Biology:SprD
| SprD | |
|---|---|
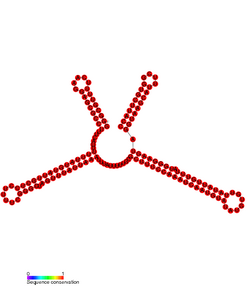 Conserved secondary structure of SprD. | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SprD |
| Rfam | RF01828 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene |
| Domain(s) | Staphylococcus aureus |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
In molecular biology SprD (Small pathogenicity island RNA D) is a non-coding RNA expressed on pathogenicity islands in Staphylococcus aureus.[1] It was identified in silico along with a number of other sRNAs (SprA-G) through microarray analysis which were confirmed using a Northern blot.[2] SprD has been found to significantly contribute to causing disease in an animal model.[1]
Function
SprD is located between genes scn and chp in the innate immune evasion cluster (IEC) of the S. aureus genome. Its placement within this region was the first indication of a virulence-factor regulatory function.[1]
SprD binds with sbi (Staphylococcus aureus binder of IgG)[3] mRNA which encodes an immune evasion protein. It occludes the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and the initiation codon of sbi, forming a sbi mRNA-SprD duplex repressing the translation of the mRNA.[1]
sbi protein interferes with the host's innate immune response by binding Factor H, Complement component 3 and IgG.[3][4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "A Staphylococcus aureus small RNA is required for bacterial virulence and regulates the expression of an immune-evasion molecule". PLOS Pathog. 6 (6): e1000927. June 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000927. PMID 20532214.
- ↑ "Small RNA genes expressed from Staphylococcus aureus genomic and pathogenicity islands with specific expression among pathogenic strains". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (40): 14249–14254. October 2005. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503838102. PMID 16183745.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "The Staphylococcus aureus protein Sbi acts as a complement inhibitor and forms a tripartite complex with host complement Factor H and C3b". PLOS Pathog. 4 (12): e1000250. December 2008. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000250. PMID 19112495.
- ↑ "A second IgG-binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus". Microbiology 144 (4): 985–991. April 1998. doi:10.1099/00221287-144-4-985. PMID 9579072. http://mic.sgmjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9579072. Retrieved 2010-08-09.
Further reading
- "Structure-function analysis of the C3 binding region of Staphylococcus aureus immune subversion protein Sbi". J. Biol. Chem. 283 (32): 22113–22120. August 2008. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802636200. PMID 18550524.
- "Interaction of human complement with Sbi, a staphylococcal immunoglobulin-binding protein: indications of a novel mechanism of complement evasion by Staphylococcus aureus". J. Biol. Chem. 283 (25): 17579–17593. June 2008. doi:10.1074/jbc.M800265200. PMID 18434316.
- "S. aureus IgG-binding proteins SpA and Sbi: host specificity and mechanisms of immune complex formation". Mol. Immunol. 45 (6): 1600–1611. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.10.021. PMID 18061675.
- "Dual RNA regulatory control of a Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor". Nucleic Acids Research 42 (8): 4847–4858. Apr 1, 2014. doi:10.1093/nar/gku119. PMID 24510101.
External links
 |

