Biology:Acentrophorus
| Acentrophorus | |
|---|---|

| |
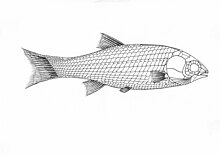
| Acentrophorus varians | |
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Clade: | Ginglymodi |
| Order: | †Semionotiformes |
| Genus: | †Acentrophorus Traquair, 1877 |
| Type species | |
| †Palaeoniscus glaphyrus Agassiz, 1835
| |
| Other Species | |
| |
Acentrophorus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish from the Wuchiapingian (Lopingian/late Permian) of England (Marl Slate) and Germany (Kupferschiefer).[2] There may also be a Triassic occurrence in Australia .[1]
Classification
The type species, Acentrophorus glaphyrus, was first described under the genus name "Palaeoniscus" (=Palaeoniscum) by Louis Agassiz.[3] Ramsay H. Traquair later errected a new genus for this species, Acentrophorus, to which he also referred the species "Palaeoniscus" abbsii, "P." altus and "P." varians.[4]
Acentrophorus has been referred to the ginglymodian order Semionotiformes.[5] Acentrophorus was proposed to be the oldest known neopterygian,[6] the group of ray-finned fish that encompasses the vast majority of extant species. However, the genus has been described as "enigmatic"[7] and "pending restudy".[8]
See also
- Prehistoric fish
- List of prehistoric bony fish
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "†Acentrophorus Traquair 1877 (ray-finned fish)". http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?a=taxonInfo&taxon_no=35134.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Romano, Carlo; Koot, Martha B.; Kogan, Ilja; Brayard, Arnaud; Minikh, Alla V.; Brinkmann, Winand; Bucher, Hugo; Kriwet, Jürgen (2016). "Permian-Triassic Osteichthyes (bony fishes): diversity dynamics and body size evolution". Biological Reviews 91 (1): 106–147. doi:10.1111/brv.12161. PMID 25431138.
- ↑ Agassiz, Louis (1833–1843). Recherches sur les poissons fossiles. Petitpierre, Neuchâtel. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/4275.
- ↑ Traquair, Ramsay H. (1877). "On the Agassizian Genera Amblypterus, Palæoniscus, Gyrolepis, and Pygopterus". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society 33 (1–4): 548–578. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1877.033.01-04.33.
- ↑ Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". Bulletins of American Paleontology 364: 560. Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. https://web.archive.org/web/20110723131237/http://strata.ummp.lsa.umich.edu/jack/showgenera.php?taxon=611&rank=class. Retrieved 2009-02-23.
- ↑ "Neopterygii: Semionotiformes". http://palaeos.com/vertebrates/neopterygii/semionotiformes.html.
- ↑ Friedman, Matt (2022). "The Macroevolutionary History of Bony Fishes: A Paleontological View" (in en). Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 53 (1): 353–377. doi:10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-111720-010447. ISSN 1543-592X. https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-111720-010447.
- ↑ Romano, Carlo (2021). "A Hiatus Obscures the Early Evolution of Modern Lineages of Bony Fishes". Frontiers in Earth Science 8: 618853. doi:10.3389/feart.2020.618853.
Wikidata ☰ Q4673086 entry
 |

