Biology:SeqA protein domain
| SeqA, C-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
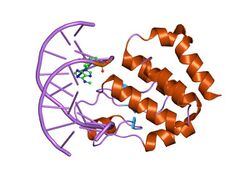 Crystal structure of the E.coli SeqA protein complexed with n6-methyladenine- guanine mismatch DNA | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | SeqA | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03925 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005621 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1lrr / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology the protein domain SeqA is one found in bacteria and archaea. The function of this protein domain is highly important in DNA replication. The protein negatively regulates the initiation of DNA replication at the origin of replication, in Escherichia coli, OriC.[1] Additionally the protein plays a further role in sequestration. The importance of this protein is vital, without its help in DNA replication, cell division and other crucial processes could not occur. This protein domain is thought to be part of a much larger protein complex which includes other proteins such as SeqB.[2]
Function
DNA replication is an energy consuming process and hence in bacteria the process only occurs at a specific checkpoint in the cell cycle. The binding of SeqA protein to hemimethylated GATC sequences is important in the negative modulation of chromosomal initiation at oriC, and in the formation of SeqA foci necessary for Escherichia coli chromosome segregation.[3]
SeqA tetramers are able to aggregate or multimerize in a reversible, concentration-dependent manner.[3] Apart from its function in the control of DNA replication, SeqA may also be a specific transcription factor.[4]
Additionally, SeqA is also thought to have a role in chromosome organisation and gene regulation.[5]
Localisation
Most of the SeqA in the cell is found bound to new DNA, at the replication fork.[5]
Structure
N terminal domain
The N-terminal domain folds into two alpha-helices and one beta-strand. This protein domain is vital in assisting multimerisation.[5]
C terminal domain
The C-terminal protein domain has an important role in binding to DNA. It binds to fully methylated and hemimethylated GATC sequences at oriC. The structure of the C-terminal domain consists of seven alpha-helices and a three-stranded beta-sheet.[5]
References
- ↑ "E. coli SeqA protein binds oriC in two different methyl-modulated reactions appropriate to its roles in DNA replication initiation and origin sequestration". Cell 82 (6): 927–36. September 1995. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90272-4. PMID 7553853. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7553853.
- ↑ "High-affinity binding of hemimethylated oriC by Escherichia coli membranes is mediated by a multiprotein system that includes SeqA and a newly identified factor, SeqB". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95 (19): 11117–21. September 1998. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.19.11117. PMID 9736699.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "SeqA protein aggregation is necessary for SeqA function". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (37): 34600–6. September 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101339200. PMID 11457824.
- ↑ "SeqA, the Escherichia coli origin sequestration protein, is also a specific transcription factor". Molecular Microbiology 40 (6): 1371–9. June 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02480.x. PMID 11442835.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "The Escherichia coli SeqA protein". Plasmid 61 (3): 141–50. May 2009. doi:10.1016/j.plasmid.2009.02.004. PMID 19254745. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19254745.

