Biology:Pseudalsophis
From HandWiki
Short description: Genus of snakes
| Pseudalsophis | |
|---|---|
| |
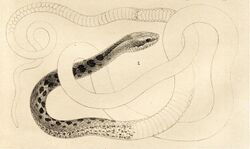
| Pseudalsophis dorsalis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Colubridae |
| Subfamily: | Dipsadinae |
| Genus: | Pseudalsophis Hussam Zaher et al., 2009 |
| Species | |
|
Ten | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Alsophis, Antillophis | |
Pseudalsophis is a genus of snakes in the family Colubridae. The genus is endemic to South America. Out of the ten species, nine are endemic to the Galapagos Islands.
Geographic range
Species in the genus Pseudalsophis are found in Ecuador (particularly the Galápagos), Chile and Peru.
Species
Ten species are recognized as being valid.[1]
- Pseudalsophis biserialis (Günther, 1860) – Galápagos racer
- Pseudalsophis darwini (Zaher, Yánez-Muñoz, Rodrigues, Graboski, Machado, Altamirano-Benavides, Bonatto, & Grazziotin, 2018) – Darwin's racer[2]
- Pseudalsophis dorsalis (Steindachner, 1876) – Central Galapagos racer
- Pseudalsophis elegans (Tschudi, 1845)
- Pseudalsophis hephaestus (Zaher et al, Yánez-Muñoz, Rodrigues, Graboski, Machado, Altamirano-Benavides, Bonatto, & Grazziotin, 2018) – Santiago racer[2]
- Pseudalsophis hoodensis (Van Denburgh, 1912) – Espanola racer
- Pseudalsophis occidentalis (Van Denburgh, 1912) – Western Galapagos racer
- Pseudalsophis slevini (Van Denburgh, 1912) – Banded Galápagos snake
- Pseudalsophis steindachneri (Van Denburgh, 1912) – Striped Galápagos snake
- Pseudalsophis thomasi (Zaher et al., 2018)[2] – Thomas's racer
Nota bene: A binomial authority in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than Pseudalsophis.
Etymology
The specific names, slevini and steidachneri, are in honor of American herpetologist Joseph Richard Slevin and Austrian herpetologist Franz Steindachner, respectively.[3]
References
- ↑ "Search results | The Reptile Database". https://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/advanced_search?genus=Pseudalsophis&submit=Search.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Zaher, Hassam; Yánez-Muños, Mario H.; Rodrigues, Miguel T.; Graboski, Roberta; Machado, Fabio A., Bonatto, Sandro L.; Grazziotin, Felipe G. (2018)}} – Darwin's racer "Origin and hidden diversity within the poorly known Galápagos radiation (Serpentes: Dipsadidae)". Systematics and Biodiversity. Published online. (Pseudalsophis darwini, new species; P. hephaestus, n. sp.; P. thomasi, n. sp.).
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN:978-1-4214-0135-5. (Antillophis slevini, p. 245; Antillophis steindachneri, p. 252).
Further reading
- Zaher, Hussam; Grazziotin, Felipe Gobbi; Cadle, John E.; Murphy, Robert W.; de Moura-Leite, Julio Cesar; Bonatto, Sandro (2009). "Molecular phylogeny of advanced snakes (Serpentes, Caenophidia) with an emphasis on South American Xenodontines: a revised classification and descriptions of new taxa". Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia 49 (11): 115–153. (Pseudalsophis, new genus). (in English, with abstracts in English and Portuguese).
Wikidata ☰ Q3409547 entry
 |

