Biology:Aprasia inaurita
| Aprasia inaurita | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Pygopodidae |
| Genus: | Aprasia |
| Species: | A. inaurita
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aprasia inaurita Kluge, 1974
| |
| |
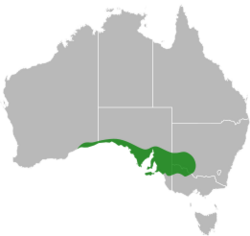
The Mallee worm-lizard (Aprasia inaurita), also known as the pink-nosed worm-lizard and the red-tailed worm-lizard, is a slender pygopid (legless lizard) species that is endemic to Australia , with recorded distribution across the four southern mainland states, although its distribution is restricted in Western Australia and New South Wales.[2]
Description
The Mallee worm-lizard (Aprasia inaurita) is identifiable by its pale olive brown or greyish-brown colouring from above, a whitish underside, with a reddish-brown hue around the Mallee worm-lizard’s head and neck and a distinctly bright reddish-orange tail.[2] The Mallee worm-lizard also lacks an external ear opening and has very small black eyes, with the lack of an external ear opening being what distinguishes Aprasia inaurita from Aprasia aurita, the eared worm-lizard, which is also confusingly known as the Mallee worm-lizard in the state of Victoria.[2]
The Mallee worm-lizard has a snout-vent length of 135mm, with studies upon body length of the species finding that females were larger than males, with the average female body size around 115.6mm and the average male body length around 101.6mm.[2][3] The same study also found that males were more common than females but this may have been attributed to the time of the year the study was conducted.[3]
Aprasia inaurita is differentiated from other Aprasia by:
- The dorsal surface of the head and body being uniformly pigmented with a faint lateral head pattern rarely present.[4]
- The nasal and first subpralabial scales being distinct posterior to nostril and the nasal contacts the second supralabial.[4]
- Containing two or three postorbital scales and usually 10 nuchal scales.[4]
- Containing 14 midbody scale rows with usually 3 preanal scales.[4]
- Containing ventral scales averaging 149.7 in males and 154.6 in females.[4]
Habitat
The Mallee worm-lizard inhabits semi-arid areas of red sandy soils and woodlands of the Mallee region and surrounds.[2] Thought to be dependent on spinifex (Triodia scariosa), the Mallee worm-lizard is often found sheltering in sand, beneath mallee stumps, through leaf litter, or as a fossorial species inhabiting ant tunnels.[2][5][6] The Mallee worm-lizard is also said to require mature habitats with a well-developed surface debris layer.[7] To burrow through loose soil and to crawl through narrow earth cracks and insect tunnels, Aprasia species use lateral undulations for locomotion.[5]
Ecology
The Aprasia species are myrmecophagous, with the Mallee worm-lizard specifically targeting the Aphaenogaster sp. eggs and larvae.[8] Webb & Jones (1994) state that the Aprasia species are opportunistic “binge feeders” which feed infrequently, but when they do come across an ant brood for instance, they will feed in excess.[3] Studies on how Aprasia species can locate ant colonies, and specifically ant broods, have not yet been researched and are open for inquest, with chemoreceptors of ant pheromonal trails being a possible explanation which is a similar adaptation of some snake species.[3]
Pygopodids are predated upon by diurnal raptors, elapid snakes, goannas, feral cats and foxes, of which, they represent a minor dietary component for these predators.[5] Aprasia inaurita was observed by Rankin (1976) to raise its tail from the substrate and wave it when prodded, suggesting that the tail may be for defense purposes, and being brightly colored and blunt, it may be used as a decoy for predators.[8] Pygopodids have also been found to be predated upon by the trematode Paradistoma crucifer, the cestode Acanthotaenia striata and by the nematodes Abbreviata sp.[5]
Taxonomy and Distribution
The Mallee worm-lizard belongs to the Pygopodidae family of squamates (scaled reptiles), commonly referred to as ‘legless lizards’ for their snake-like appearance with absent forelimbs and very small vestigial hind-limb flaps which, for the Mallee worm-lizard, occur as small scaley flaps located by the cloacal vent.[2][9] The Pygopodidae family are recognised as a being closely related to two families of gecko, the Carphodactylidae and Diplodactylidae, and are represented by 47 species, of which, 35 species are placed into two subfamilies, the Lialisinae and the Pygopodinae, with 7 genera: Lialis (two species), Delma (22 species), Paradelma (monotypic), Pygopus (five species), Ophidiocephalus (monotypic), Aprasia (15 species), Pletholax (two species).[10][11]
The Aprasia species are noted as one of the most divergent genera from the Pygopodidae family.[3] The Mallee worm-lizard (Aprasia inaurita) is a part of the Aprasia genus which is predominately found in Southern Australia, with the Mallee worm-lizard itself being distributed across a narrow band which stretches from the southeast of Western Australia, across southern South Australia, the northwest corner of Victoria and southwestern New South Wales.[7] The IBRA (Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia) regions that the Mallee worm-lizard occurs in NSW are the Murray Darling Depression and Riverina regions, with 8% occurrence across New South Wales’ reserves.[2] More specifically, the Mallee worm-lizard has been discovered through the Mallee region between Balranald and Gol Gol with centralised recordings of the Mallee worm-lizard in the Mallee Cliffs National Park area.[2][5] Recordings of the Mallee worm-lizard have also been found in the central mallee region around Pulletop and Gubbata Nature Reserves and around the Scotia Mallee area.[2]
Due to the severely fragmented distribution of this species, local populations of the Mallee worm-lizard are vulnerable to extinction from stochastic events.[7]
Reproduction
Pygopodids are noted as being oviparous (egg laying) and will have a usual clutch size of two with an incubation period of 66 to 77 days, which is common for the Mallee worm-lizard which will mate in Spring and lay in October.[5]
