Chemistry:1,3-Dibromobenzene
From HandWiki
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,3-Dibromobenzene
| |
| Other names
m-Dibromobenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1904538 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 363342 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4Br2 | |
| Molar mass | 235.906 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid[1] |
| Density | 1.9523 g/cm3 at 20.4 °C |
| Melting point | −7.0 °C (19.4 °F; 266.1 K) |
| Boiling point | 218–220 °C (424–428 °F; 491–493 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1,3-Dibromobenzene (m-dibromobenzene) is an isomer of dibromobenzene that is a colorless liquid at room temperature.[1]
Preparation
1,3-Dibromobenzene may be prepared by diazotization of 3-bromoaniline, followed by a Sandmeyer reaction with cuprous bromide.[2]
Uses
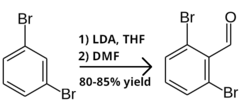
1,3-Dibromobenzene has been used as a starting material in the synthesis of antiviral Lufotrelvir, in human clinical trials for the treatment of COVID-19.[3] The first step is formylation of 1,3-dibromobenzene to 2,6-dibromobenzaldehyde, by lithiation with lithium diisopropylamide in THF, followed by quenching with dimethylformamide.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "1,3-Dibromobenzene". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7927.
- ↑ Hartwell, Jonathan L. (1944). "o-Chlorobromobenzene". Organic Syntheses 24: 22. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.024.0022.
- ↑ Allais, Christophe; Bernhardson, David; Brown, Adam R.; Chinigo, Gary M.; Desrosiers, Jean-Nicolas; Dirico, Kenneth J.; Hotham, Ian; Jones, Brian P. et al. (3 February 2023). "Early Clinical Development of Lufotrelvir as a Potential Therapy for COVID-19". Organic Process Research & Development 27 (12): 2223–2239. doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.2c00375. PMID 37552749.
 |