Gaussian quadrature
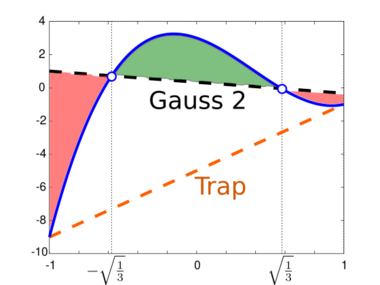
The blue curve shows the function whose definite integral on the interval [−1, 1] is to be calculated (the integrand). The trapezoidal rule approximates the function with a linear function that coincides with the integrand at the endpoints of the interval and is represented by an orange dashed line. The approximation is apparently not good, so the error is large (the trapezoidal rule gives approximation of the integral equal to y(–1) + y(1) = –10, while the correct value is 2⁄3). To obtain more exact result, the interval must be partitioned to many subintervals and then composite trapezoidal rule must be used, which requires much more calculations.
The Gaussian quadrature chooses more suitable points instead, so even a linear function approximates the function better (the black dashed line). As the integrand is the polynomial of degree 3 (y(x) = 7x3 – 8x2 – 3x + 3), the 2-point Gaussian quadrature rule even returns an exact result.
In numerical analysis, an n-point Gaussian quadrature rule, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss,[1] is a quadrature rule constructed to yield an exact result for polynomials of degree 2n − 1 or less by a suitable choice of the nodes xi and weights wi for i = 1, ..., n.
The modern formulation using orthogonal polynomials was developed by Carl Gustav Jacobi in 1826.[2] The most common domain of integration for such a rule is taken as [−1, 1], so the rule is stated as [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{-1}^1 f(x)\,dx \approx \sum_{i=1}^n w_i f(x_i), }[/math]
which is exact for polynomials of degree 2n − 1 or less. This exact rule is known as the Gauss-Legendre quadrature rule. The quadrature rule will only be an accurate approximation to the integral above if f (x) is well-approximated by a polynomial of degree 2n − 1 or less on [−1, 1].
The Gauss-Legendre quadrature rule is not typically used for integrable functions with endpoint singularities. Instead, if the integrand can be written as
[math]\displaystyle{ f(x) = \left(1 - x\right)^\alpha \left(1 + x\right)^\beta g(x),\quad \alpha,\beta \gt -1, }[/math]
where g(x) is well-approximated by a low-degree polynomial, then alternative nodes xi' and weights wi' will usually give more accurate quadrature rules. These are known as Gauss-Jacobi quadrature rules, i.e.,
[math]\displaystyle{ \int_{-1}^1 f(x)\,dx = \int_{-1}^1 \left(1 - x\right)^\alpha \left(1 + x\right)^\beta g(x)\,dx \approx \sum_{i=1}^n w_i' g\left(x_i'\right). }[/math]
Common weights include [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} }[/math] (Chebyshev–Gauss) and [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{1 - x^2} }[/math]. One may also want to integrate over semi-infinite (Gauss-Laguerre quadrature) and infinite intervals (Gauss–Hermite quadrature).
It can be shown (see Press, et al., or Stoer and Bulirsch) that the quadrature nodes xi are the roots of a polynomial belonging to a class of orthogonal polynomials (the class orthogonal with respect to a weighted inner-product). This is a key observation for computing Gauss quadrature nodes and weights.
Gauss–Legendre quadrature
For the simplest integration problem stated above, i.e., f(x) is well-approximated by polynomials on [math]\displaystyle{ [-1, 1] }[/math], the associated orthogonal polynomials are Legendre polynomials, denoted by Pn(x). With the n-th polynomial normalized to give Pn(1) = 1, the i-th Gauss node, xi, is the i-th root of Pn and the weights are given by the formula[3] [math]\displaystyle{ w_i = \frac{2}{\left( 1 - x_i^2 \right) \left[P'_n(x_i)\right]^2}. }[/math]
Some low-order quadrature rules are tabulated below (over interval [−1, 1], see the section below for other intervals).
