Chemistry:Enloplatin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Enloplatine, enloplatino, enloplatinum |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% (IV) |
| Protein binding | > 85% |
| Elimination half-life | 56±40 hours (Whole blood) 52±40 hours (Blood plasma)[1] |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H20N2O5Pt |
| Molar mass | 479.396 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 260 to 263[2] °C (500 to 505 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 450[lower-alpha 1] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
Enloplatin is a water-soluble cancer medication. It is a platinum-based antineoplastic investigated for treatment of platinum-refractory ovarian cancer, in which it was demonstrated to have minimal activity.[3] This cancer is suspected to be at least partially cross-resistant with another third-generation platinum analog, zeniplatin, which also shows minimal antitumor activity in this type of cancer. It was found to be cross-resistant with carboplatin.[1]
Like zeniplatin and carboplatin, use of enloplatin causes manageable nephrotoxicity, no significant neurotoxicity or ototoxicity, and dose-limiting myelosuppression.[1]
The drug was original developed by Wyeth, but no further development since 2000 has been reported.[4]
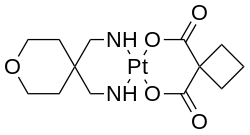
Structure
Like any platinum-based antineoplastic drug enloplatin is a coordination complex of platinum. Its two bidentate ligands are a tetrahydropyran-containing amine and cyclobutane dicarboxylic acid (CBDCA). Its CBDCA ligand is identical to that of carboplatin. It was found to have similar pharmokinetics to carboplatin, indicating it is the CBDCA ligand and not the amine that most influences plasma pharmokinetics of these platinum complexes.[1]
Notes
- ↑ As hydrate.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "A phase II and pharmacokinetic study of enloplatin in patients with platinum refractory advanced ovarian carcinoma". Anti-Cancer Drugs (Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)) 8 (7): 649–656. August 1997. doi:10.1097/00001813-199708000-00001. PMID 9311439.
- ↑ "Water-soluble third generation antitumor platinum complexes, [2,2-bis (aminomethyl)-1,3-propanediol-N,N']-[1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato (2-)-O,O']platinum(II) and [1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato(2-)-O,O'] [tetrahydro-4H-pyran-4,4-dimethanamine-N,N']platinum(II)". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (American Chemical Society (ACS)) 32 (8): 2015–2020. August 1989. doi:10.1021/jm00128a052. PMID 2754720.
- ↑ "Analysis of enloplatin by liquid chromatography and of platinum by atomic absorption spectrometry in various biological fluids". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis (Elsevier BV) 12 (8): 1023–1033. August 1994. doi:10.1016/0731-7085(94)e0035-y. PMID 7819376.
- ↑ "Enloplatin". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800002455.
 |


