Biology:Ascocarp
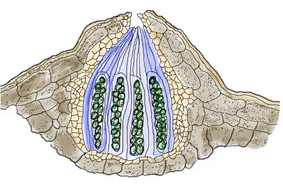
An ascocarp, or ascoma (pl.: ascomata), is the fruiting body (sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia).[1][2][better source needed]
Classification
The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called epigeous if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed hypogeous. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character is important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks of ground pepper.
Apothecium

An apothecium (plural: apothecia) is a wide, open, saucer-shaped or cup-shaped fruit body. It is sessile and fleshy. The structure of the apothecium chiefly consists of three parts: hymenium (upper concave surface), hypothecium, and excipulum (the "foot"). The asci are present in the hymenium layer. The asci are freely exposed at maturity. An example are the members of Dictyomycetes. Here the fertile layer is free, so that many spores can be dispersed simultaneously. The morel, Morchella, an edible ascocarp, not a mushroom, favored by gourmets, is a mass of apothecia fused together in a single large structure or cap. The genera Helvella and Gyromitra are similar.

Cleistothecium
A cleistothecium (plural: cleistothecia) is a globose, completely closed fruit body with no special opening to the outside. The ascomatal wall is called peridium and typically consists of densely interwoven hyphae or pseudoparenchyma cells. It may be covered with hyphal outgrowth called appendages. The asci are globose, deliquescent, and scattered throughout the interior cavity i.e. as in Eurotium or arising in tufts from the basal region of ascocarps as in Erysiphe. In this case the ascocarp is round with the hymenium enclosed, so the spores do not automatically get released, and fungi with cleistothecia have had to develop new strategies to disseminate their spores. The truffles, for instance, have solved this problem by attracting animals such as wild boars, which break open the tasty ascocarps and spread the spores over a wide area. Cleistothecia are found mostly in fungi that have little room available for their ascocarps, for instance those that live under tree bark, or underground like truffles.
Gymnothecium
Similar to a cleistothecium, a gymnothecium is a completely enclosed structure containing globose or pear-shaped, deliquescent asci. However, unlike the cleistothecium, the peridial wall of a gymnothecium consists of a loosely woven "tuft" of hyphae, often ornamented with elaborate coils or spines. Examples are the Gymnoascus, Talaromyces and the dermatophyte Arthroderma.
Perithecium

Perithecia are flask shaped structures opening by a pore or ostiole (short papilla opening by a circular pore) through which the ascospores escape. The ostiolar canal may be lined by hair-like structures called periphyses. The unitunicate asci are usually cylindrical in shape, borne on a stipe (stalk), released from a pore, developed from the inner wall of the perithecium and arise from a basal plectenchyma-centrum. Examples are members of Sphaeriales and Hypocreales. Perithecia are also found in Xylaria (Dead Man's Fingers, Candle Snuff), Nectria, Claviceps and Neurospora.
Sometimes the perithecia are "free" (individually visible from the outside), but in many species they are embedded in a dense sterile tissue of haploid cells called a stroma (plural: stromata).[3]
Pseudothecium
This is similar to a perithecium, but the asci are not regularly organised into a hymenium and they are bitunicate, having a double wall that expands when it takes up water and shoots the enclosed spores out suddenly to disperse them. Example species are Apple scab (Venturia inaequalis) and the horse chestnut disease Guignardia aesculi.
See also
References
- ↑ "ascocarp (fruiting structure of fungi)". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/37968/ascocarp. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ↑ "Atlas of Clinical Fungi (glossary)". Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute. http://www.clinicalfungi.org/Biolomics.aspx?Table=Glossary&Genlist=t.
- ↑ See page 30 and glossary of Læssøe, H.; Petersen, Jens (2019). Fungi of Temperate Europe. Princeton University Press. p. 30. ISBN 9780691180373.
de:Schlauchpilze#Das Ascokarp
 |