| Number of points, n | Points, xi | Weights, wi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 2 | ||
| 2 | [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} }[/math] | ±0.57735... | 1 | |
| 3 | 0 | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{8}{9} }[/math] | 0.888889... | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{3}{5}} }[/math] | ±0.774597... | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{5}{9} }[/math] | 0.555556... | |
| 4 | [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{3}{7} - \frac{2}{7}\sqrt{\frac{6}{5}}} }[/math] | ±0.339981... | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{18 + \sqrt{30}}{36} }[/math] | 0.652145... |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{3}{7} + \frac{2}{7}\sqrt{\frac{6}{5}}} }[/math] | ±0.861136... | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{18 - \sqrt{30}}{36} }[/math] | 0.347855... | |
| 5 | 0 | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{128}{225} }[/math] | 0.568889... | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\frac{1}{3}\sqrt{5 - 2\sqrt{\frac{10}{7}}} }[/math] | ±0.538469... | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{322 + 13\sqrt{70}}{900} }[/math] | 0.478629... | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\frac{1}{3}\sqrt{5 + 2\sqrt{\frac{10}{7}}} }[/math] | ±0.90618... | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{322 - 13\sqrt{70}}{900} }[/math] | 0.236927... | |
Change of interval
An integral over [a, b] must be changed into an integral over [−1, 1] before applying the Gaussian quadrature rule. This change of interval can be done in the following way: [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b f(x)\,dx = \int_{ -1}^1 f\left(\frac{b-a}{2}\xi + \frac{a+b}{2}\right)\,\frac{dx}{d\xi}d\xi }[/math]
with [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{dx}{d\xi} = \frac{b-a}{2} }[/math]
Applying the [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] point Gaussian quadrature [math]\displaystyle{ (\xi, w) }[/math] rule then results in the following approximation: [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b f(x)\,dx \approx \frac{b-a}{2} \sum_{i=1}^n w_i f\left(\frac{b-a}{2}\xi_i + \frac{a+b}{2}\right). }[/math]
Example of two-point Gauss quadrature rule
Use the two-point Gauss quadrature rule to approximate the distance in meters covered by a rocket from [math]\displaystyle{ t = 8\mathrm{s} }[/math] to [math]\displaystyle{ t = 30\mathrm{s}, }[/math] as given by [math]\displaystyle{ x = \int_{8}^{30}{\left( 2000\ln\left[ \frac{140000}{140000 - 2100t} \right] - 9.8t \right){dt}} }[/math]
Change the limits so that one can use the weights and abscissae given in Table 1. Also, find the absolute relative true error. The true value is given as 11061.34 m.
Solution
First, changing the limits of integration from [math]\displaystyle{ \left[ 8,30 \right] }[/math] to [math]\displaystyle{ \left[ - 1,1 \right] }[/math] gives
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \int_{8}^{30} {f(t) dt} &= \frac{30 - 8}{2} \int_{- 1}^{1}{f\left( \frac{30 - 8}{2}x + \frac{30 + 8}{2} \right){dx}} \\ &= 11\int_{- 1}^{1}{f\left( 11x + 19 \right){dx}} \end{align} }[/math]
Next, get the weighting factors and function argument values from Table 1 for the two-point rule,
- [math]\displaystyle{ c_1 = 1.000000000 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1 = - 0.577350269 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ c_2 = 1.000000000 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_2 = 0.577350269 }[/math]
Now we can use the Gauss quadrature formula [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} 11\int_{-1}^{1}{f\left( 11x + 19 \right){dx}} & \approx 11\left[ c_1 f\left( 11 x_1 + 19 \right) + c_2 f\left( 11 x_2 + 19 \right) \right] \\ &= 11\left[ f\left( 11( - 0.5773503) + 19 \right) + f\left( 11(0.5773503) + 19 \right) \right] \\ &= 11\left[ f(12.64915) + f(25.35085) \right] \\ &= 11\left[ (296.8317) + (708.4811) \right] \\ &= 11058.44 \end{align} }[/math] since [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} f(12.64915) & = 2000\ln\left[ \frac{140000}{140000 - 2100(12.64915)} \right] - 9.8(12.64915) \\ &= 296.8317 \end{align} }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} f(25.35085) & = 2000\ln\left[ \frac{140000}{140000 - 2100(25.35085)} \right] - 9.8(25.35085) \\ &= 708.4811 \end{align} }[/math]
Given that the true value is 11061.34 m, the absolute relative true error, [math]\displaystyle{ \left| \varepsilon_{t} \right| }[/math] is [math]\displaystyle{ \left| \varepsilon_{t} \right| = \left| \frac{11061.34 - 11058.44}{11061.34} \right| \times 100\% = 0.0262\% }[/math]
Other forms
The integration problem can be expressed in a slightly more general way by introducing a positive weight function ω into the integrand, and allowing an interval other than [−1, 1]. That is, the problem is to calculate [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b \omega(x)\,f(x)\,dx }[/math] for some choices of a, b, and ω. For a = −1, b = 1, and ω(x) = 1, the problem is the same as that considered above. Other choices lead to other integration rules. Some of these are tabulated below. Equation numbers are given for Abramowitz and Stegun (A & S).
| Interval | ω(x) | Orthogonal polynomials | A & S | For more information, see ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [−1, 1] | 1 | Legendre polynomials | 25.4.29 | § Gauss–Legendre quadrature |
| (−1, 1) | [math]\displaystyle{ \left(1 - x\right)^\alpha \left(1 + x\right)^\beta,\quad \alpha, \beta \gt -1 }[/math] | Jacobi polynomials | 25.4.33 (β = 0) | Gauss–Jacobi quadrature |
| (−1, 1) | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} }[/math] | Chebyshev polynomials (first kind) | 25.4.38 | Chebyshev–Gauss quadrature |
| [−1, 1] | [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{1 - x^2} }[/math] | Chebyshev polynomials (second kind) | 25.4.40 | Chebyshev–Gauss quadrature |
| [0, ∞) | [math]\displaystyle{ e^{-x}\, }[/math] | Laguerre polynomials | 25.4.45 | Gauss–Laguerre quadrature |
| [0, ∞) | [math]\displaystyle{ x^\alpha e^{-x},\quad \alpha\gt -1 }[/math] | Generalized Laguerre polynomials | Gauss–Laguerre quadrature | |
| (−∞, ∞) | [math]\displaystyle{ e^{-x^2} }[/math] | Hermite polynomials | 25.4.46 | Gauss–Hermite quadrature |
Fundamental theorem
Let pn be a nontrivial polynomial of degree n such that [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b \omega(x) \, x^k p_n(x) \, dx = 0, \quad \text{for all } k = 0, 1, \ldots, n - 1. }[/math]
Note that this will be true for all the orthogonal polynomials above, because each pn is constructed to be orthogonal to the other polynomials pj for j<n, and xk is in the span of that set.
