the texts by Wisdom. The <w> and <y> are semivowels.
The ordering of terms would be that the consonants follows after the non glottal versions. Besides, words with rearticulated root vowels follow after their corresponding short vowels.
Therefore, the order of presentation will be as follows: a, aʼ, b, bʼ, ch, chʼ, d, e, eʼ, g, i, iʼ, j, k, kʼ, l, m, n, o, oʼ, p, r, s, t, tʼ, tz, tzʼ, u, uʼ, w, x, y.
Vowels
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u |
| Mid | e | o |
| Open | a | |
The vowels consist of a, e, i, o, and u.[11]
Vowel clusters
| Characters we use | Sometimes also used | IPA symbol | Chʼortiʼ pronunciation |
|---|---|---|---|
| aa | ā, aꞏ, a꞉ | a | Like regular a but held longer |
| ee | ē, eꞏ, e꞉ | e | Like e only held longer |
| ii | ī, iꞏ, i꞉ | i | Like i only held longer |
| oo | ō, oꞏ, o꞉ | o | Like o only held longer |
| uu | ū, uꞏ, u꞉ | u | Like u only held longer |
When two vowels are put together in Chʼortiʼ the second vowel always takes precedence and then is always followed by a glottal stop. Chʼortiʼ doesn't have any long vowels. According to historians, long vowels occur in Classical Mayan, but have been lost in modern Chʼortiʼ.
In Chʼortiʼ language, aa or a꞉ is used as aʼ or Aʼ, we can see this pattern with all vowel clusters including eʼ, Iʼ, oʼ and uʼ.
Some examples of words with vowel clusters are꞉
- Jaʼx [xaʔʃ] = Her, ella
- Weʼr [weʔr] = meat, carne
- Bʼiʼx [pʼiʔʃ] = seed, semilla
- Tunoʼron [tunoʔɾon] = everyone, todos
- Kuʼm [kuʔm] = egg, huevo [12]
Syntax
The aspectual system of Chʼortiʼ language changed to a tripartite pronominal system which comes with different morphemes used for the subject of transitive verbs, the object of transitive verbs and the subject of intransitive completive verbs, and a third set of pronouns only used for the subject of incompletive intransitive verbs.[13]
Chʼortiʼ tripartite pronominal system (data from Hull 2005)
Transitive Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Intransitive completive Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Intransitive incompletive Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Basic word order
In the Chʼortiʼ language and other Mayan sentences it always starts with verbs but also there are agents or patients added and in which they are commonly represented by the acronym VOS, meaning verb-object-subject. The following rules apply VSO, SVO, SOV,OVS, OSV.[14]
In most of the Chʼortiʼ language there are phrases surrounding transitive verbs and they are order subject first (first-most) and it's followed by the verb then the object (SVO).[15]
Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Adjectives with attributive function
The adjective works together with the nouns as a modifier formed with a noun phrase that plays some syntactic role, object etc.[14]
Predicative adjective indicate the size, color or state
Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Chʼortiʼ has many other different forms, in the following sentence the words that appear to be bold is a preposition and underline one is a relational noun.[14]
Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Vocabulary Examples
The following list contains examples of common words in the Chʼortiʼ language:
| English | Chʼortiʼ | English | Chʼortiʼ |
|---|---|---|---|
| big | nixiʼ | fire | kʼajkʼ |
| bird | mut | here | tara |
| cold | insis | what | tukʼa |
| dog | txʼiʼ | husband | noxibʼ |
| day | kʼin | man | winik' |
| beverage | uchʼe | moon | uj |
| earth | rum | mountain | witzir |
According to "A Dictionary of Chʼortiʼ Maya, Guatemala" by Kerry Hull, some words may be used as nouns (as shown above) or can double as a verb as well. For example "Witzir" can mean mountain as a noun, or 'to go uphill' as a verb. [10]
Morphology
Verb inflection
| Ergative (Set A) | Absolutive (Set B) | Subjective (Set C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1S | in-/ni- | -en | in- |
| 2S | a- | -et | i- |
| 3S | u- | -Ø | a- |
| 1P | ka- | -on | ka- |
| 2P | i- | -ox | ix- |
| 3P | u-...-obʼ | -obʼ | aʼ...-obʼ |
Examples of inflected verbs from Isidro González's stories (John Fought, 1972):
| Uninflected Verb | Definition | Inflected Verb | gloss | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ixin | "to go" | ixinobʼ | go-A3-PL | "they went" |
| ira | “to see” | uwira | E3-see-A3 | “he sees it” |
| kojko | “to guard” | ukojkobʼ | E3-guard-A3-PL | “they guard over it” |
| ixin | “to go” | aʼxin | S3-go | “he goes” |
Possessions
Tak is plural for women and childrenʼ
- ijchʼok-tak "little girls"
- max-tak "children, young ones, family" (max does not occur without -tak)
- ixik-tak "women"
These are the only instances encountered. It is worthy of notice that ixkaʼr "wife", chʼurkabʼ "baby" and ar "offspring" take -ob'.
obʼ is a general plural. The suffix can be found in nouns, verbs, adjectives, and participials.
Examples on possessives:
Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Script error: No such module "Interlinear".
Language Organizations
There are currently multiple organizations and projects that are currently working on the revitalization, documentation, and education of the Chʼortiʼ language.
Proyecto Lingüístico Francisco Marroquín (PLFM)
The PLFM was founded in 1969. When the foundation was opened the two main purposes of the organization were to teach Spanish Language with native Spanish speakers from Guatemala as well as to teach, investigate, and preserve the Mayan Languages spoken around Guatemala.
“The program... has published dictionaries, grammars, and other pedagogical materials on many Mayan languages. The organization sustains itself by offering Spanish-language classes to foreigners and applying the proceeds to their trainings and publications”
The PLFM hosts a variety of projects regarding the preservation of Mayan languages, such as Chʼortiʼ, including cooperation with: Academy of Mayan Languages of Guatemala -ALMG-, the Indigenous Municipality of Sololá, the Ancient Maya organization for the Mayas -MAM- and liaison with brothers of the Mayan Linguistic Communities of the Mesoamerican area, the University of Tulane USA, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee USA, the Tojolab'al Language Research Center, Chiapas – Mexico, Intercultural University of Chiapas – Mexico. UNICH.[18][19]
Academia de Lenguas Mayas de Guatemala (ALMG)
The Academia de Lenguas Mayas de Guatemala was founded in 1990 by a group of Guatemalan professionals interested in the research, development and promotion of the indigenous languages existing in the country. The academy is currently considered by some to be "the highest governing body for the promotion and development of Mayan languages in the country". The ALMG is an organization of the State of Guatemala that regulates the use, writing and promotion of Mayan languages.
The ALMG website provides a variety of information and resources regarding Chʼortiʼ, as well as many other Mayan languages. For Chʼorti, there are historical as well as pedagogical documents available, all of which are in a mixture of Chʼortiʼ and Spanish.[20]
The Chʼortiʼ Project Collaboration
The Chʼortiʼ Project is a community-based language documentation, revitalization, and reclamation project focused on the Chʼortiʼ (Mayan) language of Guatemala and Honduras. It was founded in 2013 by Dr. Rebecca Forgash and Dr. Robin Quizar. The project is a collaborative effort involving MSU Denver faculty, students, Chʼortiʼ community members, and others. The project is run out of and in association with MSU Anthropology's Ethnography Lab. The project is multidisciplinary and multifaceted in that it has engaged in work on producing Chʼortiʼ language educational materials, preparing Chʼortiʼ stories from legacy texts in the local writing system, and conducting linguistic research on various aspects of the language, among other things.
Current elements of the project include putting all previously written texts into the official Chʼortiʼ alphabet with English and Spanish word-for-word translations, supporting individual research projects for faculty and students with on-campus and on-the-ground fieldwork, and working with archaeologists and museums to highlight the Chʼortiʼ language and cultural connection with the Classic Maya civilization. A free-access internet platform of written resources available to Guatemalan scholars and Chʼortiʼ speakers is also in the works, as is an initiative to help reconnect the Chʼortiʼ community with the heritage held within the Classic Maya script.[21][22]
CONIMCHH
“CONIMCHH – the Consejo Nacional Indigena Maya Ch'ortí de Honduras – is a private nonprofit organization in Honduras that facilitates the comprehensive development of its affiliated communities, including efforts promoting economic development, the recovery of ancestral lands, cultural recognition and general education.”
Through strategic planning, the systematic payment of the membership dues, and the efficient use of funds and resources, they plan to achieve the technical training to introduce our goals of sustainable development to all of the necessary program areas for the communities to reach financial sustainability and the quality of the life the community members deserve, where an open community and a duty to human service prevail.
The organization is divided into smaller groups that represent both geographical location as well as specific projects. They have a long history of fighting for social causes to try and benefit the conditions for Chʼortiʼ people in Honduras.[23]
References
- ↑ Chʼortiʼ at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Chorti". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/chor1273.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Houston, S, J Robertson, and D Stuart. "The language of Classic Maya inscriptions." Current Anthropology 41.3 (2000): 321–356. Print.