A study on the sex of Aprasia inaurita determined that adult males of the species contained the presence of 'spurs' on their hindlimb flaps which were found to not be present in the adult females or juveniles of the species.[8] The males of all Aprasia species also had toothed premaxilla, as opposed to juveniles and females with none, or being vestigial in females.[3] This dimorphism has been inferred to either assist males in bouts with other males, to hold down females during copulation, or to assist males in taking down larger prey.[3]
Pygopodids have lived up to 7 years in captivity; however, little else is known of the life history of Pygopodids, in particular, the Mallee worm-lizard.[5]
Threats
A major threat to the Mallee worm-lizard is habitat destruction through clearing, as well as agriculture and land management practices, which thereby remove debris and ground cover that the Mallee worm-lizard depends upon.[2] With mallee vegetation once covering 383,000 km2, 35% of this has since been removed through land clearing.[12] Agricultural practices can also increase soil compaction through machinery and livestock, from which, livestock can feed upon and also trample on important food resources.[2] The Mallee worm-lizard is also under threat by introduced pest species, i.e., the introduced European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) and the house cat (Felis catus).[2]
Altered fire regimes may also pose a threat to the Mallee worm-lizard through the reduced availability of spinifex habitat which would thereby increase the chances of predators to find and prey upon the Mallee worm-lizard.[2] Although the immediate effects of fire on the Mallee worm-lizard found no observed effect on this species after a fire event, it is however affected by impacts upon its habitat.[13]
Status
The Mallee worm-lizard is described as being of least concern by the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) red list, however, in 2004 the Mallee worm-lizard (Aprasia inaurita) is listed as an endangered species within the Australian state of New South Wales.[7] The New South Wales scientific committee confirming that if the circumstances and factors that threaten the survival of the Mallee worm-lizard do not cease than the Mallee worm-lizard is likely to become extinct in nature within New South Wales.[7]
Due to this status within New South Wales, the Mallee worm-lizard has been assigned to the landscape management stream according to the New South Wales Saving our Species (SoS) program which focuses on the threats of habitat destruction and the impacts of landscape clearing, with the aim of securing the Mallee worm-lizards in the wild in New South Wales and extending, or maintaining, its New South Wales’ geographical range.[14]
References
- ↑ Cogger, H.; Shea, G. (2017). "Aprasia inaurita". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T102827758A102827860. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T102827758A102827860.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/102827758/102827860. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 Office of Environment and Heritage (OEH). 2017. Mallee Worm-lizard profile. https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/threatenedspeciesapp/profile.aspx?id=10060
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Webb, J. K. Shine, R. 1994. Feeding habits and reproductive biology of Australian Pygopodid lizards of the genus Aprasia. American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists (ASIH), 1994(2), 390-398.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Kluge, A. G. 1974. A taxonomic revision of the lizard family Pygopodidae. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Report No. 147.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Shea, G. M. 1983. Family Pygopodidae; In Glasby, C. G. Ross, G. J. B. Beesley, P. L. (Eds.). Fauna of Australia – Volume 2a Amphibia and Reptilia. AGPS Canberra.
- ↑ Cogger, H. G. (2014). Reptiles and amphibians of Australia. CSIRO Publishing.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Adam, P. 2004. Mallee worm-lizard (Aprasia inaurita) – endangered species listing. NSW Department of Plannning and Environment. https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/topics/animals-and-plants/threatened-species/nsw-threatened-species-scientific-committee/determinations/final-determinations/2004-2007/mallee-worm-lizard-aprasia-inaurita-endangered-species-listing
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Jones, S. R. 1999. Conservation biology of the Pink-tailed legless lizard – Aprasia parapulchella. University of Canberra Applied Ecology Research Group.
- ↑ Cogger, H. G. (2000). Reptiles and amphibians of Australia. Reed Books: Chatswood.
- ↑ Gamble, T. Greenbaum, E. Jackman, T. R. Russell, A. P. Bauer, A. M. 2012. Repeated origin and loss of adhesive toepads in geckos. PLOS ONE. 7 (6): e39429. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...739429G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039429. PMC 3384654. PMID 22761794.
- ↑ Jennings, B. W. 2021. Evolutionary relationships among the snakelike pygopodid lizards: a review of phylogenetic studies of an enigmatic Australian adaptive radiation. PeerJ. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11502
- ↑ Driscoll, D. Henderson, M. 2008. Managing remnant mallee vegetation for biodiversity using fire and fox control. Australia and Pacific Science Foundation. http://www.apscience.org.au/apsf_05_3/
- ↑ Driscoll, D. Henderson, M. 2008. How many common reptile species are fire specialists? A replicated natural experiment highlights the predictive weakness of a fire succession model. Biological Conservation, 141(2), 460-471.
- ↑ Office of Environment and Heritage (OEH). n.d. Mallee Worm-lizard (Aprasia inaurita) – Saving our Species strategy. Department of Planning Industry and Environment. https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/savingourspeciesapp/project.aspx?ProfileID=10060
Wikidata ☰ Q6452066 entry
 |