If we pick the n nodes xi to be the zeros of pn, then there exist n weights wi which make the Gauss-quadrature computed integral exact for all polynomials h(x) of degree 2n − 1 or less. Furthermore, all these nodes xi will lie in the open interval (a, b).[4]
To prove the first part of this claim, let h(x) be any polynomial of degree 2n − 1 or less. Divide it by the orthogonal polynomial pn to get [math]\displaystyle{ h(x) = p_n(x) \, q(x) + r(x). }[/math] where q(x) is the quotient, of degree n − 1 or less (because the sum of its degree and that of the divisor pn must equal that of the dividend), and r(x) is the remainder, also of degree n − 1 or less (because the degree of the remainder is always less than that of the divisor). Since pn is by assumption orthogonal to all monomials of degree less than n, it must be orthogonal to the quotient q(x). Therefore [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b \omega(x)\,h(x)\,dx = \int_a^b \omega(x)\,\big( \, p_n(x) q(x) + r(x) \, \big)\,dx = \int_a^b \omega(x)\,r(x)\,dx. }[/math]
Since the remainder r(x) is of degree n − 1 or less, we can interpolate it exactly using n interpolation points with Lagrange polynomials li(x), where [math]\displaystyle{ l_i(x) = \prod _{j \ne i} \frac{x-x_j}{x_i-x_j}. }[/math]
We have [math]\displaystyle{ r(x) = \sum_{i=1}^n l_i(x) \, r(x_i). }[/math]
Then its integral will equal [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b \omega(x)\,r(x)\,dx = \int_a^b \omega(x) \, \sum_{i=1}^n l_i(x) \, r(x_i) \, dx = \sum_{i=1}^n \, r(x_i) \, \int_a^b \omega(x) \, l_i(x) \, dx = \sum_{i=1}^n \, r(x_i) \, w_i, }[/math]
where wi, the weight associated with the node xi, is defined to equal the weighted integral of li(x) (see below for other formulas for the weights). But all the xi are roots of pn, so the division formula above tells us that [math]\displaystyle{ h(x_i) = p_n(x_i) \, q(x_i) + r(x_i) = r(x_i), }[/math] for all i. Thus we finally have [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b \omega(x)\,h(x)\,dx = \int_a^b \omega(x) \, r(x) \, dx = \sum_{i=1}^n w_i \, r(x_i) = \sum_{i=1}^n w_i \, h(x_i). }[/math]
This proves that for any polynomial h(x) of degree 2n − 1 or less, its integral is given exactly by the Gaussian quadrature sum.
To prove the second part of the claim, consider the factored form of the polynomial pn. Any complex conjugate roots will yield a quadratic factor that is either strictly positive or strictly negative over the entire real line. Any factors for roots outside the interval from a to b will not change sign over that interval. Finally, for factors corresponding to roots xi inside the interval from a to b that are of odd multiplicity, multiply pn by one more factor to make a new polynomial [math]\displaystyle{ p_n(x) \, \prod_i (x - x_i). }[/math]
This polynomial cannot change sign over the interval from a to b because all its roots there are now of even multiplicity. So the integral [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b p_n(x) \, \left( \prod_i (x - x_i) \right) \, \omega(x) \, dx \ne 0, }[/math] since the weight function ω(x) is always non-negative. But pn is orthogonal to all polynomials of degree n-1 or less, so the degree of the product [math]\displaystyle{ \prod_i (x - x_i) }[/math] must be at least n. Therefore pn has n distinct roots, all real, in the interval from a to b.
