Biology:Naultinus
| Naultinus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Northland green gecko (Naultinus grayii) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Diplodactylidae |
| Genus: | Naultinus Gray, 1842 |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
| |
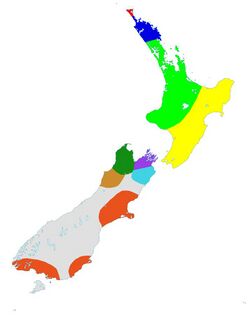
| Naultinus range species indicated
| |
Naultinus is a genus of geckos that are endemic to New Zealand.[1] On account of their striking colouration, species in the genus Naultinus are commonly known as green geckos. There are nine described species in the genus.[2] Species in the genus share a number of traits that set them apart as quite different from the rest of the world's two thousand odd gecko species, which are generally brown in colour, ovivaparous, short-lived and nocturnal. In contrast, Naultinus are green (with the exceptions of males in two South Island species which exhibit sexual dimorphism in colouration), ovovivaparous, live up to 30 years or more and are strictly diurnal. New Zealand has a temperate, maritime climate, and in terms of distribution Naultinus is one of the southernmost gecko genera in the world — some species live in habitats in the South Island which receive regular snowfall in winter. Animals in this genus possess several physiological and behavioural adaptations to cope with these periods of low temperatures and adverse weather.
While historically widespread and quite common in areas of native forest all over the country, all species in this genus are of conservation concern in the present day. All nine species of Naultinus are declining in the wild and are much harder to find than they used to be; the populations of the various species are highly fragmented and approaching extinction, while others in the genus have already gone extinct. Entire populations of certain species, with unique traits and distinctive genetic profiles, have disappeared in the last 20 years. The primary known agents of this catastrophic decline include predation by invasive mammalian and avian species, habitat destruction and poaching for the illegal pet trade. Vespid wasp predation is speculated to be another possible contributing cause. Legal protection in the form of longer prison sentences for poachers caught with New Zealand protected species has been increased in recent years and translocations of various species to pest free islands have been undertaken with mixed results, but the task of saving these animals remains daunting. The behavioural and visually cryptic nature of these animals also pose challenges to their conservation management. The genus is, in general, in "dire need of research, particularly into factors that are causing their apparent decline", certain aspects of which remain unexplained.[3]
Taxonomy
The following nine described species are recognized as being valid.[4] A binomial authority in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than Naultinus.
- Naultinus elegans Gray, 1842 – Auckland green gecko
- Naultinus flavirictus Hitchough, Nielsen, Lysaght, & Bauer, 2021 – Aupouri green gecko, North Cape green gecko, yellow-lipped green gecko[5][6]
- Naultinus gemmeus (McCann, 1955) – jewelled gecko
- Naultinus grayii Bell, 1843 – Northland green gecko, Gray's tree gecko
- Naultinus manukanus (McCann, 1955) – Marlborough green gecko, northern tree gecko
- Naultinus punctatus Gray, 1843 – Wellington green gecko
- Naultinus rudis (Fischer, 1881) – rough gecko, natural tree gecko
- Naultinus stellatus Hutton, 1872 – Nelson green gecko, starry tree gecko
- Naultinus tuberculatus (McCann, 1955) – West Coast green gecko,[7] Lewis Pass green gecko
Defining what constitutes a species among different populations within this genus has proved difficult and is still a matter of some scientific debate. Genetic evidence suggests that all nine species share an ancestor which is "very recent" in deep time terms and that hybridization between them is quite common. All species will interbreed in the wild, which has led some biologists to reject the notion of multiple Naultinus species and to instead view each "species" as a separate "race" or subspecies of a single, very widespread species of this genus. However, there are many clear differences between recognized species in colouration, breeding times and even scale morphology. Many neighbouring species have slightly different mating seasons and behaviour, which is thought to explain why the species maintain their differences despite "strong reproductive compatibility". These differences are the basis for the present consensus in the scientific community that Nautilnus is constituted of nine species instead of nine races of a single species.[3]
Genetically speaking, the jewelled gecko (N. gemmeus) of the southern South Island is the most genetically distinct of the recognized species. In fact, it is thought that this species is the one that is ancestral to all other species in the genus.[8] There are three distinct populations of N. gemmeus in Southland, Otago and Canterbury, differentiated by coloration and the time of their breeding seasons.[2] In addition to recognizing gemmeus as one of a number of separate species within the genus, some biologists[who?] think that the three different populations of this species should be elevated to subspecies status to place more emphasis on their conservation management.[8]
Description
