Biology:Ricefield rat
| Ricefield rat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Muridae |
| Genus: | Rattus |
| Species: | R. argentiventer
|
| Binomial name | |
| Rattus argentiventer (Robinson & Kloss, 1916)
| |
| |
The ricefield rat (Rattus argentiventer) is a species of rat found throughout Southeast Asia.
Description
The ricefield rat is a medium-sized rat with a grizzled yellow-brown and black pelage. Its belly is gray in the midline with whiter flanks. The tail is uniformly medium brown. They have chisel-like incisor. The ricefield rat is between 304–400 mm long with a tail length of 140–200 mm and a skull length of 37–41 mm. The average weight of Rattus argentiventer is around 97 to 219 g. Female have 12 mammae. Young have an orange-colored tuft in front of each ear.
Behavior
The ricefield rat lives in large groups which consist of a dominant male and high ranking female. When attacked or disturbed they will make squeals and whistles sound. Rattus argentiventer's main diet includes termites, insects, grasshopper, snails, seeds, nuts, rice, vegetables, and fruits. They feed at night and actively moving at dusk and dawn. During daytime, they can be seen among vegetation, weeds or maturing field. It undergoes 3 week gestation giving birth about 5 to 10 young per litters.
Habitat
Biomes
Distribution
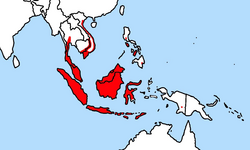
The ricefield rat can be found throughout Southeast Asia consists of Indochina region, Thailand, Peninsular Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippine, and New Guinea as major rodent pest in rice field area.
Although not a part of staple human diet in Cambodia, a growing market has developed there with most exports going to Vietnam.[2] Rat-catching season reaches its height after the rice harvest in June and July when rats have little to eat. That lack of food coincides with seasonal rains that force the rodents onto higher ground, where traps are set up to catch them.
Parasites
Parasites of the ricefield rat include:
References
- ↑ Ruedas, L.; Aplin, K.; Lunde, D. (2008). "Rattus argentiventer". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008. https://www.iucnredlist.org/details/19322/0. Retrieved 1 January 2009. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of least concern
- ↑ Doyle, Kevin (24 August 2014). "Cambodian rat meat: A growing export market". https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-28863315.
- ↑ Inder Singh, K.; Krishnasamy, M.; Ambu, S.; Rasul, R.; Chong, N. L. (1997). "Studies on animal schistosomes in Peninsular Malaysia: Record of naturally infected animals and additional hosts of Schistosoma spindale". The Southeast Asian journal of tropical medicine and public health 28 (2): 303–307. PMID 9444010.
- Junaidi, P.; F.M.Charlesl; & P.Karen. (1985). A Field Guide To The Mammals Of Borneo. The Sabah Society.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q1641012 entry
 |


