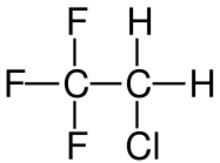
Chemistry:2-Chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1983 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2ClF3 | |
| Molar mass | 118.48 g/mol |
| Appearance | Gas |
| Density | 1.389 g/mol (liquid at 0 °C) |
| Melting point | −105.3 °C (−157.5 °F; 167.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 6.1 °C (43.0 °F; 279.2 K) |
| 0.89 g/l | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3092 (liquid at 0 °C) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane, also known as 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane or Freon 133a, is an alkyl halide belonging to the category of hydrochlorofluorocarbons, having chemical formula F3C-CH2-Cl. Under standard conditions, it appears as a colorless gas, partially soluble in water. It is used as a refrigerant, as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
It can be made by the reaction of trichloroethylene and hydrogen fluoride.
References
 |