Naultinus species are commonly known as "green geckos" in New Zealand for their striking bright green colouration. In addition, they are diurnal, which allows them to take advantage of warmer day-time temperatures.[2] Both of these features are shared only with the day geckos (Phelsuma) of Madagascar . Almost every other type of gecko in the world is nocturnal and brown or grey in colour.[2] All Naultinus are arboreal, and though most of them are predominantly green, their skin patterns are known to be plain (N. manukanus, N. punctatus), spotted (N. elegans, N. flavirictus, N. gemmeus, N. grayii, N. punctatus, N. rudis, N. stellatus, N. tuberculatus), or striped (N. gemmeus). Occasionally, individuals of an overall lemon-yellow colour are encountered; this is a rare genetic colour morph similar to albinism.[citation needed] The distinctive green colouration is almost universally predominant; with the two exceptions of male N. rudis as well as males of some populations of the Canterbury form of N. gemmeus, which are sexually dichromatic.[9] While females are green, the males of N. rudis are grey with white and brown splotches, and in Canterbury, N. gemmeus females are always predominantly green as compared to the grey, brown or white males.[9] The inside of the mouth, which is revealed in a threat display in some species, is deep blue, orange, pink or red.[3] The broad fleshy tongue, which has a major function in cleaning the transparent scales which cover the eyes, is also brightly coloured; depending on the species it is red, orange, pink, yellow or black.[3] The ears of New Zealand geckos appear as small openings on the side of the head behind the eyes, and the eardrum is visible a short distance inside this opening.[9]

Naultinus species and indeed, New Zealand lizards in general, are very conservative in their evolutionary development of scales.[2] Most have the standard gecko-type scales which are small and granular, giving the skin a dull, velvety appearance. The two exceptions to this rule are two South Island members of the genus; the rough gecko (N. rudis) and, to a lesser extent, the Marlborough green gecko (N. manukanus). The rough gecko has enlarged conical scales which are both significantly wider and which protrude much further from the body than ordinary scales. These enlarged scales are scattered all over the body except for the underside of the animal.[10] The Marlborough green gecko also has enlarged scales, but they are confined to the dorsal, pelvic area, and sometimes even in rows along the side of the animal. In any case, they are never found over all upper surfaces of the body as in the rough gecko.[10]
All Naultinus species also possess very long, finely tapered, strongly prehensile tails which they use as a "fifth limb" for grasping when they climb among the twigs and leaves of their arboreal habitat.[11] They can hang by their tails if necessary.[10] They also have comparatively slender toes, another adaptation to their arboreal lifestyle.[10] The arboreal Naultinus use their toes in a grasping action on twigs and leaves, but there is some lamellar function as well.[9]
Summary table of the key differences between Naultinus and Hoplodactylus
There are many key differences in physiology and behaviour between species of NZ gecko in the two endemic genera, summarised in the table below:[10][12]
| Hoplodactylus | Naultinus |
|---|---|
| Mainly grey-brown | Mainly green |
| Nocturnal | Diurnal |
| Terrestrial, sometimes on tree trunks | Arboreal, on foliage |
| Active-prey-searching | Sit-and-wait predator |
| Generally fast-moving | Generally slow-moving |
| Can change intensity of skin colour | Skin colour intensity cannot be changed |
| Wide, non-prehensile tails, readily shed | Narrow, tapering prehensile tails, reluctantly shed |
| Some have wider toe pads with claws, adapted for climbing smooth, vertical surfaces | Thin toe pads adapted for grasping twigs and foliage |
Distribution and habitat
The nine described species of Naultinus are found throughout the North and South islands of New Zealand and on a number of offshore islands. Historically, Naultinus species lived throughout the length of New Zealand, from the coast to as much as 1400 metres above sea level. However, all species have now undergone massive declines, and populations nationwide are fragmented and few (see "Conservation") Four species; elegans, grayii, flavirictus and punctatus are found only in the North Island.[10] What was previously thought to be a distinct population of grayii, found only in the far north on the Aupōuri Peninsula has been determined from genetic work in the early 2000s to be a new species, more closely related, in fact, to elegans.[2] It was described as N. flavirictus in 2021. The remaining five species: gemmeus, manukanus, rudis, stellatus, and tuberculatus are found only in the South Island.[10] South Island Naultinus were, in the past, placed in a separate genus called Heteropholis but this taxon was abandoned when new genetic research in the 1980s showed little phylogenetic basis for this taxonomic division.[11]
None of the Naultinus gecko populations are sympatric, presumably because each species is very finely adapted to its local environment and also because their respective ecological niches are incredibly similar.[13]
Behaviour and ecology
Activity patterns and diet
Most of the world's two thousand-odd species of geckos are active by night (nocturnal) whereas all species of Naultinus are active by day (diurnal).[3] Unlike their close relatives in the genus Hoplodactylus, Naultinus species lack the ability to alter their skin color.[10] These geckos are omnivores. Diet for members of this genus consists of flying insects such as moths and flies[11] but also of flightless invertebrates such as amphipods and spiders.[9] All New Zealand geckos will supplement their primarily insectivorous diet and consume nectar and berries (the small purple fruits of Māhoe for example) and there is evidence that, in doing so, they may have a function in New Zealand ecosystems as pollinators and seed dispersers for certain species of native plant.[9] In captivity they will thrive on a simple diet of moths and flies caught in traps.
