Biology:Nephilidae
| Nephilidae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Female Nephila pilipes | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Animalia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Arthropoda |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Chelicerata |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Arachnida |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Araneae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Araneomorphae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Araneoidea |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Nephilidae Simon, 1894 |
| Genera | |
|
See text. | |
| Diversity | |
| 7 genera | |
| |
Nephilidae is a spider family commonly referred to as golden orb-weavers.[1] The various genera in Nephilidae were formerly placed in Tetragnathidae and Araneidae. All nephilid genera partially renew their webs.[2]
Reproductive behavior
The genera Herennia, Nephilengys and Nephilingis display extreme sexually driven selection. The pedipalps of these genera have become highly derived by evolving enlarged, complex palpal bulbs which break off inside the females' copulatory openings after copulation. The broken palps serve as mating plugs, which makes future matings with a mated female more difficult.[3] These genera of spiders also participate in mate guarding; a mated male will stand guard by his female and chase off other males, thereby increasing the mated male's paternity share. Mated males are castrated in the process of mate plugging, though this may be an advantage in mate guarding, as mated males have been observed to fight more aggressively and win more frequently than virgin males.[4] So while the female spiders are still at least potentially polygamous, the males have become monogamous.
Taxonomy
Up to the late 1980s, following Eugène Simon in 1894, Nephila and its close relatives were considered to make up the subfamily Nephilinae of the family Araneidae. In 1986, Herbert Walter Levi suggested that Nephila and Nephilengys belonged in the family Tetragnathidae, based on the structure of the male palp. Cladistic studies in the 1990s appeared to confirm the relationship between nephilines and Tetragnathidae. Further studies refuted this proposal, but did not resolve the relationship with araneids. In 2006, Matjaž Kuntner removed the group from Araneidae and raised the subfamily Nephilinae to the family Nephilidae. However, molecular phylogenetic studies from 2004 onwards consistently placed nephilids within Araneidae. Accordingly, in 2016, Dimitar Dimitrov et al. returned the group to their traditional position as a subfamily of Araneidae.[5] In 2023, the subfamily was resurrected back to family-level and is recognized as a family in the World Spider Catalog.[6][7]
Phylogeny
A 2013 molecular phylogenetic study suggested the genera of Nephilinae were related as shown in the cladogram below. It was this study that supported the split between Nephilengys and Nephilingis.[8]
| Nephilinae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Although Nephila appears not to be monophyletic, the authors of the study did not suggest splitting the genus. The phylogeny suggests that male enforced monogamy, via plugging of the female copulatory ducts by males leaving behind their palpal bulbs, is ancestral to the nephilides, and was lost in Nephila and Clitaetra.[8]
Genera
As of August 2023[update], the World Spider Catalog accepts the following genera:[7]
- Clitaetra Simon, 1889 – Africa, Madagascar, Sri Lanka
- Herennia Thorell, 1877 – South Asia, Australia
- Indoetra (previously a subgenus of Clitaetra) Kuntner, 2006 – Sri Lanka
- Nephila Leach, 1815 – pantropical
- Nephilengys L. Koch, 1872 – South Asia to north Australia
- Nephilingis Kuntner, 2013 – tropical South America and Africa
- Trichonephila (previously a subgenus of Nephila) Dahl, 1911 – pantropical
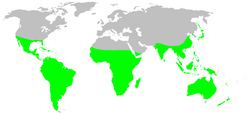
Distribution
The family has a pan-tropical distribution: species of Nephilia, in particular, are found in tropical and subtropical environments in the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Australia.
See also
References
- ↑ Kuntner, Matjaž; Hamilton, Chris A; Cheng, Ren-Chung; Gregorič, Matjaž; Lupše, Nik; Lokovšek, Tjaša; Lemmon, Emily Moriarty; Lemmon, Alan R et al. (July 2019). "Golden Orbweavers Ignore Biological Rules: Phylogenomic and Comparative Analyses Unravel a Complex Evolution of Sexual Size Dimorphism". Systematic Biology 68 (4): 555–572. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syy082. PMID 30517732.
- ↑ Kuntner, Matjaž (2005). "A revision of Herennia (Araneae : Nephilidae : Nephilinae), the Australasian 'coin spiders'". Invertebrate Systematics (CSIRO Publishing) 19 (5): 391–436. doi:10.1071/IS05024.
- ↑ Kuntner, Matjaž; Coddington, Jonathan A.; Schneider, Jutta M. (2009). "Intersexual arms race? Genital coevolution in nephilid spiders (Araneae, Nephilidae)". Evolution 63 (6): 1451–1463. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2009.00634.x. PMID 19492993.
- ↑ Fromhage, Lutz; Schneider, Jutta M. (2005). "Virgin doves and mated hawks: contest behaviour in a spider". Animal Behaviour 70 (5): 1099–1104. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2005.02.020.
- ↑ Dimitrov, Dimitar; Benavides, Ligia R.; Arnedo, Miquel A.; Giribet, Gonzalo; Griswold, Charles E.; Scharff, Nikolaj; Hormiga, Gustavo (2016). "Rounding up the usual suspects: a standard target-gene approach for resolving the interfamilial phylogenetic relationships of ecribellate orb-weaving spiders with a new family-rank classification (Araneae, Araneoidea)". Cladistics 33 (3): 221–250. doi:10.1111/cla.12165. http://macroecointern.dk/pdf-reprints/Dimitrov_Cladistics_2016.pdf. Retrieved 2016-10-18.
- ↑ Kuntner, Matjaž; Čandek, Klemen; Gregorič, Matjaž; Turk, Eva; Hamilton, Chris A.; Chamberland, Lisa; Starrett, James; Cheng, Ren-Chung et al. (2023). "Increasing Information Content and Diagnosability in Family-Level Classifications". Systematic Biology 72 (4): 964–971. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syad021. https://academic.oup.com/sysbio/article/72/4/964/7158815.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Family: Nephilidae Banks, 1892". Natural History Museum Bern. http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/family/62.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Kuntner, M.; Arnedo, M.A.; Trontelj, P.; Lokovsek, T.; Agnarsson, I. (2013). "A molecular phylogeny of nephilid spiders: evolutionary history of a model lineage". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 69 (3): 961–979. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2013.06.008. PMID 23811436.
Further reading
- Kuntner, M (2006). "Phylogenetic systematics of the Gondwanan nephilid spider lineage Clitaetrinae (Araneae, Nephilidae)". Zoologica Scripta 35 (1): 19–62. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.2006.00220.x. http://www.nephilidae.com/mk/articles/Kuntner2006Clitaetrinae.pdf.
- Agnarsson, I (2003a). "Spider webs as habitat patches - The distribution of kleptoparasites (Argyrodes, Theridiidae) among host webs (Nephila, Tetragnathidae)". Journal of Arachnology 31 (3): 344–349. doi:10.1636/s02-21. http://www.gwu.edu/~spiders/content/publications/Agnarsson%202003a.pdf.
- Nephila of Southern Africa
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q10670 entry
 |
