Biology:Yfr2
| Yfr2 / Cyano-1 | |
|---|---|
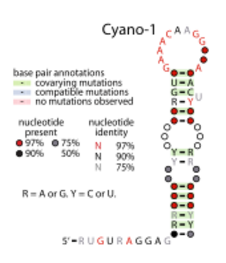 Consensus secondary structure of Yfr2 / Cyano-1 RNAs. Note that Yfr2 contains the terminator sequence and Cyano-1 does not. This figure is adapted from a previous publication.[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Unk |
| Rfam | RF01701 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; sRNA; |
| Domain(s) | Cyanobacteria; |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
Yfr2 (cYanobacterial functional RNA-2[2] later published as Cyano-1 RNA motif)[1] is a family of non-coding RNAs. Members of the Yrf2 family have been identified in almost all studied species of cyanobacteria. The family was identified through a bioinformatics screen of published cyanobacterial genomes,[3] having previously been grouped in a family of Yfr2–5.[2][4]
The cyano-1 RNA motif family is essentially a synonym for Yfr2, although Cyano-1 does not include the terminator sequence and Yfr2 does.[1][2]
The function of this ncRNA is unknown,[3][4] though it has been hypothesised that family members interact with RNA targets through kissing complexes using their highly conserved exposed central consensus element (CSE: IUPAC 5′-RKT SGA AAC WHG GHM ASA M-3′).[3] Earlier studies noted a similarity to quorum sensing ncRNAs in Vibrio bacteria.[5]
The family can be divided into two subgroups, one found in marine cyanobacteria (e.g. the Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus genera) and the other from freshwater cyanobacteria. Both subgroups have lengths of 63–100 nucleotides (with the marine subgroup genes being on average 22nt longer),[3] a conserved 5′ region and the characteristic Yfr2 CSE. Their secondary structures differ, however, with Yfr2 from marine picocyanobacteria having an additional stem loop.[3] The position of Yfr2 genes is generally unconserved,[2] but yfr2a orthologs were identified as being located 3′ to the gene 50S ribosomal subunit gene rplL in almost all marine cyanobacteria studied.[3] In the genus Prochlorococcus, Yfr2 genes are found adjacent to Yfr10 and a potential interaction between the two ncRNAs has been theorised.[6]
The initial bioinformatics scan which identified yfr2 also identified yfr1, a functional RNA which is upregulated during stress conditions.[2] Yfr families have now been identified up to yfr21.[6]
See also
- Non-coding RNA
- Yfr1
- Cyano-2 RNA motif
- Cyano-S1 RNA motif
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea and their metagenomes". Genome Biol 11 (3): R31. March 2010. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r31. PMID 20230605.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Identification of cyanobacterial non-coding RNAs by comparative genome analysis". Genome Biol. 6 (9): R73. 2005. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-9-r73. PMID 16168080.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "The Yfr2 ncRNA family, a group of abundant RNA molecules widely conserved in cyanobacteria". RNA Biol 6 (3): 222–227. July 2009. doi:10.4161/rna.6.3.8921. PMID 19502815.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Ecological genomics of marine picocyanobacteria". Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 73 (2): 249–299. June 2009. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00035-08. PMID 19487728.
- ↑ "The small RNA chaperone Hfq and multiple small RNAs control quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio cholerae". Cell 118 (1): 69–82. July 2004. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.009. PMID 15242645.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "The challenge of regulation in a minimal photoautotroph: non-coding RNAs in Prochlorococcus". PLOS Genet. 4 (8): e1000173. August 2008. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000173. PMID 18769676.
External links
 |