- ↑ Keys, David. "'Lost' Sacred Language of the Maya Is Rediscovered." Mayanmajix.com. N.p., 07 Dec. 2003. Web page: [1]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hull, Kerry M. (2003). Verbal art and performance in Chʼortiʼ and Maya hieroglyphic writing [electronic resource]. Doctoral dissertation, The University of Texas at Austin. Available electronically from http://hdl.handle.net/2152/1240
- ↑ Mathews,Peter and Bíró,Péter Maya Hieroglyphs and Mayan Languages.[electronic resource] Available electronically from [2]
- ↑ • McAnany, Patricia, and Shoshaunna Parks. "Casualties of Heritage Distancing Children, Chʼortiʼ Indigeneity, and the Copan Archaeoscape." Current Anthropology 53.1 (2012): 80–107. Print.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 • "World Directory of Minorities and Indigenous Peoples." Minority Rights Group International : Honduras : Lenca, Miskitu, Tawahka, Pech, Maya, Chortis and Xicaque. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Oct. 2013. <"Minority Rights Group International : Honduras : Lenca, Miskitu, Tawahka, Pech, Maya, Chortis and Xicaque". http://www.minorityrights.org/2572/honduras/lenca-miskitu-tawahka-pech-maya-chortis-and-xicaque.html.>.
- ↑ Chenier, Jacqueline, and Steve Sherwood. "Copan: Collaboration for Identity, Equity and Sustainability (Honduras)." Ciesin.Columbia. Community-Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM), n.d. Web. 27 Oct. 2013. <http://srdis.ciesin.columbia.edu/cases/Honduras-Paper.html>."http://www.everyculture.com/Middle-America-Caribbean/Ch-orti.html[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Hull, Kerry. (2005) "A Dictionary of Chʼortiʼ Maya, Guatemala." FAMSI.org Web. Available online:http://www.famsi.org/reports/03031/03031Hull01.pdf.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Pérez Martínez, Vitalino(1994) Gramática del idioma chʼortíʼ. Antigua, Guatemala: Proyecto Lingüístico Francisco Marroquín.
- ↑ "Chorti Maya Pronunciation Guide, Alphabet and Phonology". http://www.native-languages.org/chorti_guide.htm.
- ↑ Law, Danny, John Robertson, and Stephen Houston. "Split Ergativity In The History Of The Chʼolan Branch Of The Mayan Language Family." International Journal of American Linguistics 72.4 (2006): 415–450.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Pérez, Lauro (2004–2008). "GRAMÁTICA PEDAGÓGICA Chʼortiʼ.". https://www.almg.org.gt/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/GRAMATICA-PEDAGOGICA..pdf?__cf_chl_jschl_tk__=9aefae3b50c0990fb52169ce7595c0c596ef85dd-1607327367-0-AdVpEkLNKohiKs2VsdRy-r6wdNidSzhhVWOZ3gtz-3Bd8uJvdMnMYMA_W7jNxiGV4kFH1j0RvPF4W51xaSMFwCBKM2oBIuzEB5qq4E0vxFALuO1lKx88YExj2pqDjtDRpuQDNVFsfOF-yrf0l6Wwq49C0D4bxFMYJh1Otw2v2oIwtoJ0Qa3SXskENhDtkzVb42PW7hGQ4v3t75nMtS8UhBBOANgkzNrV6oSchVhWBk8uNWRAMHky9yVLoV0TDmznWgU0Td-vhBopba4zAGjS1wTecRBMFRFCza9kSM-PFWESw5QYfh1gTDYTTlZrMc81OB0EEDcL0lW9m0xn43492knjhpUKw3WqbF5kX4qw0mR2y450LZLCzoYVnejgml8pOw.
- ↑ Dugan, James (May 20, 2013). "The grammar of Chʼortiʼ Maya Folktales". https://digitallibrary.tulane.edu/islandora/object/tulane%3A27759/datastream/PDF/view.
- ↑ Quizar, Robin. 1994. "Motion Verbs in Chʼortiʼ." Función 15–16. 211–229.
- ↑ Wichmann, Søren (1999). A CHʼORTIʼ MORPHOLOGICAL SKETCH. pp. 153.
- ↑ "About Us". https://spanishschoolplfm.com/about-us/.
- ↑ "Mayan Language Institute in Guatemala // Roger Thayer Stone Center for Latin American Studies at Tulane University". https://stonecenter.tulane.edu/pages/detail/320/Mayan-Language-Institute-in-Guatemala.
- ↑ https://www.almg.org.gt/portfolio-item/c-l-chorti
- ↑ "Reconnecting with Chʼortiʼ". 11 December 2019. https://red.msudenver.edu/2019/reconnecting-with-chorti.html.
- ↑ Quizar, Robin (22 August 2021). "The Chʼortiʼ Project Collaboration". Colorado Research in Linguistics. https://journals.colorado.edu/index.php/cril/article/view/1347/1189.
- ↑ "CONIMCHH English – CONIMCHH". http://en.conimchh.org/index.html.
External links
- Online version of Wisdom's Chorti Dictionary (1950)
- Oral Histories of the Chʼortiʼ Maya (2011)
- Mayan Languages Collection of John Fought at the Archive of the Indigenous Languages of Latin America, containing several hundred recordings of Chʼortiʼ made between 1964 and 1967 in Guatemala, field notes and photographs.
- Information about Chʼortiʼ language
 |