Chemistry:Sanguiin H-6
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
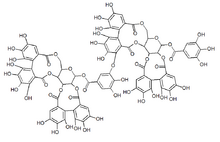
(10aR,11S,12aR,25aR,25bS)-2,3,4,5,6,7,17,18,19,20,21,22-Dodecahydroxy-9,15,24,27-tetraoxo-9,10a,11,12a,13,15,24,25a,25b,27-decahydrodibenzo[g,i]dibenzo[6′,7′:8′,9′][1,4]dioxecino[2′,3′:4,5]pyrano[3,2-b][1,5]dioxacycloundecin-11-yl 3-({(10aR,11R,12aR,25aR,25bS)-2,3,4,5,6,7,17,18,19,20,21-hendecahydroxy-9,15,24,27-tetraoxo-11-[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]-9,10a,11,12a,13,15,24,25a,25b,27-decahydrodibenzo[g,i]dibenzo[6′,7′:8′,9′][1,4]dioxecino[2′,3′:4,5]pyrano[3,2-b][1,5]dioxacycloundecin-22-yl}oxy)-4,5-dihydroxybenzoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C82H54O52 | |
| Molar mass | 1871.282 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sanguiin H-6 is an ellagitannin.
Natural occurrence
Sanguiin H-6 can be found in Rosaceae such as the great burnet (Sanguisorba officinalis),[1] in strawberries (Fragaria × ananassa)[2] and in Rubus species such as red raspberries (Rubus idaeus)[3][4] or cloudberries (Rubus chamaemorus).[4]
Chemistry
Sanguiin H-6 is dimer of casuarictin linked by a bond between the gallic acid residue and one of the hexahydroxydiphenic acid units. It has sanguisorbic acid ester groups as linking units between glucopyranose moieties.[5] Sanguiin H-6 contributes to the in vitro antioxidant activity of raspberries.[6]
References
- ↑ Bastow, K.; Bori, I.; Fukushima, Y.; Kashiwada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I.; Lee, K. -H. (2007). "Inhibition of DNA Topoisomerases by Sanguiin H-6, a Cytotoxic Dimeric Ellagitannin fromSanguisorba officinalis1". Planta Medica 59 (3): 240–245. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959659. PMID 8391144.
- ↑ Seeram, N. P.; Lee, R.; Scheuller, H. S.; Heber, D. (2006). "Identification of phenolic compounds in strawberries by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy". Food Chemistry 97: 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.02.047. https://cloudfront.escholarship.org/dist/prd/content/qt6526f1m8/qt6526f1m8.pdf.
- ↑ Mullen, W.; Stewart, A. J.; Lean, M. E.; Gardner, P.; Duthie, G. G.; Crozier, A. (2002). "Effect of freezing and storage on the phenolics, ellagitannins, flavonoids, and antioxidant capacity of red raspberries". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 50 (18): 5197–5201. doi:10.1021/jf020141f. PMID 12188629.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kähkönen, M.; Kylli, P.; Ollilainen, V.; Salminen, J. P.; Heinonen, M. (2012). "Antioxidant Activity of Isolated Ellagitannins from Red Raspberries and Cloudberries". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60 (5): 1167–1174. doi:10.1021/jf203431g. PMID 22229937.
- ↑ Vrhovsek, U.; Guella, G.; Gasperotti, M.; Pojer, E.; Zancato, M.; Mattivi, F. (2012). "Clarifying the Identity of the Main Ellagitannin in the Fruit of the Strawberry, Fragaria vesca and Fragaria ananassa Duch". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60 (10): 2507–2516. doi:10.1021/jf2052256. PMID 22339338.
- ↑ Borges, G.; Degeneve, A.; Mullen, W.; Crozier, A. (2010). "Identification of Flavonoid and Phenolic Antioxidants in Black Currants, Blueberries, Raspberries, Red Currants, and Cranberries†". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 58 (7): 3901–3909. doi:10.1021/jf902263n. PMID 20000747.
External links
 |

