Biology:Silent synapse
In neuroscience, a silent synapse is an excitatory glutamatergic synapse whose postsynaptic membrane contains NMDA-type glutamate receptors but no AMPA-type glutamate receptors.[1] These synapses are named "silent" because normal AMPA receptor-mediated signaling is not present, rendering the synapse inactive under typical conditions. Silent synapses are typically considered to be immature glutamatergic synapses. As the brain matures, the relative number of silent synapses decreases. However, recent research on hippocampal silent synapses shows that while they may indeed be a developmental landmark in the formation of a synapse, that synapses can be "silenced" by activity, even once they have acquired AMPA receptors. Thus, silence may be a state that synapses can visit many times during their lifetimes.
Synaptic transmission

Normal transmission across a glutamatergic synapse relies on the neurotransmitter glutamate, the glutamate-specific AMPA receptor (AMPAR), and calcium ions. Calcium ion entry into the presynaptic terminal causes the presynaptic release of glutamate, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft, binding to glutamate receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. There are four subtypes of glutamate receptors: AMPA receptors (AMPARs) (formerly known as quisqualate receptors), NMDA receptors (NMDARs), kainate receptors, and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). Most research has been focused on the AMPARs and the NMDARs. When glutamate binds to AMPARs located on the postsynaptic membrane, they permit a mixed flow of Na+ and K+ to cross the cells membrane, causing a depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. This localized depolarization is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP).
Silent synapses release glutamate as do prototypical glutamatergic synapses, but their postsynaptic membranes contain only NMDA—and possibly mGlu—receptors able to bind glutamate. Though AMPA receptors are not expressed in the postsynaptic membranes of silent synapses, they are stored in vesicles inside the postsynaptic cells, where they cannot detect extracellular glutamate, but can be quickly inserted into the postsynaptic cell membrane in response to a tetanizing stimulus. The NMDAR is functionally similar to AMPAR except for two major differences: NMDARs carry ion currents composed of Na+, K+, but also (unlike most AMPAR) Ca2+; NMDARs also have a site inside their ion channel that binds magnesium ions (Mg2+). This magnesium binding site is located in the pore of the channel, at a place within the electrical field generated by the membrane potential. Normally, current will not flow through the NMDAR channel, even when it has bound glutamate. This is because the ion channel associated with this receptor is plugged by magnesium, acting like a cork in a bottle. However, since the Mg2+ is charged and is bound within the membrane's electric field, depolarization of the membrane potential above threshold can dislodge the magnesium, allowing current flow through the NMDAR channel. This gives the NMDAR the property of being voltage-dependent, in that it requires strong postsynaptic depolarization to allow ion flux.
Characteristics
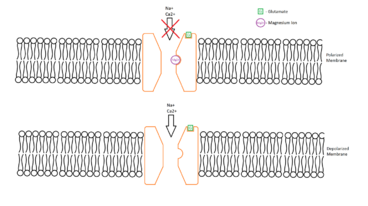
Silent synapses were proposed as an explanation for differences in quantal content of excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) mediated by AMPARs and NMDARs in hippocampal neurons.[2] More direct evidence came from experiments where only a few axons were stimulated. The stimulation of a silent synapse does not elicit EPSCs when the postsynaptic cell is clamped at -60 mV. Stimulation of a silent synapse will elicit EPSCs when the postsynaptic cell is depolarized beyond -40 mV.[3] This is because they lack surface AMPAR to pass current at hyperpolarized potentials, but do possess NMDARs that will pass current at more positive potentials (because of relief of magnesium block). Moreover, the EPSCs elicited with depolarized membrane potentials can be completely blocked by D-APV, a selective NMDAR blocker.[4]
Activation
Silent synapses are activated via the insertion of AMPARs into the postsynaptic membrane, a phenomenon commonly called "AMPA receptor trafficking."[5]
When glutamate binds to a strongly-depolarized postsynaptic cell (e.g., during Hebbian LTP), Ca2+ quickly enters and binds to calmodulin. Calmodulin activates calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), which — among other things — acts on AMPAR-containing vesicles near the postsynaptic membrane. CaMKII phosphorylates these AMPARs, which serves as a signal to insert them into the postsynaptic membrane. Once AMPARs are inserted, the synapse is no longer silent; activated synapses no longer require simultaneous pre- and postsynaptic activity in order to elicit EPSPs. After initial activation (Early Long Term Potentiation), if the post synaptic neuron continues to be stimulated, it will adjust to become permanently excitable (Late Long Term Potentiation). It does this by changing its level of AMPA Receptor production which are then inserted into the membrane at the synapse.
Evidence suggests that dendrite arborization and synapse maturation 1 (Dasm1), an Ig superfamily member, is involved in the maturation of synapses, essentially "awakening" the silent synapses.
