Girth (graph theory)
In graph theory, the girth of an undirected graph is the length of a shortest cycle contained in the graph.[1] If the graph does not contain any cycles (that is, it is a forest), its girth is defined to be infinity.[2] For example, a 4-cycle (square) has girth 4. A grid has girth 4 as well, and a triangular mesh has girth 3. A graph with girth four or more is triangle-free.
Cages
A cubic graph (all vertices have degree three) of girth g that is as small as possible is known as a g-cage (or as a (3,g)-cage). The Petersen graph is the unique 5-cage (it is the smallest cubic graph of girth 5), the Heawood graph is the unique 6-cage, the McGee graph is the unique 7-cage and the Tutte eight cage is the unique 8-cage.[3] There may exist multiple cages for a given girth. For instance there are three nonisomorphic 10-cages, each with 70 vertices: the Balaban 10-cage, the Harries graph and the Harries–Wong graph.
The Petersen graph has a girth of 5
The Heawood graph has a girth of 6
The McGee graph has a girth of 7
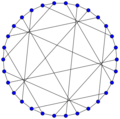
The Tutte–Coxeter graph (Tutte eight cage) has a girth of 8
Girth and graph coloring
For any positive integers g and χ, there exists a graph with girth at least g and chromatic number at least χ; for instance, the Grötzsch graph is triangle-free and has chromatic number 4, and repeating the Mycielskian construction used to form the Grötzsch graph produces triangle-free graphs of arbitrarily large chromatic number. Paul Erdős was the first to prove the general result, using the probabilistic method.[4] More precisely, he showed that a random graph on n vertices, formed by choosing independently whether to include each edge with probability n(1–g)/g, has, with probability tending to 1 as n goes to infinity, at most n⁄2 cycles of length g or less, but has no independent set of size n⁄2k . Therefore, removing one vertex from each short cycle leaves a smaller graph with girth greater than g, in which each color class of a coloring must be small and which therefore requires at least k colors in any coloring.
Explicit, though large, graphs with high girth and chromatic number can be constructed as certain Cayley graphs of linear groups over finite fields.[5] These remarkable Ramanujan graphs also have large expansion coefficient.
Related concepts
The odd girth and even girth of a graph are the lengths of a shortest odd cycle and shortest even cycle respectively.
The circumference of a graph is the length of the longest (simple) cycle, rather than the shortest.
Thought of as the least length of a non-trivial cycle, the girth admits natural generalisations as the 1-systole or higher systoles in systolic geometry.
Girth is the dual concept to edge connectivity, in the sense that the girth of a planar graph is the edge connectivity of its dual graph, and vice versa. These concepts are unified in matroid theory by the girth of a matroid, the size of the smallest dependent set in the matroid. For a graphic matroid, the matroid girth equals the girth of the underlying graph, while for a co-graphic matroid it equals the edge connectivity.[6]
Computation
The girth of an undirected graph can be computed by running a breadth-first search from each node, with complexity [math]\displaystyle{ O(nm) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is the number of vertices of the graph and [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is the number of edges.[7] A practical optimization is to limit the depth of the BFS to a depth that depends on the length of the smallest cycle discovered so far.[8] Better algorithms are known in the case where the girth is even[9] and when the graph is planar.[10] In terms of lower bounds, computing the girth of a graph is at least as hard as solving the triangle finding problem on the graph.
References
- ↑ R. Diestel, Graph Theory, p.8. 3rd Edition, Springer-Verlag, 2005
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Girth". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Girth.html.
- ↑ Brouwer, Andries E., Cages, http://www.win.tue.nl/~aeb/drg/graphs/. Electronic supplement to the book Distance-Regular Graphs (Brouwer, Cohen, and Neumaier 1989, Springer-Verlag).
- ↑ Erdős, Paul (1959), "Graph theory and probability", Canadian Journal of Mathematics 11: 34–38, doi:10.4153/CJM-1959-003-9.
- ↑ Davidoff, Giuliana; Sarnak, Peter; Valette, Alain (2003), Elementary number theory, group theory, and Ramanujan graphs, London Mathematical Society Student Texts, 55, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615825, ISBN 0-521-82426-5
- ↑ Cho, Jung Jin; Chen, Yong; Ding, Yu (2007), "On the (co)girth of a connected matroid", Discrete Applied Mathematics 155 (18): 2456–2470, doi:10.1016/j.dam.2007.06.015.
- ↑ Question 3: Computing the girth of a graph
- ↑ Völkel, Christoph Dürr, Louis Abraham and Finn (2016-11-06). "Shortest cycle" (in en-US). https://tryalgo.org/en/cycles/2016/11/06/shortest-cycle/.
- ↑ "ds.algorithms - Optimal algorithm for finding the girth of a sparse graph?" (in en). https://cstheory.stackexchange.com/questions/10983/optimal-algorithm-for-finding-the-girth-of-a-sparse-graph.
- ↑ Chang, Hsien-Chih; Lu, Hsueh-I. (2013). "Computing the Girth of a Planar Graph in Linear Time". SIAM Journal on Computing 42 (3): 1077–1094. doi:10.1137/110832033. ISSN 0097-5397.
 |