Predators and parasites
New Zealand geckos have very few natural predators;[9] although several species of native bird will take them as prey only the sacred kingfisher kills very many.[9] The Tuatara, a large, ground dwelling, generalist predator, will feed on native geckos, including Naultinus, where the two occur together on a few predator-free offshore islands.[9] All New Zealand geckos, including Naultinus (but particularly Hoplodactylus species) carry small orange-red skin mites which gather around the eyes, the base of limbs, ear openings and skin folds.[11] These mites, while essentially harmless, do suck small amounts of blood from their hosts, in time becoming quite swollen and taking on their characteristically vivid colouration as a result.[11]
Thermoregulation
As ectotherms, Naultinus geckos will move to positions of higher or lower temperature in order to thermoregulate. Because Naultinus spend most of their time on the top of plant foliage, they gain much of their heat directly from the sun.[9] Thus, control of the upper limits of temperature is achieved by moving from the outside of the foliage in areas of direct sunlight, to shaded areas beneath the outside of the vegetation.[9] Control of the lower limits of temperature involves more movement for the animals. Because New Zealand has a temperate climate, Naultinus geckos live in areas which are at times (particularly in winter) exposed to very cold temperatures and high levels of rainfall. In such adverse weather animals will descend from an arboreal position in vegetation and seek shelter on the ground in and around the base of these same plants or under rocks and other debris, where they are insulated to some degree against the cold air of the atmosphere.[3] Because external temperatures essentially dictate rates of metabolism in ectotherms, the amount of food that these geckos will consume varies depending on the temperature and weather;[9] they will feed frequently in spring and summer and much less in the colder seasons of autumn and winter.
Defensive behaviour in North Island Naultinus
The four species of North Island Naultinus exhibit, to varying degrees, defensive behaviours which involve "gaping" to reveal the vivid coloration of the interior of their mouthes - bright red in flavirictus and deep blue in grayi, elegans and punctatus -[2] and, in some cases, aggressive lunges and a strange sort of vocalization which has been described as a "barking sound".[8] These behaviours are an adaptation to startle and scare off potential predators and so to prevent the lizards from being eaten and have even been observed by people working against quite large mammalian predators such as the domestic cat.[14] All four North Island Naultinus species will exhibit "gaping" behaviour when threatened but in addition grayi and punctatus will lunge aggressively at the potential predator in question, often barking as they do so.[2] One source suggests that this pugnacious beahviour is more a function of protection for an adult's young, as they are only said to exhibit this behaviour in the presence of juveniles – the source saying that, by contrast, "in the absence of young individuals (they) are usually very docile and easy to handle".[11] Like all New Zealand lizards, Naultinus species will shed their tails to escape from predators but because they are prehensile and used for grasping as they climb, they are much more reluctant to shed them than their close relatives in genus Hoplodactylus.[10]
Reproduction and life history
While most species of geckos in other parts of the world live for just a few years, Naultinus are very long lived in comparison - they have been known to live for 30 years or more[3] All New Zealand geckos and indeed, all New Zealand lizards – except one species of skink – are viviparous, which is in contrast to most of the world geckos which are oviparous.[2] Females will actively move from areas of higher or lower temperature to thermoregulate, in order to provide optimal temperatures for the development of their young inside them.[2] The young of all species are born a rich, velvety green, often with a series of markings on either side of the spine which can be white, yellow or tan.[11] The colouration changes to the normal pattern and colour of the adult at 15–18 months, around the time that young animals move out of their parental territories to set up territories of their own.[11] One explanation postulated for this is that; " the function is recognition of juveniles by adults, it ensures that there is no danger of very young males being attacked or driven away from the family group by territorially minded adult males".[11] Gestation period in New Zealand geckos is variable but observations of animals in captivity suggest that it is usually a relatively long process, usually around 8–9 months -[9] similar to that of humans.
Naultinus and humans
In culture
Reptiles in New Zealand were well known to Māori in pre-European times and featured in many carvings,[9] some of which obviously depict tuatara and others which depict lizards.[9] The body shape of many examples suggests that they are geckos, though skinks also seem to be depicted.[9] With the exception of the Tuatara, which was frequently eaten, lizards were regarded with abhorrence by Māori and Naultinus in particular; sightings of Naultinus were regarded as bad omens.[9]
As pets
Naultinus can legally be kept in captivity as pets in New Zealand, provided one has an appropriate permit from DOC and hundreds are kept in private collections all over the country.[15] Elegans, grayii and punctatus can all be kept on an "A permit", which is the entry level license given to new keepers, while the remaining species in the genus require a "B permit" for which several years experience keeping geckos is required. In the past, animals could be collected from the wild to add to captive collections and this is how people typically used to enter the hobby;[9] this changed in 1981 when all species of native gecko were granted legal protection,[9] with the exception of two species of Hoplodactylus, the forest gecko (Hoplodactylus ganulatus) and common gecko (Hoplodactylus maculatus) - these two species were later also granted full protection in 1996.[9] These days, keepers must obtain their founder stock from an existing, licensed breeder and animals can only be given away or swapped; sale of any sort of native lizard commercially is illegal. A condition for granting an "A permit" is an inspection by DOC to ensure adequate quality of caging is provided and detailed records of changes in a collection must be kept;[9] recording births, deaths, escapes and animals exchanged, received or given away, in annual forms submitted to DOC, are all legal requirement of the permit.[9] Many Naultinus keepers are members of The New Zealand Herpetological Society, which acts as a community hub for New Zealand Herpetoculturalists. Naultinus in private collections are often seletively bred for certain colours and patterns of colouration.[9] DOC has in recent years begun sourcing Naultinus (particularly punctatus) for reintroductions to predator-free offshore islands from private collections, on the condition that the animals are in good health and of pure genetic origin (i.e.: they haven't hybridized with other species).[16]
Naultinus are also kept in captivity by enthusiasts in overseas countries but it should be stressed that trade is incredibly difficult, and one must obtain adequate CITES permits for importation and exportation. This process is regulated by the CITES Management Authority, which ascertains whether or not founding stock were obtained by a keeper in a particular country prior to 1981. This is often quite difficult, and usually prohibitive of international trade between Europe (where most stock resides outside of New Zealand) and other countries.
Threats and decline
Collectively, the species of genus Naultinus have a very wide range over most of New Zealand's land area and yet all of them are now increasingly rare and hard to find.[8] This is in stark contrast to anecdotal reports among NZ herpetoculturalists who found them abundant in suitable habitat (such as regenerating bush in the Marlborough Sounds) in the 1960s from which they have now all but vanished. The three major factors thought to be responsible for this decline are; habitat destruction, predation by introduced mammalian species and poaching for the illegal pet trade.
