Chemistry:2-Acetylthiophene
From HandWiki
Revision as of 09:04, 17 July 2022 by imported>Scavis2 (linkage)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-acetothienone, methyl thienyl ketone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6OS | |
| Molar mass | 126.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow liquid |
| Melting point | 9 °C (48 °F; 282 K) |
| Boiling point | 214 °C (417 °F; 487 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P322, P330, P361, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
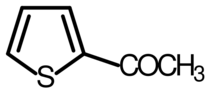
2-Acetylthiophene is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3C(O)C4H3S. A yellow liquid, it is the more useful of the two isomers of acetylthiophene. It is of commercial interest as a precursor to both thiophene-2-carboxylic acid and thiophene-2-acetic acid.[2] It is prepared by the reaction of thiophene with acetyl chloride in the presence of stannic chloride.[3]
References
- ↑ "2-Acetylthiophene" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6920#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Swanston, Jonathan (2006). "Thiophene". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_793.pub2. ISBN 3527306730.
- ↑ John R. Johnson, G. E. May (1938). "2-Acetothienone". Organic Syntheses 18: 1. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0001.
 |

