Biology:Percomorpha
| Percomorpha | |
|---|---|
| |
| Rose fish | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Superorder: | Acanthopterygii |
| Clade: | Percomorpha Cope, 1871 |
| Subgroups | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Percomorpha (from la perca 'perch', and grc μορφή (morphḗ) 'shape, appearance') is a large clade of ray-finned fish with more than 17 000 known species that includes the tuna, seahorses, gobies, cichlids, flatfish, wrasse, perches, anglerfish, and pufferfish.[1][2][3][4][5][6]
Evolution
Percomorpha are the most diverse group of teleost fish today. Teleosts, and percomorphs in particular, thrived during the Cenozoic era. Fossil evidence shows that there was a major increase in size and abundance of teleosts immediately after the mass extinction event at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary ca. 66 Ma ago.[7] The oldest known percomorph fossils are of the early tetraodontiforms Protriacanthus and Cretatriacanthidae from the Santonian to Campanian of Italy and Slovenia.[8] A higher diversity of early percomorphs is also known from the Campanian of Nardò, Italy, and these also show some level of diversification into modern orders, with representatives of the Syngnathiformes and Tetraodontiformes known.[9] Possibly the oldest percomorph is Plectocretacicus from the Cenomanian of Lebanon, which may be a stem-tetraodontiform; however, some morphological analyses indicate that it shows similarities with non-percomorph groups.[8][10]
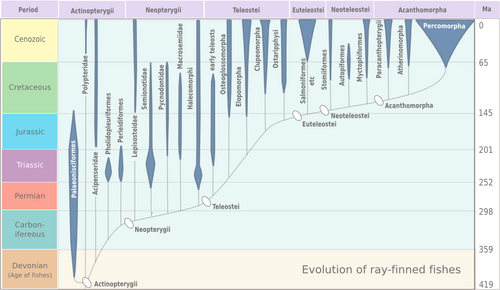
Phylogeny
External relationships
The two cladograms below are based on Betancur-R et al., 2017.[5] Percomorphs are a clade of teleost fishes. The first cladogram shows the interrelationships of percomorphs with other living groups of teleosts.
Lua error: Internal error: The interpreter exited with status 1.
Internal relationships
The following cladogram shows the evolutionary relationships of the various groups of extant percomorph fishes:
Lua error: Internal error: The interpreter exited with status 1.
References
- ↑ Phylogenetic analyses of ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) using collagen type I protein sequences
- ↑ Thomas J. Near (2012). "Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification". PNAS 109 (34): 13698–13703. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206625109. PMID 22869754. Bibcode: 2012PNAS..10913698N.
- ↑ Betancur-R, Ricardo (2013). "The Tree of Life and a New Classification of Bony Fishes". PLOS Currents Tree of Life 5 (Edition 1). doi:10.1371/currents.tol.53ba26640df0ccaee75bb165c8c26288. PMID 23653398.
- ↑ Laurin, M.; Reisz, R.R. (1995). "A reevaluation of early amniote phylogeny". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 113 (2): 165–223. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1995.tb00932.x.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Betancur-R, Ricardo; Wiley, Edward O.; Arratia, Gloria; Acero, Arturo; Bailly, Nicolas; Miya, Masaki; Lecointre, Guillaume; Ortí, Guillermo (6 July 2017). "Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes". BMC Evolutionary Biology 17 (1): 162. doi:10.1186/s12862-017-0958-3. ISSN 1471-2148. PMID 28683774.
- ↑ Nelson, Joseph S.; Grande, Terry C.; Wilson, Mark V. H. (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons. pp. 314–526. doi:10.1002/9781119174844. ISBN 978-1-118-34233-6. https://sites.google.com/site/fotw5th/.
- ↑ Sibert, E. C.; Norris, R. D. (2015-06-29). "New Age of Fishes initiated by the Cretaceous−Paleogene mass extinction". PNAS 112 (28): 8537–8542. doi:10.1073/pnas.1504985112. PMID 26124114. Bibcode: 2015PNAS..112.8537S.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Arcila, Dahiana; Alexander Pyron, R.; Tyler, James C.; Ortí, Guillermo; Betancur-R., Ricardo (2015-01-01). "An evaluation of fossil tip-dating versus node-age calibrations in tetraodontiform fishes (Teleostei: Percomorphaceae)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 82: 131–145. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2014.10.011. ISSN 1055-7903. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1055790314003625.
- ↑ Friedman, Matt; V. Andrews, James; Saad, Hadeel; El-Sayed, Sanaa (2023-06-16). "The Cretaceous–Paleogene transition in spiny-rayed fishes: surveying “Patterson’s Gap” in the acanthomorph skeletal record André Dumont medalist lecture 2018" (in en). Geologica Belgica. doi:10.20341/gb.2023.002. ISSN 1374-8505. https://popups.uliege.be/1374-8505/index.php?id=7048.
- ↑ Carnevale, Giorgio; Johnson, G. David (2015). "A Cretaceous Cusk-Eel (Teleostei, Ophidiiformes) from Italy and the Mesozoic Diversification of Percomorph Fishes". Copeia 103 (4): 771–791. doi:10.1643/CI-15-236. ISSN 0045-8511. https://bioone.org/journals/copeia/volume-103/issue-4/CI-15-236/A-Cretaceous-Cusk-Eel-Teleostei-Ophidiiformes-from-Italy-and-the/10.1643/CI-15-236.full.
Lua error: Internal error: The interpreter exited with status 1.
Lua error: Internal error: The interpreter exited with status 1. Wikidata ☰ Q22109111 entry
Lua error: Internal error: The interpreter exited with status 1.