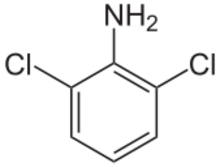
Chemistry:2,6-Dichloroaniline
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6-Dichloroaniline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1590 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5Cl2N | |
| Molar mass | 162.01 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H317, H331, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P361, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,6-Dichloroaniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2(NH2). It is one of several isomers of dichloroaniline. It is a colorless or white solid. Derivatives include the drugs clonidine and diclofenac.
Preparation
It is produced by hydrogenation of 2,6-dichloronitrobenzene.[1]
In the laboratory, it can be prepared by halogenation of sulfanilamide followed by desulfonation.[2]
References
- ↑ P. F. Vogt; J. J. Gerulis (2005). "Amines, Aromatic". Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_037. ISBN 9783527303854.
- ↑ Margaret K. Seikel (1944). "2,6-Dichloroaniline and 2,6-Dibromoaniline". Org. Synth. 24: 47. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.024.0047.
 |

