Astronomy:SWEAP
The Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) is an instrument on the Parker Solar Probe, designed for an unmanned mission to the Sun's outer corona.[1] The Parker Solar Probe was launched by a Delta IV Heavy on 12 August 2018 from Cape Canaveral, Florida.[2] SWEAP includes two types of instruments: the Solar Probe Cup (SPC) and Solar Probe Analyzers (SPAN).[3] SWEAP has four sensors overall, and is designed to take measurements of solar wind including electrons, ions of hydrogen (protons), and helium (the main components of solar wind and the coronal plasma).[4]
Background
Scientists studying emission spectra of the Sun's corona during total solar eclipses thought they had found the presence of a new element they called "coronium." In the late 1930s, Walter Grotrian and Bengt Edlén postulated instead that these spectra were from highly ionized known elements, particularly iron. Since the levels of ionization they proposed required temperatures in the millions of Kelvins, this idea was initially not accepted as those temperatures were far higher than the actual surface of the Sun. This disparity was thought impossible as the corona should be cooler than the Sun, given that it lacks any apparent heat source of its own. Later measurements of the corona's temperature by other means suggested this idea was correct. Why this apparent disparity exists, now called the coronal heating problem, is still not known for certain.[5][6]
Some theories suggest that interactions between the various atomic particles in the plasma of the corona could account for the extra heat. To test those theories, NASA decided that it would be useful to collect data from the corona itself. They then commissioned the Solar Probe Plus for a 2018 launch (which was later renamed the Parker Solar Probe (PSP), after Eugene Parker, who predicted the existence of the later-proven solar wind in the 1950s, the first time NASA had ever named a space mission after a then-living person[7][lower-alpha 1]). Following a gravity assist from Earth and Mars, it used further gravity assists from Venus to make ever-closer orbits to the Sun.[9]
Design
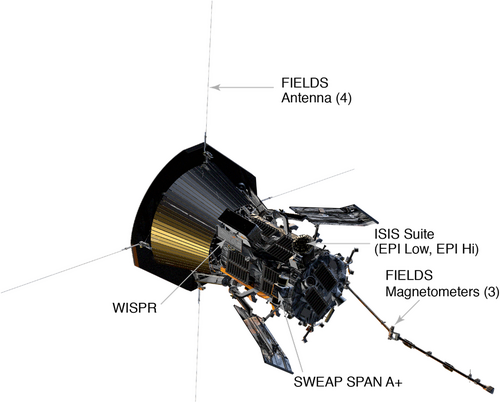
SWEAP consists of the Solar Probe Cup (SPC), a Faraday cup that faces the Sun and is designed to measure mostly protons and alphas with the occasional measurement of electrons in the space environment near the Sun: the Solar Probe Analyzers (SPAN-A and SPAN-B);[10][11] and the SWEAP electronics module (SWEM).
The Solar Probe Cup is a Sun-facing instrument directly exposed to the Sun, and it had to be designed to handle the high temperature conditions at 9-10 Solar radii from the Sun that are planned for the mission.[12] In operation, it peeks out from the probe’s Sun shield, and it is made entirely of refractory materials to endure these conditions. The hottest portion, the grid in front of the cup, can be heated to 3,000 °F (1,650 °C)[13] and is made of tungsten. The wiring connecting to the electronics is made of niobium with sapphire insulators.
SPAN-A and B are behind the heat shield, oriented forward ("ram side") and backward along the spacecraft's orbit, and take electron and ion measurements over a wide field of view.[14] SPAN-A measure ions and electrons and SPAN-B measures electrons.[15]
Summary:[16]
- Solar Probe Cup (SPC): Outside solar shield directly exposed to the Sun
- Solar Probe Analyzers (SPAN)
- SPAN-Ai: ion electrostatic analyzer (ESA) on the ram side
- SPAN-Ae: electron electrostatic analyzer on the ram side
- SPAN-B: electron electrostatic analyzer on the anti-ram side
- SWEAP Electronics Module (SWEM)
Operations
By September 2018, SWEAP had been turned on, and its first light data was returned.[17]
The data collected from the first and second encounters were released in November 2019 and are publicly available.[18]
Location
See also
- Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (also can measure ions, on the Juno Jupiter orbiter)
- JEDI (also can measure ions, on the Juno Jupiter orbiter)
- SWAP (New Horizons), measures the Solar Wind on the New Horizons mission to Pluto and beyond
- Other instruments on PSP
Notes
References
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.. "The SWEAP Investigation for Parker Solar Probe". https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/sweap/about_sweap.html.
- ↑ Brown, Geoffrey; Brown, Dwayne; Fox, Karen (12 August 2018). "Parker Solar Probe Launches on Historic Journey to Touch the Sun". Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. http://parkersolarprobe.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/Show-Article.php?articleID=94.
