Balding–Nichols model
From HandWiki
Short description: Model in population genetics
|
Probability density function 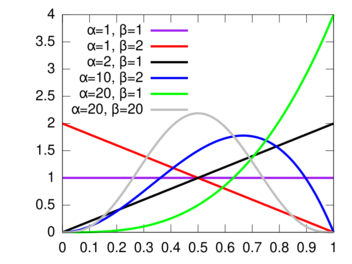 | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 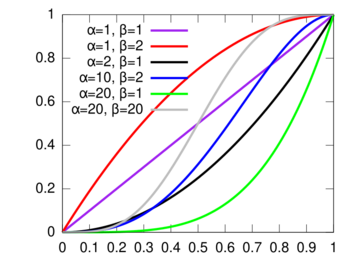 | |||
| Parameters |
[math]\displaystyle{ 0 \lt F \lt 1 }[/math](real) [math]\displaystyle{ 0\lt p \lt 1 }[/math] (real) For ease of notation, let [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha=\tfrac{1-F}{F}p }[/math], and [math]\displaystyle{ \beta=\tfrac{1-F}{F}(1-p) }[/math] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | [math]\displaystyle{ x \in (0; 1)\! }[/math] | ||
| [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{x^{\alpha-1}(1-x)^{\beta-1}} {\mathrm{B}(\alpha,\beta)}\! }[/math] | |||
| CDF | [math]\displaystyle{ I_x(\alpha,\beta)\! }[/math] | ||
| Mean | [math]\displaystyle{ p\! }[/math] | ||
| Median | [math]\displaystyle{ I_{0.5}^{-1}(\alpha,\beta) }[/math] no closed form | ||
| Mode | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{F-(1-F)p}{3F-1} }[/math] | ||
| Variance | [math]\displaystyle{ Fp(1-p)\! }[/math] | ||
| Skewness | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{2F(1-2p)}{(1+F)\sqrt{F(1-p)p}} }[/math] | ||
| MGF | [math]\displaystyle{ 1 +\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \left( \prod_{r=0}^{k-1} \frac{\alpha+r}{\frac{1-F}{F}+r}\right) \frac{t^k}{k!} }[/math] | ||
| CF | [math]\displaystyle{ {}_1F_1(\alpha; \alpha+\beta; i\,t)\! }[/math] | ||
In population genetics, the Balding–Nichols model is a statistical description of the allele frequencies in the components of a sub-divided population.[1] With background allele frequency p the allele frequencies, in sub-populations separated by Wright's FST F, are distributed according to independent draws from
- [math]\displaystyle{ B\left(\frac{1-F}{F}p,\frac{1-F}{F}(1-p)\right) }[/math]
where B is the Beta distribution. This distribution has mean p and variance Fp(1 – p).[2]
The model is due to David Balding and Richard Nichols and is widely used in the forensic analysis of DNA profiles and in population models for genetic epidemiology.
References
- ↑ Balding, DJ; Nichols, RA (1995). "A method for quantifying differentiation between populations at multi-allelic loci and its implications for investigating identity and paternity.". Genetica (Springer) 96 (1–2): 3–12. doi:10.1007/BF01441146. PMID 7607457.
- ↑ Alkes L. Price; Nick J. Patterson; Robert M. Plenge; Michael E. Weinblatt; Nancy A. Shadick; David Reich (2006). "Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies". Nature Genetics 38 (8): 904–909. doi:10.1038/ng1847. PMID 16862161. http://genepath.med.harvard.edu/~reich/Price%20et%20al.pdf. Retrieved 2009-02-19.
 |

