Astronomy:Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy
| Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy | |
|---|---|
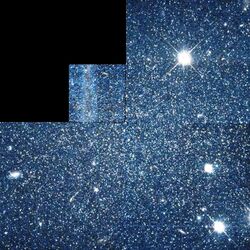 Hubble Space Telescope image of Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Right ascension | 23h 51m 46.3s[1] |
| Declination | +24° 34′ 57″[1] |
| Redshift | −354 ± 3 km/s[1] |
| Distance | 2.7 ± 0.1 Mly (820 ± 20 kpc)[2][3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 14.2[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | dSph[2] |
| Apparent size (V) | 4.0′ × 2.0′[1] |
| Notable features | - |
| Other designations | |
| Pegasus II,[1] Andromeda VI,[1] Peg dSph,[1] KKH 99,[1] PGC 2807158 | |
The Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal (also known as Andromeda VI or Peg dSph for short) is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy about 2.7 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. The Pegasus Dwarf is a member of the Local Group and a satellite galaxy of the Andromeda Galaxy (M31).
General information
The Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal is a galaxy with mainly metal-poor stellar populations.[4] Its metallicity is [Fe/H] ≃ −1.3.[5] It is located at the right ascension 23h51m46.30s and declination +24d34m57.0s in the equatorial coordinate system (epoch J2000.0), and in a distance of 820 ± 20 kpc from Earth and a distance of 294 ± 8 kpc[a] from the Andromeda Galaxy.
The galaxy was discovered in 1999[6] by various authors on the Second Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS II) films.[7]
See also
- List of Andromeda's satellite galaxies
- Pegasus Dwarf Irregular Galaxy (Peg DIG)
- Pegasus galaxy, the Stargate Atlantis fictional location (probably the Pegasus Dwarf Irregular Galaxy).
Notes
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal. http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 Karachentsev, I. D.; Kashibadze, O. G. (2006). "Masses of the local group and of the M81 group estimated from distortions in the local velocity field". Astrophysics 49 (1): 3–18. doi:10.1007/s10511-006-0002-6. Bibcode: 2006Ap.....49....3K.
- ↑ I. D. Karachentsev; V. E. Karachentseva; W. K. Hutchmeier; D. I. Makarov (2004). "A Catalog of Neighboring Galaxies". Astronomical Journal 127 (4): 2031–2068. doi:10.1086/382905. Bibcode: 2004AJ....127.2031K.
- ↑ Van den Bergh, Sidney (May 15, 2000). The Galaxies of the Local Group. Cambridge Astrophysics. p. 240. ISBN 978-1-139-42965-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=H0JMeoqFqEcC&pg=PA240.
- ↑ McConnachie, A. W.; Irwin, M. J.; Ferguson, A. M. N.; Ibata, R. A.; Lewis, G. F.; Tanvir, N. (2005). "Distances and metallicities for 17 Local Group galaxies". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 356 (4): 979–997. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08514.x. Bibcode: 2005MNRAS.356..979M.
- ↑ Pritzl, Barton J.; Armandroff, Taft E.; Jacoby, George H.; Da Costa, G. S. (May 2005). "The Dwarf Spheroidal Companions to M31: Variable Stars in Andromeda I and Andromeda III". The Astronomical Journal 129 (5): 2232–2256. doi:10.1086/428372. Bibcode: 2005AJ....129.2232P.
- ↑ Wallace Sargent. "The Second Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS II)". Caltech. http://www.astro.caltech.edu/~wws/poss2.html.
External links
- NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database: Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal
- Armandroff, Jacoby, & Davies, "Low Surface Brightness Galaxies around M31", Astrophys. J. 118, 1220-1229 (1999).
 |


