Chemistry:Mordant brown 33
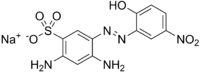
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Sodium 2,4-diamino-5-[2-(3-nitro-6-oxocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ylidene)hydrazin-1-yl]benzene-1-sulfonate | |
| Other names
Mordant brown 33
Chrome Brown RH Sodium 2,4-diamino-5-[2-(3-nitro-6-oxocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ylidene)hydrazin-1-yl]benzenesulfonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | MB33 |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10N5NaO6S | |
| Molar mass | 375.29 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H317, H318, H341 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P272, P280, P281, P302+352, P305+351+338, P308+313, P310, P321, P333+313, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Mordant brown 33 (MB33) is 2,4-diamino-5-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenylazo) benzene sulfonic acid sodium salt.
The UV-Visible spectra of MB33 in all mixtures investigated display three absorption bands in 50% ethanol within all the pH ranges 1.5-13.3 using Thiel buffer the maximum absorption of these bands is located at 438, 453 and a double head band at 410 and 475 nm . The band at 438 nm corresponds to absorption attributed to the cationic form (LH6) of MB33 (whereas L indicates to the parent structure of ligand without hydrogen protons) and disappears at pH > 3.0. The band at 453 nm corresponds to the absorption of the neutral form of the reagent (LH5-). The double head bands at 410 and 475 nm correspond to the di-anionic (LH42−) of MB33.[1]
References
- ↑ M. M. Seleim, M. S. Abu-Bakr, E.Y. Hashem and A. M. El-Zohry; Spectrophotometric determination of manganese (II) with Mordant Brown 33 in the presence of Tween 20 in some foods; Canadian Journal of Analytical Sciences and Spectroscopy, Volume 54, No. 2, 2009. - www.researchgate.net
 |