General formula for the weights
The weights can be expressed as
-
[math]\displaystyle{ w_{i} = \frac{a_{n}}{a_{n-1}} \frac{\int_{a}^{b} \omega(x) p_{n-1}(x)^2 dx}{p'_{n}(x_{i}) p_{n-1}(x_{i})} }[/math]
()
where [math]\displaystyle{ a_{k} }[/math] is the coefficient of [math]\displaystyle{ x^{k} }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ p_{k}(x) }[/math]. To prove this, note that using Lagrange interpolation one can express r(x) in terms of [math]\displaystyle{ r(x_{i}) }[/math] as [math]\displaystyle{ r(x) = \sum_{i=1}^{n} r(x_{i}) \prod_{\begin{smallmatrix} 1 \leq j \leq n \\ j \neq i \end{smallmatrix}}\frac{x-x_{j}}{x_{i}-x_{j}} }[/math] because r(x) has degree less than n and is thus fixed by the values it attains at n different points. Multiplying both sides by ω(x) and integrating from a to b yields [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)r(x)dx = \sum_{i=1}^{n} r(x_{i}) \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\prod_{\begin{smallmatrix} 1 \leq j \leq n \\ j \neq i \end{smallmatrix}} \frac{x-x_{j}}{x_{i}-x_{j}}dx }[/math]
The weights wi are thus given by [math]\displaystyle{ w_{i} = \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\prod_{\begin{smallmatrix}1\leq j\leq n\\j\neq i\end{smallmatrix}}\frac{x-x_{j}}{x_{i}-x_{j}}dx }[/math]
This integral expression for [math]\displaystyle{ w_{i} }[/math] can be expressed in terms of the orthogonal polynomials [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n-1}(x) }[/math] as follows.
We can write [math]\displaystyle{ \prod_{\begin{smallmatrix} 1 \leq j \leq n \\ j \neq i \end{smallmatrix}} \left(x-x_{j}\right) = \frac{\prod_{1\leq j\leq n} \left(x - x_{j}\right)}{x-x_{i}} = \frac{p_{n}(x)}{a_{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right)} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ a_{n} }[/math] is the coefficient of [math]\displaystyle{ x^n }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x) }[/math]. Taking the limit of x to [math]\displaystyle{ x_{i} }[/math] yields using L'Hôpital's rule [math]\displaystyle{ \prod_{\begin{smallmatrix} 1 \leq j \leq n \\ j \neq i \end{smallmatrix}} \left(x_{i}-x_{j}\right) = \frac{p'_{n}(x_{i})}{a_{n}} }[/math]
We can thus write the integral expression for the weights as
-
[math]\displaystyle{ w_{i} = \frac{1}{p'_{n}(x_{i})}\int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\frac{p_{n}(x)}{x-x_{i}}dx }[/math]
()
In the integrand, writing [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{x-x_i} = \frac{1 - \left(\frac{x}{x_i}\right)^{k}}{x - x_i} + \left(\frac{x}{x_i}\right)^{k} \frac{1}{x - x_i} }[/math]
yields [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b\omega(x)\frac{x^kp_n(x)}{x-x_i}dx = x_i^k \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\frac{p_n(x)}{x-x_i}dx }[/math]
provided [math]\displaystyle{ k \leq n }[/math], because [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1-\left(\frac{x}{x_{i}}\right)^{k}}{x-x_{i}} }[/math] is a polynomial of degree k − 1 which is then orthogonal to [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x) }[/math]. So, if q(x) is a polynomial of at most nth degree we have [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\frac{p_{n}(x)}{x-x_{i}} dx = \frac{1}{q(x_{i})} \int_{a}^{b} \omega(x)\frac{q(x) p_n(x)}{x-x_{i}}dx }[/math]
We can evaluate the integral on the right hand side for [math]\displaystyle{ q(x) = p_{n-1}(x) }[/math] as follows. Because [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{p_{n}(x)}{x-x_{i}} }[/math] is a polynomial of degree n − 1, we have [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{p_{n}(x)}{x-x_{i}} = a_{n}x^{n-1} + s(x) }[/math] where s(x) is a polynomial of degree [math]\displaystyle{ n - 2 }[/math]. Since s(x) is orthogonal to [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n-1}(x) }[/math] we have [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\frac{p_{n}(x)}{x-x_{i}}dx=\frac{a_{n}}{p_{n-1}(x_{i})} \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)p_{n-1}(x)x^{n-1}dx }[/math]
We can then write [math]\displaystyle{ x^{n-1} = \left(x^{n-1} - \frac{p_{n-1}(x)}{a_{n-1}}\right) + \frac{p_{n-1}(x)}{a_{n-1}} }[/math]
The term in the brackets is a polynomial of degree [math]\displaystyle{ n - 2 }[/math], which is therefore orthogonal to [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n-1}(x) }[/math]. The integral can thus be written as [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)\frac{p_{n}(x)}{x-x_{i}}dx = \frac{a_{n}}{a_{n-1} p_{n-1}(x_{i})} \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x) p_{n-1}(x)^{2} dx }[/math]
According to equation (2), the weights are obtained by dividing this by [math]\displaystyle{ p'_{n}(x_{i}) }[/math] and that yields the expression in equation (1).
[math]\displaystyle{ w_{i} }[/math] can also be expressed in terms of the orthogonal polynomials [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x) }[/math] and now [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n+1}(x) }[/math]. In the 3-term recurrence relation [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n+1}(x_{i}) = (a) p_{n}(x_{i}) + (b) p_{n-1}(x_{i}) }[/math] the term with [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x_{i}) }[/math] vanishes, so [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n-1}(x_{i}) }[/math] in Eq. (1) can be replaced by [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{b} p_{n+1} \left(x_i\right) }[/math].
