Astronomy:RD1
| RD1 (0140+326 RD1) | |
|---|---|
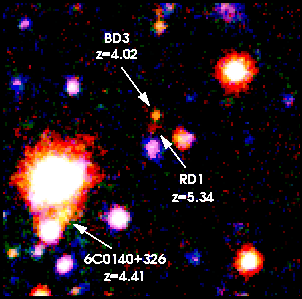 RD1 as viewed by the W. M. Keck Observatory | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Triangulum |
| Right ascension | 01h 43m 42.8s |
| Declination | +32° 54′ 00.0″ |
| Redshift | 5.34[1] |
| Distance | around 12.5 billion light-years (light travel distance)[2] ~26 billion light-years (present comoving distance)[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 26.1 |
| Other designations | |
| [DS98] 6C 0140+326 RD1 | |
RD1 or 0140+326 RD1 is a distant galaxy, it once held the title of most distant galaxy known.[3] RD1 was discovered in March 1998, and is at z = 5.34,[1] and was the first object found to exceed redshift 5.[4] It bested the previous recordholders, a pair of galaxies at z=4.92 lensed by the galaxy cluster CL 1358+62 (CL 1358+62 G1 & CL 1358+62 G2). It was the most distant object known to mankind for a few months in 1998, until BR1202-0725 LAE was discovered at z = 5.64.
Distance measurements
The "distance" of a far away galaxy depends on the chosen distance measurement. With a redshift of 5.34,[1] light from this galaxy is estimated to have taken around 12.5 billion years to reach us.[2] But since this galaxy is receding from Earth, the present comoving distance is estimated to be around 26 billion light-years.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 arXiv, Dey, Arjun; Spinrad, Hyron; Stern, Daniel; Graham, James R.; Chaffee, Frederic H. (1998). "A Galaxy at z = 5.34". The Astrophysical Journal 498 (2): L93–L97. doi:10.1086/311331. Bibcode: 1998ApJ...498L..93D. (209 KB), 11 March 1998
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Edward L. (Ned) Wright. "Cosmology Calculator I". Astronomy @ UCLA. http://www.astro.ucla.edu/~wright/CosmoCalc.html. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ↑ Astronomy Picture of the Day, A Baby Galaxy , March 24, 1998
- ↑ New York Times, Peering Back in Time, Astronomers Glimpse Galaxies Aborning , October 20, 1998
 |

