Biology:Russet-throated puffbird
| Russet-throated puffbird | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Piciformes |
| Family: | Bucconidae |
| Genus: | Hypnelus |
| Species: | H. ruficollis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hypnelus ruficollis (Wagler, 1829)
| |
| |
The russet-throated puffbird (Hypnelus ruficollis) is a species of near-passerine bird in the family Bucconidae, the puffbirds, nunlets, and nunbirds. It is found in Colombia and Venezuela.[1]
Taxonomy and systematics
The taxonomy of the russet-throated puffbird is complicated. BirdLife International's Handbook of the Birds of the World (HBW) assigns three subspecies, the nominate H. r. ruficolis, H. r. decolor, and H. r. coloratus. The International Ornithological Committee (IOC) adds H. r. striaticollis. Like HBW, the Clements taxonomy does not recognize striaticollis; both include it within decolor. But Clements adds H. r. bicinctus and H. r. stoicus, which the other two systems assign to the two-banded puffbird (H. bicinctus). The South American Classification Committee of the American Ornithological Society (SACC) recognizes that treating H. bicinctus as a species might be valid but has not received a formal proposal for the split.[2][1][3][4]
Description
The russet-throated puffbird is 20 to 22 cm (7.9 to 8.7 in) long and weighs 41 to 57 g (1.4 to 2.0 oz). The adult of the nominate subspecies has a dark brown crown with pale brown spots, a reddish spot just over the bill, a white patch around the eye and on the cheek, and a black patch below and behind the white one. The nape has a narrow buffy or white collar. The upperparts are dull brown with grayish mottling while the closed wing is dull brown with buffy "scales". The tail is long and dark brown with thin pale edges to the feathers. The chin is white and the throat and upper breast rich rufous. Under them are a thin white and a wide black band across the chest. The rest of the underparts are reddish buff with black bars or spots on the flanks. The bill is black, the eye yellow to white, and the feet black or dull green.[5]
H. r. decolor is paler above than the nominate, its lower breast and belly are whiter, and there is less dark barring on the flanks. H. r. coloratus compared to the nominate has blacker cheeks, a deeper orange throat, and underparts that are a richer orange-buff.[5]
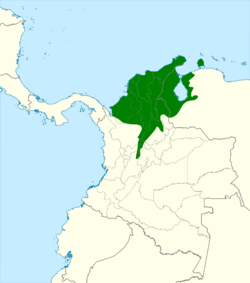
Distribution and habitat
The four subspecies of russet-throated puffbird recognized by the IOC are distributed thus:[1][5]
- H. r. decolor, extreme northeastern Colombia into western Venezuela
- H. r. ruficollis, northern Colombia and western Venezuela
- H. r. striaticollis, northwestern Venezuela's Zulia and Falcón states
- H. r. coloratus, western Venezuela south of Lake Maracaibo
The species inhabits a variety of open to semi-open landscapes including the interior and edges of open deciduous forest, treed savanna, dense secondary forest, and arid scrub with scattered trees. In elevation it has been recorded up to 700 m (2,300 ft) in Venezuela and as high as about 1,300 m (4,300 ft) in Colombia. It is thought to be a year-round resident throughout its range.[5]
Behavior
Feeding
The russet-throated puffbird still-hunts from a perch up to 8 m (26 ft) above ground. It sallies to capture prey on the ground, in vegetation, or on branches or trunks. Its diet is mostly insects but also includes small vertebrates like lizards and some fruits.[5]
Breeding
The russet-throated puffbird has been documented breeding in May in Colombia and in August and September in Venezuela. It usually excavates a burrow in an arboreal termitarium and occasionally uses the oven-shaped nest of pale-legged hornero (Furnarius leucopus). The clutch size is three eggs.[5]
Vocalization
The russet-throated puffbird's song is "repeated rhythmic 'woduk' notes in crescendo for up to 20 seconds, then diminishing". It is usually sung at dawn and often by both members of a pair. They also make a "seeeeep" call.[5]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the russet-throated puffbird as being of Least Concern. It has a large range, and though its population size has not been determined it is believed to be stable.[6] It occurs in at least one protected area in each of Colombia and Venezuela.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (July 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.2)". https://www.worldbirdnames.org/.
- ↑ HBW and BirdLife International (2020) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world Version 5. Available at: http://datazone.birdlife.org/userfiles/file/Species/Taxonomy/HBW-BirdLife_Checklist_v5_Dec20.zip [.xls zipped 1 MB] retrieved May 27, 2021
- ↑ Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2021. The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2021. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved August 25, 2021
- ↑ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 August 2021. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved August 24, 2021
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Rasmussen, P. C., N. Collar, and G. M. Kirwan (2020). Russet-throated Puffbird (Hypnelus ruficollis), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (S. M. Billerman, B. K. Keeney, P. G. Rodewald, and T. S. Schulenberg, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.rutpuf1.01 retrieved November 3, 2021
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedIUCN
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q1271806 entry
 |


