Chemistry:Cyclen
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4,7,10-Tetrazacyclododecane | |
| Other names
Tetraaza-12-crown-4
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H20N4 | |
| Molar mass | 172.276 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 110–113 °C (230–235 °F; 383–386 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
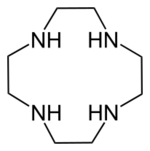
Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Being structurally simple, symmetrical, and polyfunctional, cyclen has been widely investigated.[1]
Synthesis
Some syntheses exploit the Thorpe-Ingold effect to facilitate ring-formation. Illustrative is the reaction of the deprotonated tosylamides with ditosylates:[2]
- TsN(CH2CH2NTsNa)2 + TsN(CH2CH2OTs)2 → (TsNCH2CH2)4
The resulting macrocycle can be deprotected with strong acid. Base gives the tetramine.
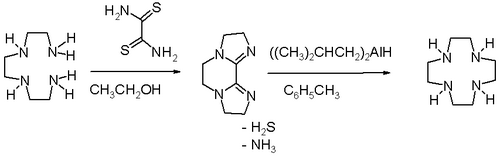
High dilution conditions result in a low reaction rate penalty and this disadvantage is removed in an alternative procedure starting from triethylenetetraamine and dithiooxamide to a bisamidine – also a bis(imidazoline) – followed by reduction and ring expansion with DIBAL.[3]
Coordination complexes

Coordination complexes of cyclen have been studied extensively.[5][6] With a 12-membered ring, it tends to bind to four contiguous sites on octaheral metal centers. In contrast the larger cyclam ligand tens to form attach to four coplanar sites. It also forms complexes of the type [Ln(cyclen)2]3+ where Ln = lanthanide.[7]
References
- ↑ Lejault, Pauline; Duskova, Katerina; Bernhard, Claire; Valverde, Ibai E.; Romieu, Anthony; Monchaud, David (2019). "The Scope of Application of Macrocyclic Polyamines Beyond Metal Chelation". European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2019 (36): 6146–6157. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201900870. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02268694v2/file/Lejault%20et%20al%20-%20EurJOC%202019.pdf.
- ↑ Atkins, T. J.; Richman, J. E.; Oettle, W. F. (1978). "1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexaazacyclooctadecane". Org. Synth. 58: 86. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.058.0086.
- ↑ Reed, David P.; Weisman, Gary R. (2002). "1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane". Org. Synth. 78: 73. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.078.0073.
- ↑ Scott, Brian; Brewer, Karen J.; Spreer, Larry O.; Craig, Carl A.; Otvos, John W.; Calvin, Melvin; Taylor, Scott (1990). "A Novel Conformation for a Coordinated Macrocycle: The Crystal Structure of [Ni(12-aneN4)(OH2)2](CIO4)2·H2O; (12-aneN4= 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane)". Journal of Coordination Chemistry 21 (4): 307–313. doi:10.1080/00958979009408193.
- ↑ Gunnlaugsson, Thorfinnur; Leonard, Joseph P. (2005). "Responsive lanthanide luminescent cyclen complexes: From switching/Sensing to supramolecular architectures". Chemical Communications (25): 3114–3131. doi:10.1039/b418196d. PMID 15968347.
- ↑ Joshi, Tanmaya; Graham, Bim; Spiccia, Leone (2015). "Macrocyclic Metal Complexes for Metalloenzyme Mimicry and Sensor Development". Accounts of Chemical Research 48 (8): 2366–2379. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00142. PMID 26244894.
- ↑ Barraza, Ramiro; Sertage, Alexander G.; Kajjam, Aravind B.; Ward, Cassandra L.; Lutter, Jacob C.; Schlegel, H. Bernhard; Allen, Matthew J. (2022). "Properties of Amine-Containing Ligands That Are Necessary for Visible-Light-Promoted Catalysis with Divalent Europium". Inorganic Chemistry 61 (49): 19649–19657. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c02911. PMID 36417708.
Further reading
- Suchý, M.; Hudson, R. H. E. (2008). "Synthetic Strategies Toward N-Functionalized Cyclens". Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008 (29): 4847–4865. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200800636.
 |