Chemistry:Ammonium cyanate
From HandWiki
Short description: Ionic chemical compound with formula [NH4]+ [OCN]-
| |
| |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| [NH 4][OCN] | |
| Molar mass | 60.056 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
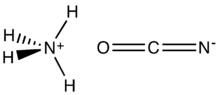
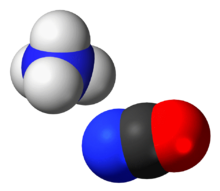
Ammonium cyanate is an inorganic compound with the formula [NH
4]+
[OCN]−
. It is a colorless, solid salt.
Structure and reactions
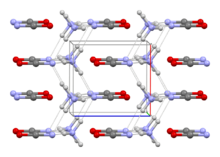
The structure of this salt was verified by X-ray crystallography. The respective C–O and C–N distances are 1.174(8) and 1.192(7) Å, consistent with the O=C=N−
description. Ammonium cation [NH
4]+
forms hydrogen bonds with cyanate anion O=C=N−
, but to N, not to O.[1]
The compound is notable as the precursor in the Wöhler synthesis of urea, an organic compound, from inorganic reactants.[2] This led to the discarding of the Vital force theory, suggested earlier by Berzelius.
- NH+
4 + OCN−
→ (NH
2)
2CO[3]
References
- ↑ MacLean, Elizabeth J.; Harris, Kenneth D. M.; Kariuki, Benson M.; Kitchin, Simon J.; Tykwinski, Rik R.; Swainson, Ian P.; Dunitz; Jack D. (2003). "Ammonium cyanate shows N-H···N hydrogen bonding, not N-H···O". Journal of the American Chemical Society 125 (47): 14449–14451. doi:10.1021/ja021156x. PMID 14624593.
- ↑ Friedrich Wöhler (1828). "Ueber künstliche Bildung des Harnstoffs". Annalen der Physik und Chemie 88 (2): 253–256. doi:10.1002/andp.18280880206. Bibcode: 1828AnP....88..253W. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k15097k/f261.chemindefer.
- ↑ Shorter, J. (1978). "The conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea. A saga on Reaction mechanisms". Chemical Society Reviews 7: 1–14. doi:10.1039/CS9780700001.
 |

