Chemistry:Ilomastat
From HandWiki
Revision as of 06:38, 6 May 2022 by imported>OrgMain (over-write)
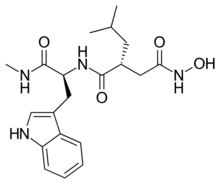
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3R)-N1-Hydroxy-N4-{(1S)-1-[(1H-indol-3-yl)methyl]-2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl}-3-(2-methylpropyl)butanediamide | |
| Other names
Galardin, GM6001
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | GM6 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| MeSH | GM6001 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H28N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 388.468 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ilomastat (INN),[1] (codenamed GM6001, proprietary name Galardin®) is a broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor.[2][3][4]
This chemotherapy agent is considered to have application in skincare products for its antiaging properties.
Ilomastat is a member of the hydroxamic acid class of reversible metallopeptidase inhibitors. The anionic state of the hydroxamic acid group forms a bidentate complex with the active site zinc.[5]
Examples of enzymes that ilomastat inhibit include rabbit MMP9,[6] thermolysin,[2] peptide deformylase,[7] and anthrax lethal factor endopeptidase (LF) produced by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis.[8][9]
References
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 36". World Health Organization. p. 148. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/RL36.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Inhibition of human skin fibroblast collagenase, thermolysin, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase by peptide hydroxamic acids". Biochemistry 31 (31): 7152–4. August 1992. doi:10.1021/bi00146a017. PMID 1322694.
- ↑ "Treatment of alkali-injured rabbit corneas with a synthetic inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 33 (12): 3325–31. November 1992. PMID 1385350.
- ↑ "Galardin (GM 6001), a broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, blocks bombesin- and LPA-induced EGF receptor transactivation and DNA synthesis in rat-1 cells". Exp. Cell Res. 290 (2): 437–46. November 2003. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00355-0. PMID 14568001.
- ↑ "Small-molecule inhibitor J16.402: galardin". MEROPS - the Peptidase Database. Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. 2010-09-07. http://merops.sanger.ac.uk/cgi-bin/smi_summary?mid=J16.402.
- ↑ "An inhibitor of the matrix metalloproteinase synthesized by rabbit corneal epithelium". Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 32 (11): 2997–3001. 1991. PMID 1655675.
- ↑ "Metalloprotease inhibitors GM6001 and TAPI-0 inhibit the obligate intracellular human pathogen Chlamydia trachomatis by targeting peptide deformylase of the bacterium". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (24): 16691–9. June 2006. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513648200. PMID 16565079.
- ↑ "Metalloproteinase inhibitors, nonantimicrobial chemically modified tetracyclines, and ilomastat block Bacillus anthracis lethal factor activity in viable cells". Infect. Immun. 73 (11): 7548–57. November 2005. doi:10.1128/IAI.73.11.7548-7557.2005. PMID 16239558.
- ↑ PDB: 1PWU; "The structural basis for substrate and inhibitor selectivity of the anthrax lethal factor". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11 (1): 60–6. January 2004. doi:10.1038/nsmb708. PMID 14718924.
 |

