Chemistry:Contryphan
| Contryphan | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
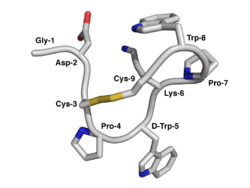 NMR structure of Contryphan-Vn. The peptide backbone is depicted by a curved tube while the amino acid side-chains are represented by capped sticks. Carbon atoms are colored grey, nitrogen atoms blue, oxygen atoms red, and sulfur atoms yellow.[1] . | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Contryphan_CS | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF02950 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR011062 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PS60027 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 2cco / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The contryphans (conus + tryptophan) are a family of peptides that are active constituents of the potent venom produced by cone snail (genus Conus). The two amino acid cysteine residues in contryphans are linked by a disulfide bond. In addition, contryphans undergo an unusual degree of post-translational modification including epimerization of leucine and tryptophan, tryptophan bromination, amidation of the C-terminus, and proline hydroxylation.[2] In the broader scheme of genetic conotoxin classification, contryphans are members of "Conotoxin Superfamily O2."[3]
Family members
Contryphan family members include:
| Peptide | Sequence | Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Des(Gly1)contryphan-R | COwEPWC-NH2 | C. radiatus | [4] |
| Contryphan-R | GCOwEPWC-NH2 | Conus radiatus | [4] |
| Bromocontyphan-R | GCOwEPXC-NH2 | C. radiatus | [5] |
| Contryphan-Sm | GCOwQPWC-NH2 | Conus stercusmuscarum | [6] |
| Contryphan-P | GCOwDPWC-NH2 | C. purpurascens | [6] |
| Contryphan-R/Tx | GCOwEPWC-NH2 | Conus textile | [6] |
| Contryphan-Tx | GCOWQPYC-NH2 | Conus textile | [6] |
| Contryphan-Vn | GDCPwKPWC-NH2 | Conus ventricosus | [7] |
| Leu-contryphan-P | GCVlLPWC-OH | Conus purpurascens | [8] |
| Leu-contryphan-Tx | CVlYPWC-NH2 | Conus textile | [6] |
| Glaconryphan-M | NγSγCPWHPWC-NH2 | Conus marmoreus | [2] |
where the sequence abbreviations stand for:
- O = 4-trans-hydroxyproline,
- l = D-leucine, L = L-leucine,
- w = D-tryptophan, W = L-tryptophan,
- γ = gamma-carboxyglutamic acid,
- NH2 = C-terminal amidation
and the remainder of the letters refer to the standard one letter abbreviations for amino acids.
Mechanism of toxicity
The venom of cone snails cause paralysis of their fish prey. The molecular target has not been determined for all contryphan peptides, however it is known that contryphan-Vn is a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel modulator,[7] while glacontryphan-M is a L-type calcium channel blocker.[2]
References
- ↑ PDB: 1NXN; "Solution structure of the cyclic peptide contryphan-Vn, a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel modulator". Biopolymers 74 (3): 189–98. June 2004. doi:10.1002/bip.20025. PMID 15150794.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "The first gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing contryphan. A selective L-type calcium ion channel blocker isolated from the venom of Conus marmoreus". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (31): 32453–63. July 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313825200. PMID 15155730.
- ↑ "Conotoxin gene superfamilies". Marine Drugs 12 (12): 6058–101. December 2014. doi:10.3390/md12126058. PMID 25522317.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Contryphan is a D-tryptophan-containing Conus peptide". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 271 (45): 28002–5. November 1996. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.45.28002. PMID 8910408.
- ↑ "Bromocontryphan: post-translational bromination of tryptophan". Biochemistry 36 (5): 989–94. February 1997. doi:10.1021/bi962840p. PMID 9033387.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 "The contryphans, a D-tryptophan-containing family of Conus peptides: interconversion between conformers". The Journal of Peptide Research 51 (3): 173–9. March 1998. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.1998.tb01213.x. PMID 9531419.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Contryphan-Vn: a novel peptide from the venom of the Mediterranean snail Conus ventricosus". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 288 (4): 908–13. November 2001. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5833. PMID 11688995.
- ↑ "A novel D-leucine-containing Conus peptide: diverse conformational dynamics in the contryphan family". The Journal of Peptide Research 54 (2): 93–9. August 1999. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3011.1999.00093.x. PMID 10461743.
External links
- Contryphan at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |


