Buchstab function
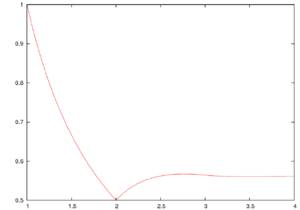
The Buchstab function (or Buchstab's function) is the unique continuous function defined by the delay differential equation
In the second equation, the derivative at u = 2 should be taken as u approaches 2 from the right. It is named after Alexander Buchstab, who wrote about it in 1937.
Asymptotics
The Buchstab function approaches rapidly as where is the Euler–Mascheroni constant. In fact,
where ρ is the Dickman function.[1] Also, oscillates in a regular way, alternating between extrema and zeroes; the extrema alternate between positive maxima and negative minima. The interval between consecutive extrema approaches 1 as u approaches infinity, as does the interval between consecutive zeroes.[2]
Applications
The Buchstab function is used to count rough numbers. If Φ(x, y) is the number of positive integers less than or equal to x with no prime factor less than y, then for any fixed u > 1,
Notes
References
- Бухштаб, А. А. (1937), "Асимптотическая оценка одной общей теоретикочисловой функции" (in Russian), Matematicheskii Sbornik 2(44) (6): 1239–1246, http://mi.mathnet.ru/msb5649
- "Buchstab Function", Wolfram MathWorld. Accessed on line Feb. 11, 2015.
- §IV.32, "On Φ(x,y) and Buchstab's function", Handbook of Number Theory I, József Sándor, Dragoslav S. Mitrinović, and Borislav Crstici, Springer, 2006, ISBN 978-1-4020-4215-7.
- "A differential delay equation arising from the sieve of Eratosthenes", A. Y. Cheer and D. A. Goldston, Mathematics of Computation 55 (1990), pp. 129–141.
- "An improvement of Selberg’s sieve method", W. B. Jurkat and H.-E. Richert, Acta Arithmetica 11 (1965), pp. 217–240.
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Bukhstab function", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4, https://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Bukhstab_function
 |
