Chemistry:3-Aminobiphenyl
From HandWiki
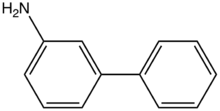
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[1,1′-Biphenyl]-3-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H11N | |
| Molar mass | 169.227 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.077 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 31–31.5 °C (87.8–88.7 °F; 304.1–304.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 177–8 °C (351–46 °F; 450–281 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Aminobiphenyl is an organic compound with the formula C6H5C6H4NH2. It is one of three monoamine derivatives of biphenyl. It is a colorless solid, although aged samples can appear colored. It is obtained from 3-bromoaniline and phenylboronic acid by Suzuki coupling.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Bin Tao, David W. Boykin (2004). "Simple Amine/Pd(OAc)2-Catalyzed Suzuki Coupling Reactions of Aryl Bromides under Mild Aerobic Conditions". J. Org. Chem. 69 (13): 4330–4335. doi:10.1021/jo040147z. PMID 15202886.
 |

