Biology:Cladonia squamosa
| Cladonia squamosa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Lecanoromycetes |
| Order: | Lecanorales |
| Family: | Cladoniaceae |
| Genus: | Cladonia |
| Species: | C. squamosa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cladonia squamosa (Scop.) Hoff. (1796)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
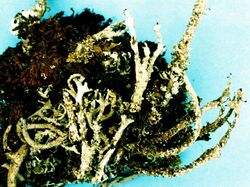
Cladonia squamosa or the dragon cup lichen[1] is a species of cup lichen in the family Cladoniaceae.[2]
Description
The primary thallus is composed of medium-sized, crenate squamules, approximately 1.5-7mm. long, and 1-5mm. wide. The upper surface is fawn or tan to cinnamon-colored varying toward greenish grey. The apothecia are small, ranging from .5–3 mm. in diameter, and are located on the margin of the cups or at the ends of branches or proliferations. They are fawn to cinnamon-colored. The paraphyses are usually simple, sometimes thickened, and are brownish towards the apex. The hymenium is pale or pale-brownish below and brownish above. The asci are lecanoralean, with a thickened tholus. There are a usually 8 ascospores, which are oblong or oblong-obtuse to fusiform in shape, between 5-17 µm. long and 2.5-3.5 µm. wide. Conidia are falcate and 3-8 µm. long.[3][4]
Range
The species is widely distributed; it is found in Europe, North and South America, Asia, and on King George Island in Antarctica.[5][6] It grows on mosses such as Chorisodontium aciphyllum, Polytrichum strictum, Andrea gainii, and Sanionia uncinata.
Biochemistry
Secondary metabolites of Cladonia squamosa include barbatic acid, decarboxythamnolic acid, thamnolic acid, squamatic acid as well as various unknown or unidentified terpenes and/or terpenoids.[4][7]
References
- ↑ "Standardized Common Names for Wild Species in Canada". 2020. https://www.wildspecies.ca.
- ↑ "Dragon Horn (Cladonia squamosa)" (in en-US). https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/117963-Cladonia-squamosa.
- ↑ Fink, Bruce (1907). Further Notes on Cladonias. IX. Cladonia squamosa and Cladonia subsquamosa. The Bryologist , Mar., 1907, Vol. 10, No. 2 (Mar., 1907), pp. 21-23. American Bryological and Lichenological Society.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "LIAS light - Item Descriptions". http://liaslight.lias.net/Descriptions/ItemID_1577.html.
- ↑ Noh, Hyun-Ju; Lee, Yung Mi; Park, Chae Haeng; Lee, Hong Kum; Cho, Jang-Cheon; Hong, Soon Gyu (2020). "Microbiome in Cladonia squamosa Is Vertically Stratified According to Microclimatic Conditions". Frontiers in Microbiology 11. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.00268. ISSN 1664-302X. PMID 32161575.
- ↑ Fink, Bruce (1907). "Further Notes on Cladonias. IX. Cladonia squamosa and Cladonia subsquamosa". The Bryologist 10 (2): 21–23. doi:10.2307/3238499. ISSN 0007-2745. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3238499.
- ↑ Culberson, Chicita F. (1970), Supplement to "Chemical and Botanical Guide to Lichen Products" The Bryologist , Summer, 1970, Vol. 73, No. 2 (Summer, 1970) p. 257, American Bryological and Lichenological Society
Wikidata ☰ Q22114140 entry}
 |