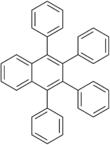
Chemistry:1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C34H24 | |||
| Molar mass | 432.55 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 199 to 201 °C (390 to 394 °F; 472 to 474 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms | 
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon commonly prepared in the undergraduate teaching laboratory as an introduction to the Diels-Alder reaction, in this case between benzyne, which acts as the dienophile, (generated in situ) and tetraphenylcyclopentadienone, which acts as the diene.[3] It has two crystalline forms, and therefore has two different melting points.
References
- ↑ 1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ "1,2,3,4-Tetraphenylnaphthalene" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/69783#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 5, p.1037 (1973); Vol. 46, p.107 (1966). Link
 |