Chemistry:Ammonium nitrite
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium nitrite
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| [NH 4]NO 2 | |
| Molar mass | 64.04 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless or pale yellow crystals |
| Density | 1.69 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | Decomposes |
| 118.3 g / 100mL | |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | Low |
| Friction sensitivity | Low |
| Detonation velocity | >1000 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Explosive |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Non-flammable | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ammonium nitrate |
Other cations
|
Sodium nitrite |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
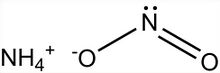
Ammonium nitrite, [NH
4]NO
2, is the ammonium salt of nitrous acid. It is not used in pure isolated form since it is highly unstable and decomposes into water and nitrogen, even at room temperature.
Preparation
Ammonium nitrite forms naturally in the air and can be prepared by the absorption of equal parts nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide in aqueous ammonia.[1]
It can also be synthesized by oxidizing ammonia with ozone or hydrogen peroxide, or in a precipitation reaction of barium or lead nitrite with ammonium sulfate, or silver nitrite with ammonium chloride, or ammonium perchlorate with potassium nitrite. The precipitate is filtered off and the solution concentrated. It forms colorless crystals which are soluble in water.
- [math]\ce{ 2NH3 + O3 -> [NH4]NO2 + H2O }[/math]
Physical and chemical properties
Ammonium nitrite may explode at a temperature of 60–70 °C,[1] and will decompose quicker when dissolved in a concentrated aqueous solution, than in the form of a dry crystal. Even in room temperature the compound slowly decomposes into water and nitrogen:
- [NH
4]NO
2 → N
2 + 2 H
2O
It decomposes when heated or in the presence of acid into water and nitrogen.[2] Ammonium nitrite solution is stable at higher pH and lower temperature. If there is any decrease in pH lower than 7.0, it may lead to an explosion, since the nitrite can react to it. A safe pH can be maintained by adding an ammonia solution. The mole ratio of ammonium nitrite to ammonia must be above 10%.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Thomas Scott; Mary Eagleson (1994). Concise encyclopedia chemistry. Walter de Gruyter. p. 66. ISBN 3-11-011451-8. https://archive.org/details/conciseencyclope00eagl.
- ↑ "VIAS Encyclopedia: Ammonium Nitrite". http://www.vias.org/encyclopedia/chem_ammonia_salts_no2.html.
 |