Barking geckos were common in shrublands all around the Wellington region up until the 1960s and 1970s[3] but populations have declined enormously since then.[3] DOC has tried to establish populations of this species on Mana Island but there are so few animals left in wild populations in the region that they have had to resort to transferring animals taken either from the jaws of pet cats or captive bred animals from private collections.[3] Both the Naultinus released on Mana and a natural population on Kapiti Island have failed to thrive, which is mysterious, because these habitats are rodent free.[3] One suggested cause about which little research has been done is vespid wasp predation, as these insects have been observed killing both adult and baby Naultinus.[3] Naultinus gemmeus are known from the mainland of Southland from a few sightings by members of the public[3] but despite numerous searches in recent years, not a single animal has been sighted or photographed here and it is speculated that this population is either critically endangered or already functionally extinct.[3]
Predation by invasive species
Naultinus are preyed on by a number of invasive mammalian species including cats, rodents (3 species of rat and the house mouse) and mustelids. While the larger predators such as stoats and cats are the normal focus of pest control efforts in New Zealand, it is thought that the effect that smaller predators such as mice and weasels may be just as great or even worse.[3] After the removal of mice from Mana Island in the '90s, lizard numbers increased massively – demonstrating that mouse predation does serious harm to native reptile populations.[3] Mice can squeeze into much smaller hiding places to take lizards as prey and they also forage year round, no matter how cold it gets -[3] this is significant because below 5 degrees Celsius lizards become torpid and can't defend themselves against attack. This would mean that Naultinus sheltering from cold weather on the ground at the base of plants or underneath debris would be particularly vulnerable to mouse predation.[3] In addition to being preyed on by certain species of invasive mammals, Naultinus are also preyed on by introduced bird species - mynas have been observed plucking Naultinus from the forest canopy in parts of Northland[3] and magpies have been observed searching scrub canopies in a similar fashion at known Naultinus sites in the South Island.[3]
Habitat destruction
Habitat destruction by the encroachment of suburban areas into forested Naultinus habitat both directly destroys the ecosystems in which the animals live, as well as also facilitating further decline by increasing the size of local cat and rodent populations.[3] A unique population of Naultinus gemmeus near Hakatarema Pass, east of Twizel which displayed unusual colouration and a distinctive genetic profile was entirely destroyed when its forest habitat was cleared by a bulldozer for urban development.[3]
Poaching
New Zealand's Naultinus are highly prized by international lizard collectors for three main reasons; firstly they have very attractive colouration and indeed, have been referred to by some as "the world's most beautiful geckos". Secondly, they are day active and so are out and about when their keepers are awake[8] and thirdly, they are cold tolerant, coming from New Zealand's strongly seasonal temperate habitats – since most collectors are wealthy hobbyists in developed countries in places like North America, Europe and Japan – also temperate areas – this means they do not require heat lamps when kept in terrariums.[8] All this adds up to strong demand for these animals on the black market for the illegal pet trade – "dozens of these protected reptiles are poached from the wild each year, when even low-level poaching could mean the difference between survival and extinction for small, isolated populations".[8] All endemic New Zealand lizard species including all species of Naultinus are protected by law both under the New Zealand Wildlife Act 1953[17] and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES). In an effort to clamp down on continual poaching, DOC attempted to get tighter controls placed on trade in Naultinus in 2002 under the CITES agreement but the request was denied,[8] however, fines and periods of imprisonment under the Wildlife Act 1953 and Trade in Endangered Species Act 1989 were increased in 2004 in an attempt to deter further illegal collecting and trading of these animals.[8]
In early 2010 a Mexican man and a Swiss national with US citizenship were caught in Christchurch airport attempting to smuggle 16 Naultinus gemmeus out of the country. They were jailed for 15 weeks – not enough to have them banned from ever returning to NZ –something that DOC are investigating changing for future cases.[18] The Judge for the case, Judge Raoul Neave commented that "a significant increase in the sentencing could be desirable" in such cases.[18] Naultinus have also been illegally taken/stolen from wildlife parks in the past; one rudis and two grayi were stolen from Orana Wildlife Park in 2006 though they were later found, unharmed, by police; their captors, two local New Zealand citizens, were arrested and charged.[19]
Conservation
There is a critical lack of scientific research that has been done on Naultinus species and this fact, combined with the behaviourally and visually cryptic nature of the genus pose major challenges to their conservation management.[20] For many Naultinus species, (examples include grayii,stellatus and rudis) there is a complete lack of accurate data in key areas such as distribution, abundance and recruitment rate (primarily because they are visually and behaviourally cryptic)- these types of information are critical to developing conservation management plans and make the conservation status of these species very difficult to determine;[8] Some species have not had a single scientific study carried out on them, simply because they are so hard to find. The behaviourally cryptic aspect relates to the previously described behaviour whereby Naultinus will descend to ground level to hide in vegetation and shelter from cold and poor weather conditions; whole populations will appear to vanish and no amount of searching will turn them up,[3] only for them to "reappear" when the weather improves.[3] These "disappearing acts" have meant that the local extinction of many Naultinus populations has been overlooked because they were temporarily dismissed as simply being hard to find while sheltering from bad weather.[3]
Searches for Naultinus are often inconclusive because the animals simply avoid detection.[3] Improved detection methods would allow scientists to monitor populations much more accurately and a number of different studies in recent years have been doing research into this area – some key ideas are a new type of cover mounted on trees for animals to hide in, pheremone lures and even terriers trained to pick up on the scent of native geckos. Naultinus have been reintroduced to some predator free areas and are present at other locations where their habitat is protected and where pest control is being carried out but because Naultinus have a very slow breeding rate, recovery of populations is inevitably a relatively slow and gradual process.[9]
References
- ↑ Van Winkel, Dylan (April 2019). Reptiles and amphibians of New Zealand : a field guide. Baling, Marleen,, Hitchmough, Rod. Auckland, New Zealand. ISBN 978-1-86940-937-1. OCLC 1048295078. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1048295078.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 Jewell, Tony (2008). Reptiles and Amphibians of New Zealand. Photographs by Rod Morris. New Holland Publishers. ISBN 978-1-86966-203-5.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 3.17 3.18 3.19 3.20 3.21 3.22 3.23 3.24 3.25 Jewell, Tony (November 2008). "Vanishing Geckos". Forest and Bird Magazine (330).
