Astronomy:List of X-ray space telescopes
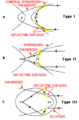
X-ray telescopes are designed to observe the x-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. X-rays from outer space cannot be observed from the ground due to absorption by the atmosphere, and so x-ray telescopes must be launched into orbit. Their mirrors require a very low angle of reflection (typically 10 arc-minutes to 2 degrees).[1] These are called glancing (or grazing) incidence mirrors. In 1952, Hans Wolter outlined three ways a telescope could be built using only this kind of mirror.[2][3]
Space-borne observatories and instruments
This list contains space-borne observatories as well as X-ray instruments as part of a larger mission, both past, present and in the proposal stage.
| Name | Launch | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Ariel 5 | 1974 | |
| Ariel 6 | 1979 | |
| ASCA | 1993 | |
| ATHENA | 2031 | Under development |
| AGILE | 2007 | |
| Apollo Telescope Mount | 1973 | Part of Skylab, operated 1973-1974 |
| Arcus | — |
Proposal, not selected for launch in 2019 |
| ALEXIS | 1993 | |
| ANS | 1974 | |
| Astrosat | 2015 | |
| BeppoSAX | 1996 | |
| BBXRT | 1990 | |
| Compton Gamma Ray Observatory | 1991 | |
| Chandra X-ray Observatory | 1999 | |
| Constellation-X Observatory | — |
2008 proposal, merged into the International X-ray Observatory proposal |
| Copernicus | 1972 | |
| Cos-B | 1975 | |
| DXS | 1993 | |
| Einstein Observatory | 1978 | originally HEAO-2 |
| EP-WXT | 2022 | |
| eROSITA | 2019 | |
| EXOSAT | 1983 | |
| Fermi | 2008 | |
| Ginga | 1987 | |
| Granat | 1989 | |
| Gravity and Extreme Magnetism | — |
2012 proposal |
| Hakucho | 1979 | |
| Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope | 2017 | (HXMT) also known as Insight (Chinese: 慧眼) |
| HEAO-1 | 1977 | |
| HEAO 3 | 1979 | |
| High Energy Transient Explorer | 1996 | |
| Hinode | 2006 | |
| Hinotori | 1981 | Originally ASTRO-A |
| Hitomi | 2016 | Originally ASTRO-H |
| IXPE | 2021 | |
| INTEGRAL | 2002 | |
| International X-ray Observatory | — |
2012 proposal, now part of ATHENA |
| LOFT | — |
Proposal |
| Lynx | 2036 | Study/proposal |
| Max Valier Sat | 2017 | |
| MAXI | 2009 | |
| Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory | 2004 | Originally Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission[4] |
| NICER | 2017 | |
| NuSTAR | 2012 | |
| OAO-1 | 1966 | |
| ORBIS | — |
Under development |
| OSO 7 | 1971 | |
| OSO 8 | 1975 | |
| RHESSI | 2002 | |
| ROSAT | 1990 | |
| RXTE | 1995 | |
| SAS-3 | 1975 | |
| SVOM | 2024 |
Under development |
| Spektr-RG | 2019 | |
| Suzaku | 2005 | |
| Tenma | 1983 | |
| Uhuru | 1970 | |
| Vela | 1963 | |
| XRISM | 2023 | Under development |
| XEUS | — |
Proposal, merged into the International X-ray Observatory proposal, now part of the ATHENA proposal |
| XMM-Newton | 1999 | |
| XPoSat | 2023 | Planned, under development |
| Yohkoh | 1991 |
High-altitude atmospheric observatories and instruments
Sometimes X-Ray observations are made from a near-space environment on sounding rockets or high-altitude balloons.
- Normal Incidence X-ray Telescope (series of sounding rocket payloads, flown in the late 1980s and 1990s)
- Multi-spectral solar telescope array (MSSTA) (series of sounding rocket payloads, flown in the 1990s and early 2000s)
- Polarised Gamma-ray Observer (PoGOLite) (balloon-borne astroparticle physics experiment, flown 2011-2013)
Gallery
Skylab S-54 instrument, an X-ray telescope
See also
- List of telescope types
- Lists of telescopes
- Calorimetric Electron Telescope (telescope type)
- Cosmic-ray observatory (mission type)
- Phase-contrast X-ray imaging (general term)
- Wolter telescope (telescope type)
- X-ray astronomy satellite (mission type)
- X-ray spectroscopy (general term)
- Lists of spacecraft
References
- ↑ Kulinder Pal Singh. "Techniques in X-ray Astronomy". http://www.ias.ac.in/resonance/Volumes/10/06/0015-0023.pdf.
- ↑ "Glancing Incidence Mirror Systems as Imaging Optics for X-rays". Annalen der Physik 10 (1): 94. 1952. doi:10.1002/andp.19524450108. Bibcode: 1952AnP...445...94W.
- ↑ "A Generalized Schwarzschild Mirror System For Use at Glancing Incidence for X-ray Imaging". Annalen der Physik 10 (4): 286. 1952. doi:10.1002/andp.19524450410. Bibcode: 1952AnP...445..286W.
- ↑ "NASA Renames Swift Observatory in Honor of Late Principal Investigator". 10 January 2018. https://www.space.com/39349-swift-observatory-name-change.html.
External links
- Comparison with of X-ray satellites
- Comparison of XMM-Newton EPIC, Chandra ACIS-S3, ASCA SIS and GIS, and ROSAT PSPC Results for G21.5-0.9, 1E0102.2-7219, and MS1-54.4-0321