Proof that the weights are positive
Consider the following polynomial of degree [math]\displaystyle{ 2n - 2 }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ f(x) = \prod_{\begin{smallmatrix} 1 \leq j \leq n \\ j \neq i \end{smallmatrix}}\frac{\left(x - x_j\right)^2}{\left(x_i - x_j\right)^2} }[/math] where, as above, the xj are the roots of the polynomial [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x) }[/math]. Clearly [math]\displaystyle{ f(x_j) = \delta_{ij} }[/math]. Since the degree of [math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math] is less than [math]\displaystyle{ 2n - 1 }[/math], the Gaussian quadrature formula involving the weights and nodes obtained from [math]\displaystyle{ p_{n}(x) }[/math] applies. Since [math]\displaystyle{ f(x_{j}) = 0 }[/math] for j not equal to i, we have [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{a}^{b}\omega(x)f(x)dx=\sum_{j=1}^{n}w_{j}f(x_{j}) = \sum_{j=1}^{n} \delta_{ij} w_j = w_{i} \gt 0. }[/math]
Since both [math]\displaystyle{ \omega(x) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math] are non-negative functions, it follows that [math]\displaystyle{ w_{i} \gt 0 }[/math].
Computation of Gaussian quadrature rules
There are many algorithms for computing the nodes xi and weights wi of Gaussian quadrature rules. The most popular are the Golub-Welsch algorithm requiring O(n2) operations, Newton's method for solving [math]\displaystyle{ p_n(x) = 0 }[/math] using the three-term recurrence for evaluation requiring O(n2) operations, and asymptotic formulas for large n requiring O(n) operations.
Recurrence relation
Orthogonal polynomials [math]\displaystyle{ p_r }[/math] with [math]\displaystyle{ (p_r, p_s) = 0 }[/math] for [math]\displaystyle{ r \ne s }[/math] for a scalar product [math]\displaystyle{ (\cdot , \cdot) }[/math], degree [math]\displaystyle{ (p_r) = r }[/math] and leading coefficient one (i.e. monic orthogonal polynomials) satisfy the recurrence relation [math]\displaystyle{ p_{r+1}(x) = (x - a_{r,r}) p_r(x) - a_{r,r-1} p_{r-1}(x) \cdots - a_{r,0}p_0(x) }[/math]
and scalar product defined [math]\displaystyle{ (f(x),g(x))=\int_a^b\omega(x)f(x)g(x)dx }[/math]
for [math]\displaystyle{ r = 0, 1, \ldots, n - 1 }[/math] where n is the maximal degree which can be taken to be infinity, and where [math]\displaystyle{ a_{r,s} = \frac{\left(xp_r, p_s\right)}{\left(p_s, p_s\right)} }[/math]. First of all, the polynomials defined by the recurrence relation starting with [math]\displaystyle{ p_0(x) = 1 }[/math] have leading coefficient one and correct degree. Given the starting point by [math]\displaystyle{ p_0 }[/math], the orthogonality of [math]\displaystyle{ p_r }[/math] can be shown by induction. For [math]\displaystyle{ r = s = 0 }[/math] one has [math]\displaystyle{ (p_1,p_0) = (x-a_{0,0}) (p_0,p_0) = (xp_0,p_0) - a_{0,0}(p_0,p_0) = (xp_0,p_0) - (xp_0,p_0) = 0. }[/math]
Now if [math]\displaystyle{ p_0, p_1, \ldots, p_r }[/math] are orthogonal, then also [math]\displaystyle{ p_{r+1} }[/math], because in [math]\displaystyle{ (p_{r+1}, p_s) = (xp_r, p_s) - a_{r,r}(p_r, p_s) - a_{r,r-1}(p_{r-1}, p_s)\cdots - a_{r,0}(p_0, p_s) }[/math] all scalar products vanish except for the first one and the one where [math]\displaystyle{ p_s }[/math] meets the same orthogonal polynomial. Therefore, [math]\displaystyle{ (p_{r+1},p_s) = (xp_r,p_s) - a_{r,s}(p_s,p_s) = (xp_r,p_s)-(xp_r,p_s) = 0. }[/math]
However, if the scalar product satisfies [math]\displaystyle{ (xf, g) = (f,xg) }[/math] (which is the case for Gaussian quadrature), the recurrence relation reduces to a three-term recurrence relation: For [math]\displaystyle{ s \lt r - 1, xp_s }[/math] is a polynomial of degree less than or equal to r − 1. On the other hand, [math]\displaystyle{ p_r }[/math] is orthogonal to every polynomial of degree less than or equal to r − 1. Therefore, one has [math]\displaystyle{ (xp_r, p_s) = (p_r, xp_s) = 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ a_{r,s} = 0 }[/math] for s < r − 1. The recurrence relation then simplifies to [math]\displaystyle{ p_{r+1}(x) = (x-a_{r,r}) p_r(x) - a_{r,r-1} p_{r-1}(x) }[/math]
or [math]\displaystyle{ p_{r+1}(x) = (x-a_r) p_r(x) - b_r p_{r-1}(x) }[/math]
(with the convention [math]\displaystyle{ p_{-1}(x) \equiv 0 }[/math]) where [math]\displaystyle{ a_r := \frac{(xp_r,p_r)}{(p_r,p_r)}, \qquad b_r := \frac{(xp_r,p_{r-1})}{(p_{r-1},p_{r-1})} = \frac{(p_r,p_r)}{(p_{r-1},p_{r-1})} }[/math]
(the last because of [math]\displaystyle{ (xp_r, p_{r-1}) = (p_r, xp_{r-1}) = (p_r, p_r) }[/math], since [math]\displaystyle{ xp_{r-1} }[/math] differs from [math]\displaystyle{ p_r }[/math] by a degree less than r).
The Golub-Welsch algorithm
The three-term recurrence relation can be written in matrix form [math]\displaystyle{ J\tilde{P} = x\tilde{P} - p_n(x) \mathbf{e}_n }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \tilde{P} = \begin{bmatrix} p_0(x) & p_1(x) & \cdots & p_{n-1}(x) \end{bmatrix}^\mathsf{T} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{e}_n }[/math] is the [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]th standard basis vector, i.e., [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{e}_n = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & \cdots & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}^\mathsf{T} }[/math], and J is the following tridiagonal matrix, called the Jacobi matrix: [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{J} = \begin{bmatrix} a_0 & 1 & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\ b_1 & a_1 & 1 & \ddots & \vdots \\ 0 & b_2 & \ddots & \ddots & 0 \\ \vdots & \ddots & \ddots & a_{n-2} & 1 \\ 0 & \cdots & 0 & b_{n-1} & a_{n-1} \end{bmatrix}. }[/math]
The zeros [math]\displaystyle{ x_j }[/math] of the polynomials up to degree n, which are used as nodes for the Gaussian quadrature can be found by computing the eigenvalues of this matrix. This procedure is known as Golub–Welsch algorithm.
For computing the weights and nodes, it is preferable to consider the symmetric tridiagonal matrix [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J} }[/math] with elements [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \mathcal{J}_{i,i} = J_{i,i} &= a_{i-1} && i=1,\ldots,n \\ \mathcal{J}_{i-1,i} = \mathcal{J}_{i,i-1} = \sqrt{J_{i,i-1}J_{i-1,i}} &= \sqrt{b_{i-1}} && i=2,\ldots,n. \end{align} }[/math]
That is,
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J} = \begin{bmatrix} a_0 & \sqrt{b_1} & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\ \sqrt{b_1} & a_1 & \sqrt{b_2} & \ddots & \vdots \\ 0 & \sqrt{b_2} & \ddots & \ddots & 0 \\ \vdots & \ddots & \ddots & a_{n-2} & \sqrt{b_{n-1}} \\ 0 & \cdots & 0 & \sqrt{b_{n-1}} & a_{n-1} \end{bmatrix}. }[/math]
J and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J} }[/math] are similar matrices and therefore have the same eigenvalues (the nodes). The weights can be computed from the corresponding eigenvectors: If [math]\displaystyle{ \phi^{(j)} }[/math] is a normalized eigenvector (i.e., an eigenvector with euclidean norm equal to one) associated to the eigenvalue xj, the corresponding weight can be computed from the first component of this eigenvector, namely: [math]\displaystyle{ w_j = \mu_0 \left(\phi_1^{(j)}\right)^2 }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ \mu_0 }[/math] is the integral of the weight function [math]\displaystyle{ \mu_0 = \int_a^b \omega(x) dx. }[/math]
See, for instance, (Gil Segura) for further details.
Error estimates
The error of a Gaussian quadrature rule can be stated as follows.[5] For an integrand which has 2n continuous derivatives, [math]\displaystyle{ \int_a^b \omega(x)\,f(x)\,dx - \sum_{i=1}^n w_i\,f(x_i) = \frac{f^{(2n)}(\xi)}{(2n)!} \, (p_n, p_n) }[/math] for some ξ in (a, b), where pn is the monic (i.e. the leading coefficient is 1) orthogonal polynomial of degree n and where [math]\displaystyle{ (f,g) = \int_a^b \omega(x) f(x) g(x) \, dx. }[/math]
In the important special case of ω(x) = 1, we have the error estimate[6] [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\left(b - a\right)^{2n+1} \left(n!\right)^4}{(2n + 1)\left[\left(2n\right)!\right]^3} f^{(2n)} (\xi), \qquad a \lt \xi \lt b. }[/math]
Stoer and Bulirsch remark that this error estimate is inconvenient in practice, since it may be difficult to estimate the order 2n derivative, and furthermore the actual error may be much less than a bound established by the derivative. Another approach is to use two Gaussian quadrature rules of different orders, and to estimate the error as the difference between the two results. For this purpose, Gauss–Kronrod quadrature rules can be useful.
Gauss–Kronrod rules
If the interval [a, b] is subdivided, the Gauss evaluation points of the new subintervals never coincide with the previous evaluation points (except at zero for odd numbers), and thus the integrand must be evaluated at every point. Gauss–Kronrod rules are extensions of Gauss quadrature rules generated by adding n + 1 points to an n-point rule in such a way that the resulting rule is of order 2n + 1. This allows for computing higher-order estimates while re-using the function values of a lower-order estimate. The difference between a Gauss quadrature rule and its Kronrod extension is often used as an estimate of the approximation error.
