Biology:Little bunting
| Little bunting | |
|---|---|

| |
| On the island of Heligoland in the North Sea | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Emberizidae |
| Genus: | Emberiza |
| Species: | E. pusilla
|
| Binomial name | |
| Emberiza pusilla Pallas, 1776
| |
| |
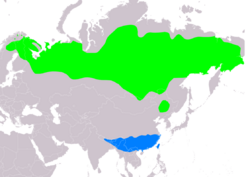
| Range of E. pusilla Breeding Non-breeding
| |
The little bunting (Emberiza pusilla) is a passerine bird belonging to the bunting family (Emberizidae).
Taxonomy
First described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1776, the little bunting is a monotypic species,[2] with no geographical variation across its extensive Palearctic range.[3]
The genus name Emberiza is from Old German Embritz, a bunting. The specific pusilla is Latin for "very small".[4]
Description
This is a small bunting, measuring only 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 in) in length.[2] It has white underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides. With its chestnut face and white malar stripe, it resembles a small female reed bunting, but has black crown stripes, a white eye-ring, and a fine dark border to the rear of its chestnut cheeks. The sexes are similar.
The call is a distinctive zik, and the song is a rolling siroo-sir-sir-siroo.
Ecology
The little bunting breeds across the taiga of the far north-east of Europe
] and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East. It is migratory, wintering in the subtropics in northern India , southern China and the northern parts of south-east Asia.[3] The birds remain in their winter quarters for quite long; specimens were taken in Yunnan in late March.[5] It is a rare vagrant to western Europe.[3] This species is adaptable; in the mountains of Bhutan for example, where small numbers winter, it is typically found in an agricultural habitat, mostly between 1,000 and 2,000 metres (3,300 and 6,600 ft) ASL.[6]
It breeds in open coniferous woodland, often with some birch or willow. Four to six eggs are laid in a tree nest. Its natural food consists of seeds, or when feeding young, insects.
A common and widely-ranging species, it is not considered threatened on the IUCN Red List.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2017). "Emberiza pusilla". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T22720954A111137474. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-1.RLTS.T22720954A111137474.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22720954/111137474. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Byers, Olsson & Curson (1995), p. 154.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Byers, Olsson & Curson (1995), p. 156.
- ↑ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London, United Kingdom: Christopher Helm. pp. 145, 325. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4. https://archive.org/details/Helm_Dictionary_of_Scientific_Bird_Names_by_James_A._Jobling.
- ↑ Bangs, Outram (1932). "Birds of western China obtained by the Kelley-Roosevelts expedition". Field Mus. Nat. Hist. Zool. Ser. 18 (11): 343–379. https://archive.org/details/birdsofwesternch1811bang.
- ↑ Inskipp, Carol; Inskipp, Tim; Sherub (2000). "The ornithological importance of Thrumshingla National Park, Bhutan". Forktail 16: 147–162. http://orientalbirdclub.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/Inskipp-Bhutan.pdf. Retrieved 2014-08-03.
Cited works
- Byers, Clive; Olsson, Urban; Curson, Jon (1995). Buntings and Sparrows: A Guide to the Buntings and North American Sparrows. Mountfield, East Sussex, UK: Pica Press. ISBN 1-873403-19-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Emberiza pusilla. |
- OBC 29 photographs (see pulldown menu at page bottom)
Wikidata ☰ Q216855 entry
 |



