Astronomy:Tholus
In planetary nomenclature, a tholus /ˈθoʊləs/ (pl. tholi /ˈθoʊlaɪ/) is a small domical mountain or hill.[1][2] The word is from the Greek θόλος, tholos (pl. tholoi),[3] which means a circular building with a conical or vaulted roof.[4] The Romans transliterated the word into the Latin tholus, which means cupola or dome.[5] In 1973, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) adopted tholus as one of a number of official descriptor terms for topographic features on Mars and other planets and satellites.[6][7] One justification for using neutral Latin or Greek descriptors was that it allowed features to be named and described before their geology or geomorphology could be determined.[8] For example, many tholi appear to be volcanic in origin, but the term does not imply a specific geologic origin.[9] Currently (March 2015), the IAU recognizes 56 descriptor terms.[1] (See Planetary nomenclature.) Tholi are present on Venus, Mars, asteroid 4 Vesta, dwarf planet Ceres, and on Jupiter's moon Io.
-
Map of the Tharsis quadrangle showing major features, several of which are tholi. Tharsis contains many volcanoes, including Olympus Mons, the tallest known volcano in the Solar System.
-
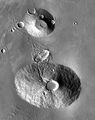
2001 Mars Odyssey THEMIS mosaic of Ceraunius Tholus (lower volcano) and Uranius Tholus (upper volcano). Ceraunius Tholus is about as high as Earth's Mount Everest.
-
Western part of Jovis Tholus, as seen by THEMIS on Mars Odyssey spacecraft. Jovis Tholus is in the Tharsis quadrangle.
Examples of tholi
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Descriptor Terms (Feature Types)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/DescriptorTerms.
- ↑ Hargitai H. (2014). "Tholus, Tholi". in H. Hargitai. Encyclopedia of Planetary Landforms. Springer New York. pp. 1. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-9213-9_371-1. ISBN 978-1-4614-9213-9. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-4614-9213-9.
- ↑ Liddell; Scott (1889). An Intermediate Greek-English Lexicon. New York: Harper & Brothers. pp. 368. https://archive.org/stream/intermediategree00lidd#page/n373/mode/1up.
- ↑ "Tholus". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/592746/tholos.
- ↑ Simpson, D.P. (1968). Cassell's New Latin Dictionary; Funk & Wagnalls: New York, p. 604.
- ↑ De Vaucouleurs G.; Davies M.; Dollfus A.; Koval I. K.; Masursky H.; Miyamoto S. et al. (September 1975). "The new Martian nomenclature of the international Astronomical Union". Icarus 26 (1): 85–98. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(75)90146-3. Bibcode: 1975Icar...26...85D. http://planetologia.elte.hu/ipcd/vaucouleurs.pdf.
- ↑ Greeley, R. (1994) Planetary Landscapes, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall: New York, pp. 35-36.
- ↑ Russell, J.F.; Snyder, C.W.; Kieffer, H.H. (1992). Origin and Use of Martian Nomenclature in Mars, H.H. Kieffer et al., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, p. 1310.
- ↑ Russell, J.F.; Snyder, C.W.; Kieffer, H.H. (1992). Origin and Use of Martian Nomenclature in Mars, H.H. Kieffer et al., Eds.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, p. 1312.
External links
 |