Gauss–Lobatto rules
Also known as Lobatto quadrature,[7] named after Dutch mathematician Rehuel Lobatto. It is similar to Gaussian quadrature with the following differences:
- The integration points include the end points of the integration interval.
- It is accurate for polynomials up to degree 2n – 3, where n is the number of integration points.[8]
Lobatto quadrature of function f(x) on interval [−1, 1]: [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{-1}^1 {f(x) \, dx} = \frac {2} {n(n-1)}[f(1) + f(-1)] + \sum_{i = 2}^{n-1} {w_i f(x_i)} + R_n. }[/math]
Abscissas: xi is the [math]\displaystyle{ (i - 1) }[/math]st zero of [math]\displaystyle{ P'_{n-1}(x) }[/math], here [math]\displaystyle{ P_m(x) }[/math]denotes the standard Legendre polynomial of m-th degree and the dash denotes the derivative.
Weights: [math]\displaystyle{ w_i = \frac{2}{n(n - 1)\left[P_{n-1}\left(x_i\right)\right]^2}, \qquad x_i \ne \pm 1. }[/math]
Remainder: [math]\displaystyle{ R_n = \frac{-n\left(n - 1\right)^3 2^{2n-1} \left[\left(n - 2\right)!\right]^4}{(2n-1) \left[\left(2n - 2\right)!\right]^3} f^{(2n-2)}(\xi), \qquad -1 \lt \xi \lt 1. }[/math]
Some of the weights are:
| Number of points, n | Points, xi | Weights, wi |
|---|---|---|
| [math]\displaystyle{ 3 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ 0 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{4}{3} }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm 1 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{3} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ 4 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \pm \sqrt{\frac{1}{5}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{5}{6} }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm 1 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{6} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ 5 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ 0 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{32}{45} }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{3}{7}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{49}{90} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm 1 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{10} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ 6 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{1}{3}-\frac{2\sqrt{7}}{21}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{14+\sqrt{7}}{30} }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{1}{3} + \frac{2\sqrt{7}}{21}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{14 - \sqrt{7}}{30} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm 1 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{15} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ 7 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ 0 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{256}{525} }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{5}{11}-\frac{2}{11}\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{124 + 7\sqrt{15}}{350} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm\sqrt{\frac{5}{11} + \frac{2}{11}\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{124 - 7\sqrt{15}}{350} }[/math] | |
| [math]\displaystyle{ \pm 1 }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{21} }[/math] |
An adaptive variant of this algorithm with 2 interior nodes[9] is found in GNU Octave and MATLAB as quadl and integrate.[10][11]
References
Citations
- ↑ Methodus nova integralium valores per approximationem inveniendi. In: Comm. Soc. Sci. Göttingen Math. Band 3, 1815, S. 29–76, Gallica, datiert 1814, auch in Werke, Band 3, 1876, S. 163–196.
- ↑ C. G. J. Jacobi: Ueber Gauß' neue Methode, die Werthe der Integrale näherungsweise zu finden. In: Journal für Reine und Angewandte Mathematik. Band 1, 1826, S. 301–308, (online), und Werke, Band 6.
- ↑ Abramowitz & Stegun 1983, p. 887
- ↑ Stoer & Bulirsch 2002, pp. 172–175
- ↑ Stoer & Bulirsch 2002, Thm 3.6.24
- ↑ Kahaner, Moler & Nash 1989, §5.2
- ↑ Abramowitz & Stegun 1983, p. 888
- ↑ Quarteroni, Sacco & Saleri 2000
- ↑ Gander, Walter; Gautschi, Walter (2000). "Adaptive Quadrature - Revisited". BIT Numerical Mathematics 40 (1): 84–101. doi:10.1023/A:1022318402393. https://www.inf.ethz.ch/personal/gander/.
- ↑ "Numerical integration - MATLAB integral". https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/integral.html.
- ↑ "Functions of One Variable (GNU Octave)". https://octave.org/doc/v4.2.2/Functions-of-One-Variable.html#XREFquadl.
Bibliography
- Implementing an Accurate Generalized Gaussian Quadrature Solution to Find the Elastic Field in a Homogeneous Anisotropic Media
- Abramowitz, Milton; Stegun, Irene Ann, eds (1983). "Chapter 25.4, Integration". Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. Applied Mathematics Series. 55 (Ninth reprint with additional corrections of tenth original printing with corrections (December 1972); first ed.). Washington D.C.; New York: United States Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards; Dover Publications. LCCN 65-12253. ISBN 978-0-486-61272-0.
- Anderson, Donald G. (1965). "Gaussian quadrature formulae for [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^1 -\ln(x)f(x) dx }[/math]". Math. Comp. 19 (91): 477–481. doi:10.1090/s0025-5718-1965-0178569-1.
