Chemistry:Gitoformate
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dynocard |
| Other names | Gitoxin 3',3'',3''',4''',16-pentaformate |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C46H64O19 |
| Molar mass | 920.999 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
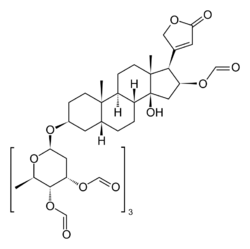
Gitoformate (INN, or pentaformylgitoxin, trade name Dynocard) is a cardiac glycoside, a type of drug that can be used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat).[1] Produced by Madaus, it is not available in the US, and does not seem to be available in Europe either.
Chemistry
Gitoformate is a derivative of the glycoside gitoxin, with five of the six free hydroxyl groups formylated, one on the aglycon and four on the sugar.[2][3] Gitoxin, a cardiac glycoside from the woolly foxglove (Digitalis lanata), has an aglycon of the cardenolide type named gitoxigenin, which is also the aglycon of lanatoside B, another Digitalis lanata glycoside.[4]
References
- ↑ "[Gitoformate and digitoxin as alternatives to kidney-dependent glycosides in the therapy of cardiac insufficiency]". Arzneimittel-Forschung 34 (8): 915–917. 1984. PMID 6541927.
- ↑ "[Plasma levels of gitoxin (by RIA and rubidium-86 uptake) and systolic time after treatment with a single dose of gitoformate]". Cardiologia 29 (5–6): 291–300. 1984. PMID 6542412.
- ↑ "Gitoxin". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/91540.
- ↑ Foye's principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2008. p. 699. ISBN 978-0-7817-6879-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=R0W1ErpsQpkC.
 |