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.. "The SWEAP Investigation for Parker Solar Probe". https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/sweap/about_sweap.html.
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.; Abiad, Robert; Austin, Gerry; Balat-Pichelin, Marianne; Bale, Stuart D.; Belcher, John W.; Berg, Peter; Bergner, Henry et al. (2015-10-29). "Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) Investigation: Design of the Solar Wind and Coronal Plasma Instrument Suite for Solar Probe Plus" (in en). Space Science Reviews 204 (1–4): 131–186. doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0206-3. ISSN 0038-6308. Bibcode: 2016SSRv..204..131K.
- ↑ Klimchuk, James (September 6–9, 2004). "How Do We Solve the Coronal Heating Problem?". SOHO 15 Conference – Solar Heating. St Andrews, Scotland: European Space Agency. pp. 355. ESA SP-575. Bibcode: 2004ESASP.575....2K. https://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-iarticle_query?bibcode=2004ESASP.575....2K&db_key=AST&page_ind=0&data_type=GIF&type=SCREEN_VIEW&classic=YES.
- ↑ Cham, Jorge (December 14, 2021). "To Touch the Sun". Physics (American Physical Society) 14: 178. doi:10.1103/Physics.14.178. ISSN 1943-2879. OCLC 819219406. Bibcode: 2021PhyOJ..14..178.. https://physics.aps.org/articles/v14/178. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ↑ Chang, Kenneth (August 10, 2018). "NASA's Parker Solar Probe Is Named for Him. 60 Years Ago, No One Believed His Ideas About the Sun". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/10/science/eugene-parker-solar-wind-nasa-probe.html. "It is the Parker Solar Probe, named after Dr. Parker, now 91 years old. It is the first time that NASA has named a mission for a living person."
- ↑ Chang, Kenneth (March 17, 2022). "Eugene N. Parker, 94, Dies; Predicted the Existence of Solar Wind". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2022/03/17/science/space/eugene-n-parker-dead.html.
- ↑ Schirber, Michael (December 14, 2021). "How to Survive Flying Too Close to the Sun". Physics (American Physical Society) 14: 176. doi:10.1103/Physics.14.176. ISSN 1943-2879. OCLC 819219406. Bibcode: 2021PhyOJ..14..176S. https://physics.aps.org/articles/v14/176. Retrieved January 15, 2024.
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.. "The SWEAP Investigation for Parker Solar Probe". https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/sweap/about_sweap.html.
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.; Abiad, Robert; Austin, Gerry; Balat-Pichelin, Marianne; Bale, Stuart D.; Belcher, John W.; Berg, Peter; Bergner, Henry et al. (2015-10-29). "Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) Investigation: Design of the Solar Wind and Coronal Plasma Instrument Suite for Solar Probe Plus" (in en). Space Science Reviews 204 (1–4): 131–186. doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0206-3. ISSN 0038-6308. Bibcode: 2016SSRv..204..131K.
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.; Abiad, Robert; Austin, Gerry; Balat-Pichelin, Marianne; Bale, Stuart D.; Belcher, John W.; Berg, Peter; Bergner, Henry et al. (2016). "Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) Investigation: Design of the Solar Wind and Coronal Plasma Instrument Suite for Solar Probe Plus". Space Science Reviews 204 (1–4): 131–186. doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0206-3. Bibcode: 2016SSRv..204..131K.
- ↑ Garner, Rob (2018-07-12). "Parker Solar Probe Instruments" (in en). NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/parker-solar-probe-instruments.
- ↑ Garner, Rob (2018-07-12). "Parker Solar Probe Instruments" (in en). NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/parker-solar-probe-instruments.
- ↑ Garner, Rob (2018-07-12). "Parker Solar Probe Instruments" (in en). NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/parker-solar-probe-instruments.
- ↑ Kasper, Justin C.; Abiad, Robert; Austin, Gerry; Balat-Pichelin, Marianne; Bale, Stuart D.; Belcher, John W.; Berg, Peter; Bergner, Henry et al. (2015-10-29). "Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) Investigation: Design of the Solar Wind and Coronal Plasma Instrument Suite for Solar Probe Plus" (in en). Space Science Reviews 204 (1–4): 131–186. doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0206-3. ISSN 0038-6308. Bibcode: 2016SSRv..204..131K.
- ↑ "Illuminating First Light Data from Parker Solar Probe – Parker Solar Probe" (in en-US). 19 September 2018. https://blogs.nasa.gov/parkersolarprobe/2018/09/19/illuminating-first-light-data-from-parker-solar-probe/.
- ↑ "Data – The Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP)" (in en). http://sweap.cfa.harvard.edu/Data.html.
 |

