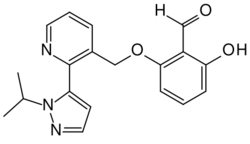
Biology:Voxelotor
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxbryta |
| Other names | GBT440, GBT-440 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620011 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H19N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 337.379 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Voxelotor, sold under the brand name Oxbryta, is a medication used for the treatment of sickle cell disease.[1][3][4][5][6] Voxelotor is the first hemoglobin oxygen-affinity modulator.[7] Voxelotor has been shown to have disease-modifying potential by increasing hemoglobin levels and decreasing hemolysis indicators in sickle cell patients.[8] It has a safe profile in sickle cell patients and healthy volunteers, without any dose-limiting toxicity.[9] It was developed by Global Blood Therapeutics, a subsidiary of Pfizer.[10]
In November 2019, voxelotor received accelerated approval in the United States for the treatment of sickle cell disease for those twelve years of age and older.[11][12] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[13] In December 2021, voxelotor received accelerated approval in the United States for the treatment of sickle cell disease for those aged four to eleven years.[14]
Side effects
Common side effects include headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, fatigue, rash and pyrexia (fever).[11]
History
Voxelotor was granted accelerated approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2019.[12][11][15] The FDA granted the application for voxelotor fast track designation and orphan drug designation.[11][16]
The approval of voxelotor was based on the results of a clinical trial with 274 participants with sickle cell disease.[11] The FDA granted the approval of Oxbryta to Global Blood Therapeutics.[11][12]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 16 December 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Oxbryta, intended for the treatment of hemolytic anemia due to sickle cell disease.[17][18] The applicant for this medicinal product is Global Blood Therapeutics Netherlands B.V.[17][18] Voxelotor (Oxbryta) was approved for medical use in the European Union in February 2022.[2][19]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Oxbryta- voxelotor tablet, film coated". 3 December 2019. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=3c557fac-29ec-483f-b691-8a935d4decc3.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Oxbryta EPAR". 14 December 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/oxbryta. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Voxelotor for Sickle Cell Disease". https://www.gbt.com/pipeline/sickle-cell-disease/.
- ↑ "Voxelotor (Previously GBT440)". https://sicklecellanemianews.com/voxelotor-gbt440-for-sickle-cell-anemia/.
- ↑ "ASH 2017: The HbS Polymerization Inhibitor Voxelotor GBT440 Has Demonstrated Positive Initial Results in Adolescents With Sickle Cell Disease". https://www.practiceupdate.com/content/ash-2017-the-hbs-polymerization-inhibitor-voxelotor-gbt440-has-demonstrated-positive-initial-results-in-adolescents-with-sickle-cell-disease/61476.
- ↑ Adamson, Laurie (22 January 2018). "Voxelotor: A New Option for Young Patients With Sickle Cell Disease?". https://www.ashclinicalnews.org/on-location/voxelotor-new-option-young-patients-sickle-cell-disease/.
- ↑ "Voxelotor". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/71602803.
- ↑ "A Phase 3 Randomized Trial of Voxelotor in Sickle Cell Disease". The New England Journal of Medicine 381 (6): 509–519. August 2019. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903212. PMID 31199090.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of voxelotor (GBT440) in healthy adults and patients with sickle cell disease". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 85 (6): 1290–1302. June 2019. doi:10.1111/bcp.13896. PMID 30743314.
- ↑ "Pfizer Completes Acquisition of Global Blood Therapeutics" (Press release). 5 October 2022.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 "FDA approves novel treatment to target abnormality in sickle cell disease". 25 November 2019. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-novel-treatment-target-abnormality-sickle-cell-disease.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "Drug Approval Package: Oxbryta". 23 December 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2019/213137Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ "New Drug Therapy Approvals 2019". 31 December 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/new-drugs-fda-cders-new-molecular-entities-and-new-therapeutic-biological-products/new-drug-therapy-approvals-2019.
- ↑ "FDA approves drug to treat sickle cell disease in patients aged 4 up to 11 years". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 17 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Drug Trials Snapshots: Oxbryta". 11 December 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/drug-trials-snapshots-oxbryta.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Voxelotor Orphan Drug Designation". 25 November 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=499715.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Oxbryta: Pending EC decision". 17 December 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/oxbryta. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "New treatment for sickle cell disease". European Medicines Agency (RMA) (Press release). 17 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ↑ "Oxbryta Product information". https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1622.htm.
External links
- "Voxelotor". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/voxelotor.
 |

