Biology:Giant wren
| Giant wren | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Troglodytidae |
| Genus: | Campylorhynchus |
| Species: | C. chiapensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Campylorhynchus chiapensis Salvin & Godman, 1891
| |
| |
The giant wren (Campylorhynchus chiapensis) is a species of bird in the family Troglodytidae. It is found in Mexico and Guatemala.[1][2]
Taxonomy and systematics
The giant wren is monotypic. Though birds in the northern part of its range are larger, the difference is too small to assign geographical subspecies.[2]
It has sometimes been treated as a subspecies of bicolored wren (Campylorhynchus griseus) and may form a superspecies with it.[3]
Description
As implied by its name, the giant wren is the largest member of its family. It is 20 to 22 cm (7.9 to 8.7 in) long and weighs 43.4 to 57 g (1.53 to 2.01 oz). The sexes are similar. Adults have a black crown, nape, and shoulders. A white supercilium separates a black stripe through the eye from the crown and the rest of the face is also white. Their upperparts are bright chestnut and the tail dark chestnut; all of the tail feathers except the middle pair have a white band near the end. Their underparts from the chin to the belly are white; the belly and vent area are buff. Juveniles are similar to the adults but their underparts are whitish, not pure white.[2]
Distribution and habitat
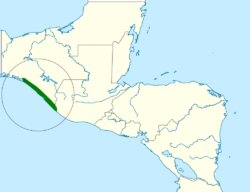
The giant wren was formerly considered endemic to Mexico's Chiapas state, from Puerto Arista south to near the Guatemalan border. However, since approximately 2010 there have been many sightings in far northwestern Guatemala. It inhabits bushland including areas much modified by humans such as farmyards, hedgerows, and fruit orchards. It occurs only within 50 km (31 mi) of the coast and from sea level to 300 m (980 ft) of elevation.[2]
Behavior
Feeding
The giant wren's diet has not been documented but it is probably mostly invertebrates. It forages on or near the ground.[2]
Breeding
The giant wren's breeding season is May through July. It possibly double-broods and there is evidence of helpers at the nest. The nest is a bulky ball with a side entrance, constructed of straw and other coarse fiber and often placed in an acacia tree. The only recorded clutch had three eggs.[2]
Vocalization
Giant wren pairs sing in unison, "rhythmic hollow phrases, chortling and rollicking" [1]. Its calls are "grating and harsh churring" [2].[2]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the giant wren as being of Least Concern. Its population apparently exceeds 20,000 and "is suspected to be stable in the absence of evidence for any declines or substantial threats."[4]
References
- ↑ Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (January 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.1)". https://www.worldbirdnames.org/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Kroodsma, D. E. and D. Brewer (2020). Giant Wren (Campylorhynchus chiapensis), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.giawre1.01 retrieved May 31, 2021
- ↑ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 23 May 2021. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved May 24, 2021
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedIUCN
Further reading
- Skutch, Alexander F. (1960). "Chiapas wren". Life Histories of Central American Birds II. Pacific Coast Avifauna, Number 34. Berkeley, California: Cooper Ornithological Society. pp. 183–185. https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/pca/pca_034.pdf#page=184.
Wikidata ☰ Q3114777 entry
 |