- Golub, Gene H.; Welsch, John H. (1969), "Calculation of Gauss Quadrature Rules", Mathematics of Computation 23 (106): 221–230, doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-69-99647-1
- Gautschi, Walter (1968). "Construction of Gauss–Christoffel Quadrature Formulas". Math. Comp. 22 (102): pp. 251–270. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1968-0228171-0.
- Gautschi, Walter (1970). "On the construction of Gaussian quadrature rules from modified moments". Math. Comp. 24: pp. 245–260. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1970-0285117-6.
- Piessens, R. (1971). "Gaussian quadrature formulas for the numerical integration of Bromwich's integral and the inversion of the laplace transform". J. Eng. Math. 5 (1): pp. 1–9. doi:10.1007/BF01535429. Bibcode: 1971JEnMa...5....1P.
- Danloy, Bernard (1973). "Numerical construction of Gaussian quadrature formulas for [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^1 (-\log x) x^\alpha f(x) dx }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^\infty E_m(x) f(x) dx }[/math]". Math. Comp. 27 (124): pp. 861–869. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1973-0331730-X.
- Kahaner, David; Moler, Cleve; Nash, Stephen (1989), Numerical Methods and Software, Prentice-Hall, ISBN 978-0-13-627258-8, https://archive.org/details/numericalmethods0000kaha
- Sagar, Robin P. (1991). "A Gaussian quadrature for the calculation of generalized Fermi-Dirac integrals". Comput. Phys. Commun. 66 (2–3): 271–275. doi:10.1016/0010-4655(91)90076-W. Bibcode: 1991CoPhC..66..271S.
- Yakimiw, E. (1996). "Accurate computation of weights in classical Gauss-Christoffel quadrature rules". J. Comput. Phys. 129 (2): 406–430. doi:10.1006/jcph.1996.0258. Bibcode: 1996JCoPh.129..406Y.
- Laurie, Dirk P. (1999), "Accurate recovery of recursion coefficients from Gaussian quadrature formulas", J. Comput. Appl. Math. 112 (1–2): 165–180, doi:10.1016/S0377-0427(99)00228-9
- Laurie, Dirk P. (2001). "Computation of Gauss-type quadrature formulas". J. Comput. Appl. Math. 127 (1–2): 201–217. doi:10.1016/S0377-0427(00)00506-9. Bibcode: 2001JCoAM.127..201L.
- Riener, Cordian; Schweighofer, Markus (2018). "Optimization approaches to quadrature: New characterizations of Gaussian quadrature on the line and quadrature with few nodes on plane algebraic curves, on the plane and in higher dimensions". Journal of Complexity 45: 22–54. doi:10.1016/j.jco.2017.10.002.
- Stoer, Josef; Bulirsch, Roland (2002), Introduction to Numerical Analysis (3rd ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-95452-3.
- Temme, Nico M. (2010), "§3.5(v): Gauss Quadrature", in Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F. et al., NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5, http://dlmf.nist.gov/3.5.v
- Press, WH; Teukolsky, SA; Vetterling, WT; Flannery, BP (2007), "Section 4.6. Gaussian Quadratures and Orthogonal Polynomials", Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing (3rd ed.), New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-88068-8, http://apps.nrbook.com/empanel/index.html?pg=179
- Gil, Amparo; Segura, Javier; Temme, Nico M. (2007), "§5.3: Gauss quadrature", Numerical Methods for Special Functions, SIAM, ISBN 978-0-89871-634-4
- Quarteroni, Alfio; Sacco, Riccardo; Saleri, Fausto (2000). Numerical Mathematics. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 422, 425. ISBN 0-387-98959-5.
- Walter Gautschi: "A Software Repository for Gaussian Quadratures and Christoffel Functions", SIAM, ISBN:978-1-611976-34-2 (2020).
- Teresa Laudadio, Nicola Mastronardi & Paul Van Dooren: "Computing Gaussian quadrature rules with high relative accuracy", Numerical Algorithms, vol.92(2023), pp.767–793.
External links
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Gauss quadrature formula", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4, https://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=p/g043510
- ALGLIB contains a collection of algorithms for numerical integration (in C# / C++ / Delphi / Visual Basic / etc.)
- GNU Scientific Library — includes C version of QUADPACK algorithms (see also GNU Scientific Library)
- From Lobatto Quadrature to the Euler constant e
- Gaussian Quadrature Rule of Integration – Notes, PPT, Matlab, Mathematica, Maple, Mathcad at Holistic Numerical Methods Institute
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Legendre-Gauss Quadrature". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Legendre-GaussQuadrature.html.
- Gaussian Quadrature by Chris Maes and Anton Antonov, Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Tabulated weights and abscissae with Mathematica source code, high precision (16 and 256 decimal places) Legendre-Gaussian quadrature weights and abscissas, for n=2 through n=64, with Mathematica source code.
- Mathematica source code distributed under the GNU LGPL for abscissas and weights generation for arbitrary weighting functions W(x), integration domains and precisions.
- Gaussian Quadrature in Boost.Math, for arbitrary precision and approximation order
- Gauss-Kronrod Quadrature in Boost.Math
- Nodes and Weights of Gaussian quadrature
 |