Chemistry:Bromotoluene
Bromotoluene is a group of three isomeric chemical compounds. They (ortho-bromotoluene, meta-bromotoluene, and para-bromotoluene) consist of a disubstituted benzene ring with one bromine atom and one methyl group.
Properties
The isomers differ in the location of the bromine, but have the same chemical formula.
| Bromotoluene isomers[1][2][3] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | ||||
| Common name | o-bromotoluene | m-bromotoluene | p-bromotoluene | |
| Structure | 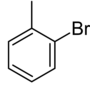
|
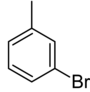
|

| |
| Systematic name | 1-bromo-2-methylbenzene | 1-bromo-3-methylbenzene | 1-bromo-4-methylbenzene | |
| Molecular formula | C7H7Br (C6H4BrCH3) | |||
| Molar mass | 171.03 g/mol | |||
| Appearance | colorless liquid, white crystalline solid | |||
| CAS number | [95-46-5] | [591-17-3] | [106-38-7] | |
| Properties | ||||
| Density and phase | 1.431 g/ml, liquid | 1.4099 g/ml, liquid | 1.3995 g/ml, solid | |
| Solubility in water | practically insoluble | |||
| Other solubilities | very soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, acetone, chloroform | |||
| Melting point | -27.8 °C (-18.0 °F; -409.63 K) | -39.8 °C (-39.6 °F; -388.03 K) | 28.5 °C (83.3 °F; 301.7 K) | |
| Boiling point | 181.7 °C (359.1 °F; 454.9 K) | 183.7 °C (362.7 °F; 456.9 K) | 184.5 °C (364.1 °F; 457.7 K) | |
Benzyl bromide is an isomer, which has a bromine substituted for one of the hydrogens of toluene's methyl group, and it is sometimes named α-bromotoluene.
Preparation
A laboratory route to p-bromotoluene proceeds from p-toluidine, which is diazotiized followed by treatment with cuprous bromide.[4]
Uses
Bromotoluenes are precursors to many organic building blocks. For example, the methyl group may be oxidized using potassium permanganate to form the corresponding bromobenzoic acid.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Template:Cite PubChem
- ↑ Template:Cite PubChem
- ↑ Template:Cite PubChem
- ↑ Bigelow, L. A. (1925). "p-BROMOTOLUENE". Organic Syntheses 5: 21. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.005.0021. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV1P0136. Retrieved January 19, 2023.
- ↑ Bigelow, L. A. (1922). "A Study of Side-Chain Oxidations with Potassium Permanganate. Ii". Journal of the American Chemical Society 44 (9): 2010–2019. doi:10.1021/ja01430a020. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja01430a020. Retrieved January 19, 2023.

