Chemistry:4-Bromoaniline
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Bromoaniline | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2811 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6BrN | |||
| Molar mass | 172.02 g mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 60 to 64 °C (140 to 147 °F; 333 to 337 K) | ||
| <0.1 g/100 mL at 23 °C | |||
| -84.06·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H302, H311, H315, H319, H332, H335, H373 | |||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P361, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
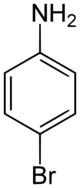
4-Bromoaniline is a compound where an aniline molecule is substituted with a bromine atom on the para position. Commercially available, this compound may be used as a building block, e.g. in the preparation of p-bromobiphenyl via the Gomberg-Bachmann reaction.[2]
Preparation
4-Bromoaniline can be made by reacting acetyl chloride-protected aniline with bromine.
Reactions
One laboratory route to 1-bromo-4-iodobenzene involves the Sandmeyer reaction. 4-Bromoaniline is treated with concentrated sulfuric acid and sodium nitrite, then potassium iodide.[3]
References
- ↑ 4-Bromoaniline, Chemblink.com
- ↑ M. Gomberg and W. E. Bachmann (1941). "p-Bromobiphenyl". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv1p0113.; Collective Volume, 1, pp. 113
- ↑ Banerjee, M.; Shukla, R.; Rathore, R. (15 January 2009). "Synthesis, Optical, and Electronic Properties of Soluble Poly-p-phenylene Oligomers as Models for Molecular Wires". Journal of the American Chemical Society 131 (5): 1780–1786. doi:10.1021/ja805102d. PMID 19146375.
 |