Competing Hypotheses
The characterization of silent synapses is an ongoing field of research and there are many things about them that are not yet known. Some of what is currently accepted about the properties of silent synapses may still prove to be incorrect in whole or in part. Some controversies about silent synapses have however, been settled. For example, until recently, there were four competing hypotheses for the mechanisms of synapse silence:[6]
- The "whispering synapse" hypothesis:
- A synapse that releases glutamate more slowly than normal, thus activating only high affinity NMDA receptors, but not low affinity AMPA receptors
- The "low Pr" synapse hypothesis:
- A synapse that is not technically silent, but appears to be so, because it has such a low presynaptic probability of release that it rarely is activated.
- The "glutamate spillover" hypothesis:
- A synapse that does not release its own presynaptic glutamate, but in which the postsynapse detects low concentrations of glutamate "spilling over" from neighboring synapses. Only the high affinity NMDARs, but not the low affinity AMPARs can detect this low level of glutamate
- The "lack of AMPA receptor" hypothesis
- A synapse that lacks postsynaptic AMPA receptors
All four of these hypotheses had their adherents, but the first three were largely ruled out as a mechanism for synapse silence by work published before 2008.[7] However, recent experiments have clearly established that silent synapses can be observed at brainstem synapses bearing postsynaptic AMPA receptors.[8] This study favors the glutamate spillover hypothesis by showing that at silent synapses the glutamate concentration is reduced. At least, this study indicates that the popular hypothesis of the postsynaptic silent synapses does not apply in all systems.
Integration with other topics
The Role of Silent Synapses in Long Term Potentiation
- Many of the mechanisms involved in Long Term Potentiation are similar if not identical to those involved in silent synapse activation.[9] Both processes require the recruitment of AMPA receptors to the synapse.
Neural Development
- During development there are certain critical periods where sensory input is essential for correct development.[10] This is necessary for sensory, motor, and cognitive functions. Activating silent synapses helps build the neural networks needed for this development.[11]
AMPA Receptor Trafficking
- Because silent synapses are activated by the insertion of AMPAR's, the trafficking of those receptors is highly applicable. Evidence suggests that the main source of AMPA receptor recruitment in Long Term Potentiation comes from the endocytic/recycling pathway,[12] but there is also evidence that lateral membrane diffusion from extrasynaptic areas could also contribute to AMPAR recruitment.[13]
See also
References
- ↑ Purves, Dale (2007). Neuroscience, Fourth Edition. Sinauer Associates. pp. 193–5.
- ↑ "Amplitude fluctuations of dual-component EPSCs in hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for long-term potentiation". Neuron 12 (5): 1111–20. May 1994. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(94)90318-2. PMID 7910467.
- ↑ "Activation of postsynaptically silent synapses during pairing-induced LTP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice". Nature 375 (6530): 400–4. June 1995. doi:10.1038/375400a0. PMID 7760933. Bibcode: 1995Natur.375..400L.
- ↑ "Evidence for silent synapses: implications for the expression of LTP". Neuron 15 (2): 427–34. August 1995. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(95)90046-2. PMID 7646894.
- ↑ "Silent synapses and the emergence of a postsynaptic mechanism for LTP". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 9 (11): 813–25. November 2008. doi:10.1038/nrn2501. PMID 18854855.
- ↑ "'Deaf, mute and whispering' silent synapses: their role in synaptic plasticity". The Journal of Physiology 557 (Pt 1): 3–12. May 2004. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.058966. PMID 15034124.
- ↑ "Pair recordings reveal all-silent synaptic connections and the postsynaptic expression of long-term potentiation". Neuron 29 (3): 691–701. March 2001. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00244-6. PMID 11301028.
- ↑ "Silent synapses in developing rat nucleus tractus solitarii have AMPA receptors". The Journal of Neuroscience 28 (18): 4624–34. April 2008. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5355-07.2008. PMID 18448639.
- ↑ "Molecular Mechanisms of Early and Late LTP". Neurochemical Research 44 (2): 281–296. February 2019. doi:10.1007/s11064-018-2695-4. PMID 30523578.
- ↑ "The Integrative Function of Silent Synapses on Subplate Neurons in Cortical Development and Dysfunction" (in en). Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 13: 41. 2019. doi:10.3389/fnana.2019.00041. PMID 31040772.
- ↑ "Silent synapse: A new player in visual cortex critical period plasticity". Pharmacological Research 141: 586–590. March 2019. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.031. PMID 30659896.
- ↑ "AMPA Receptor Trafficking for Postsynaptic Potentiation" (in en). Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 12: 361. 2018. doi:10.3389/fncel.2018.00361. PMID 30364291.
- ↑ "Postsynaptic Neurotransmitter Receptor Reserve Pools for Synaptic Potentiation" (in en). Trends in Neurosciences 39 (3): 170–182. March 2016. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2016.01.002. PMID 26833258. https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/abstract/S0166-2236(16)00003-5.
External links
 |