- ↑ "Naultinus ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org.
- ↑ Hitchmough, Rodney A.; Nielsen, Stuart V.; Lysaght, Judith A.; Bauer, Aaron M. (2021-01-22). "A new species of Naultinus from the Te Paki area, northern New Zealand" (in en). Zootaxa 4915 (3): 389–400. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4915.3.7. ISSN 1175-5334. PMID 33756565. https://www.mapress.com/j/zt/article/view/zootaxa.4915.3.7.
- ↑ "Naultinus 'North Cape' | NZHS". https://www.reptiles.org.nz/herpetofauna/native/naultinus-north-cape.
- ↑ "JCVI.org". http://jcvi.org/reptiles/search.php?submit=Search&exact%5B%5D=genus&genus=Naultinus.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 Rod Morris and Allison Ballance, Rare Wildlife of New Zealand, Random House, 2008
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 9.17 9.18 9.19 9.20 9.21 9.22 9.23 R. P. V. Rowlands,New Zealand Geckos: A Guide to Captive Maintenance and Breeding (rev. ed.), Ecoprint, 1999
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 10.8 Brian Gill and Tony Whitaker, New Zealand Frogs and Reptiles, David Bateman Pubg., 1996
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 Joan Robb, New Zealand Amphibians and Reptiles, Collins, 1980
- ↑ Gibbs, George (2006). Ghosts of Gondwana; the History of Life in New Zealand. Craig Potton Publishing.
- ↑ Rob Hitchmough- Threatened species science section, DOC, (August 2006)
- ↑ "Gecko's Bark Throws Moggy", Simon Edwards, The Hutt News, 24 May 2005
- ↑ David Wilkinson, "Analysis of Annual Returns for the 2003 Calendar Year", MOKO: Newsletter of the New Zealand Herpetological Society, February 2005
- ↑ Ngaire Jury and Heather Barton,'"Release to Mana", MOKO: Newsletter of the New Zealand Herpetological Society, June 2005
- ↑ Bruce Hudson, illustrated by TJ Thornton, "Reptiles and Amphibians in New Zealand - Handbook for species identification", Print media specialists, 1994
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "Smugglers of Wildlife face Prison", Keith Lynch, The Press, 30 March 2010
- ↑ "Stolen Geckos Found as Police Raid Home", Jarrod Booker, New Zealand Herald, 13 April 2006
- ↑ Kelly M. Hare, Joanne M. Hoare, Rodney A. Hitchmough, "Investigating Natural Population Dynamics of Naultinus Manukanus to Inform Conservation Management of New Zealand's Cryptic Diurnal Geckos", Journal of Herpetology 41(1):81-93. 2007
Further reading
- Gill, Brian; Whitaker, Tony. 1996. New Zealand Frogs and Reptiles. Glenfield, New Zealand: David Bateman Ltd. 112 pp. ISBN 978-1869532642.
- Gray, J.E. 1842. "Descriptions of two hitherto unrecorded species of Reptiles from New Zealand; presented to the British Museum by Dr. Dieffenbach". Zoological Miscellany 2: 72. (Naultinus, new genus).
- Rowlands, Rodney Peter Victor. 2011. New Zealand Geckos: A Guide to Captive Maintenance and Breeding. Auckland, New Zealand: EcoPrint. 60 pp. ISBN 978-0473103293 (2005 edition).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Naultinus. |
Wikidata ☰ Q1552227 entry
 |
